Rename embedchain to mem0 and open sourcing code for long term memory (#1474)
Co-authored-by: Deshraj Yadav <deshrajdry@gmail.com>
This commit is contained in:
10
embedchain/docs/Makefile
Normal file
10
embedchain/docs/Makefile
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,10 @@
|
||||
install:
|
||||
npm i -g mintlify
|
||||
|
||||
run_local:
|
||||
mintlify dev
|
||||
|
||||
troubleshoot:
|
||||
mintlify install
|
||||
|
||||
.PHONY: install run_local troubleshoot
|
||||
25
embedchain/docs/README.md
Normal file
25
embedchain/docs/README.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,25 @@
|
||||
# Contributing to embedchain docs
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 👩💻 Development
|
||||
|
||||
Install the [Mintlify CLI](https://www.npmjs.com/package/mintlify) to preview the documentation changes locally. To install, use the following command
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
npm i -g mintlify
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Run the following command at the root of your documentation (where mint.json is)
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
mintlify dev
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 😎 Publishing Changes
|
||||
|
||||
Changes will be deployed to production automatically after your PR is merged to the main branch.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Troubleshooting
|
||||
|
||||
- Mintlify dev isn't running - Run `mintlify install` it'll re-install dependencies.
|
||||
- Page loads as a 404 - Make sure you are running in a folder with `mint.json`
|
||||
11
embedchain/docs/_snippets/get-help.mdx
Normal file
11
embedchain/docs/_snippets/get-help.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,11 @@
|
||||
<CardGroup cols={3}>
|
||||
<Card title="Talk to founders" icon="calendar" href="https://cal.com/taranjeetio/ec">
|
||||
Schedule a call
|
||||
</Card>
|
||||
<Card title="Slack" icon="slack" href="https://embedchain.ai/slack" color="#4A154B">
|
||||
Join our slack community
|
||||
</Card>
|
||||
<Card title="Discord" icon="discord" href="https://discord.gg/6PzXDgEjG5" color="#7289DA">
|
||||
Join our discord community
|
||||
</Card>
|
||||
</CardGroup>
|
||||
19
embedchain/docs/_snippets/missing-data-source-tip.mdx
Normal file
19
embedchain/docs/_snippets/missing-data-source-tip.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,19 @@
|
||||
<p>If you can't find the specific data source, please feel free to request through one of the following channels and help us prioritize.</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<CardGroup cols={2}>
|
||||
<Card title="Google Form" icon="file" href="https://forms.gle/NDRCKsRpUHsz2Wcm8" color="#7387d0">
|
||||
Fill out this form
|
||||
</Card>
|
||||
<Card title="Slack" icon="slack" href="https://embedchain.ai/slack" color="#4A154B">
|
||||
Let us know on our slack community
|
||||
</Card>
|
||||
<Card title="Discord" icon="discord" href="https://discord.gg/6PzXDgEjG5" color="#7289DA">
|
||||
Let us know on discord community
|
||||
</Card>
|
||||
<Card title="GitHub" icon="github" href="https://github.com/embedchain/embedchain/issues/new?assignees=&labels=&projects=&template=feature_request.yml" color="#181717">
|
||||
Open an issue on our GitHub
|
||||
</Card>
|
||||
<Card title="Schedule a call" icon="calendar" href="https://cal.com/taranjeetio/ec">
|
||||
Schedule a call with Embedchain founder
|
||||
</Card>
|
||||
</CardGroup>
|
||||
16
embedchain/docs/_snippets/missing-llm-tip.mdx
Normal file
16
embedchain/docs/_snippets/missing-llm-tip.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,16 @@
|
||||
<p>If you can't find the specific LLM you need, no need to fret. We're continuously expanding our support for additional LLMs, and you can help us prioritize by opening an issue on our GitHub or simply reaching out to us on our Slack or Discord community.</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<CardGroup cols={2}>
|
||||
<Card title="Slack" icon="slack" href="https://embedchain.ai/slack" color="#4A154B">
|
||||
Let us know on our slack community
|
||||
</Card>
|
||||
<Card title="Discord" icon="discord" href="https://discord.gg/6PzXDgEjG5" color="#7289DA">
|
||||
Let us know on discord community
|
||||
</Card>
|
||||
<Card title="GitHub" icon="github" href="https://github.com/embedchain/embedchain/issues/new?assignees=&labels=&projects=&template=feature_request.yml" color="#181717">
|
||||
Open an issue on our GitHub
|
||||
</Card>
|
||||
<Card title="Schedule a call" icon="calendar" href="https://cal.com/taranjeetio/ec">
|
||||
Schedule a call with Embedchain founder
|
||||
</Card>
|
||||
</CardGroup>
|
||||
18
embedchain/docs/_snippets/missing-vector-db-tip.mdx
Normal file
18
embedchain/docs/_snippets/missing-vector-db-tip.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,18 @@
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p>If you can't find specific feature or run into issues, please feel free to reach out through one of the following channels.</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<CardGroup cols={2}>
|
||||
<Card title="Slack" icon="slack" href="https://embedchain.ai/slack" color="#4A154B">
|
||||
Let us know on our slack community
|
||||
</Card>
|
||||
<Card title="Discord" icon="discord" href="https://discord.gg/6PzXDgEjG5" color="#7289DA">
|
||||
Let us know on discord community
|
||||
</Card>
|
||||
<Card title="GitHub" icon="github" href="https://github.com/embedchain/embedchain/issues/new?assignees=&labels=&projects=&template=feature_request.yml" color="#181717">
|
||||
Open an issue on our GitHub
|
||||
</Card>
|
||||
<Card title="Schedule a call" icon="calendar" href="https://cal.com/taranjeetio/ec">
|
||||
Schedule a call with Embedchain founder
|
||||
</Card>
|
||||
</CardGroup>
|
||||
260
embedchain/docs/api-reference/advanced/configuration.mdx
Normal file
260
embedchain/docs/api-reference/advanced/configuration.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,260 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: 'Custom configurations'
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Embedchain offers several configuration options for your LLM, vector database, and embedding model. All of these configuration options are optional and have sane defaults.
|
||||
|
||||
You can configure different components of your app (`llm`, `embedding model`, or `vector database`) through a simple yaml configuration that Embedchain offers. Here is a generic full-stack example of the yaml config:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
Embedchain applications are configurable using YAML file, JSON file or by directly passing the config dictionary. Checkout the [docs here](/api-reference/app/overview#usage) on how to use other formats.
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
<CodeGroup>
|
||||
```yaml config.yaml
|
||||
app:
|
||||
config:
|
||||
name: 'full-stack-app'
|
||||
|
||||
llm:
|
||||
provider: openai
|
||||
config:
|
||||
model: 'gpt-3.5-turbo'
|
||||
temperature: 0.5
|
||||
max_tokens: 1000
|
||||
top_p: 1
|
||||
stream: false
|
||||
api_key: sk-xxx
|
||||
model_kwargs:
|
||||
response_format:
|
||||
type: json_object
|
||||
api_version: 2024-02-01
|
||||
http_client_proxies: http://testproxy.mem0.net:8000
|
||||
prompt: |
|
||||
Use the following pieces of context to answer the query at the end.
|
||||
If you don't know the answer, just say that you don't know, don't try to make up an answer.
|
||||
|
||||
$context
|
||||
|
||||
Query: $query
|
||||
|
||||
Helpful Answer:
|
||||
system_prompt: |
|
||||
Act as William Shakespeare. Answer the following questions in the style of William Shakespeare.
|
||||
|
||||
vectordb:
|
||||
provider: chroma
|
||||
config:
|
||||
collection_name: 'full-stack-app'
|
||||
dir: db
|
||||
allow_reset: true
|
||||
|
||||
embedder:
|
||||
provider: openai
|
||||
config:
|
||||
model: 'text-embedding-ada-002'
|
||||
api_key: sk-xxx
|
||||
|
||||
chunker:
|
||||
chunk_size: 2000
|
||||
chunk_overlap: 100
|
||||
length_function: 'len'
|
||||
min_chunk_size: 0
|
||||
|
||||
cache:
|
||||
similarity_evaluation:
|
||||
strategy: distance
|
||||
max_distance: 1.0
|
||||
config:
|
||||
similarity_threshold: 0.8
|
||||
auto_flush: 50
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```json config.json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"app": {
|
||||
"config": {
|
||||
"name": "full-stack-app"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"llm": {
|
||||
"provider": "openai",
|
||||
"config": {
|
||||
"model": "gpt-3.5-turbo",
|
||||
"temperature": 0.5,
|
||||
"max_tokens": 1000,
|
||||
"top_p": 1,
|
||||
"stream": false,
|
||||
"prompt": "Use the following pieces of context to answer the query at the end.\nIf you don't know the answer, just say that you don't know, don't try to make up an answer.\n$context\n\nQuery: $query\n\nHelpful Answer:",
|
||||
"system_prompt": "Act as William Shakespeare. Answer the following questions in the style of William Shakespeare.",
|
||||
"api_key": "sk-xxx",
|
||||
"model_kwargs": {"response_format": {"type": "json_object"}},
|
||||
"api_version": "2024-02-01",
|
||||
"http_client_proxies": "http://testproxy.mem0.net:8000",
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"vectordb": {
|
||||
"provider": "chroma",
|
||||
"config": {
|
||||
"collection_name": "full-stack-app",
|
||||
"dir": "db",
|
||||
"allow_reset": true
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"embedder": {
|
||||
"provider": "openai",
|
||||
"config": {
|
||||
"model": "text-embedding-ada-002",
|
||||
"api_key": "sk-xxx"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"chunker": {
|
||||
"chunk_size": 2000,
|
||||
"chunk_overlap": 100,
|
||||
"length_function": "len",
|
||||
"min_chunk_size": 0
|
||||
},
|
||||
"cache": {
|
||||
"similarity_evaluation": {
|
||||
"strategy": "distance",
|
||||
"max_distance": 1.0,
|
||||
},
|
||||
"config": {
|
||||
"similarity_threshold": 0.8,
|
||||
"auto_flush": 50,
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```python config.py
|
||||
config = {
|
||||
'app': {
|
||||
'config': {
|
||||
'name': 'full-stack-app'
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
'llm': {
|
||||
'provider': 'openai',
|
||||
'config': {
|
||||
'model': 'gpt-3.5-turbo',
|
||||
'temperature': 0.5,
|
||||
'max_tokens': 1000,
|
||||
'top_p': 1,
|
||||
'stream': False,
|
||||
'prompt': (
|
||||
"Use the following pieces of context to answer the query at the end.\n"
|
||||
"If you don't know the answer, just say that you don't know, don't try to make up an answer.\n"
|
||||
"$context\n\nQuery: $query\n\nHelpful Answer:"
|
||||
),
|
||||
'system_prompt': (
|
||||
"Act as William Shakespeare. Answer the following questions in the style of William Shakespeare."
|
||||
),
|
||||
'api_key': 'sk-xxx',
|
||||
"model_kwargs": {"response_format": {"type": "json_object"}},
|
||||
"http_client_proxies": "http://testproxy.mem0.net:8000",
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
'vectordb': {
|
||||
'provider': 'chroma',
|
||||
'config': {
|
||||
'collection_name': 'full-stack-app',
|
||||
'dir': 'db',
|
||||
'allow_reset': True
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
'embedder': {
|
||||
'provider': 'openai',
|
||||
'config': {
|
||||
'model': 'text-embedding-ada-002',
|
||||
'api_key': 'sk-xxx'
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
'chunker': {
|
||||
'chunk_size': 2000,
|
||||
'chunk_overlap': 100,
|
||||
'length_function': 'len',
|
||||
'min_chunk_size': 0
|
||||
},
|
||||
'cache': {
|
||||
'similarity_evaluation': {
|
||||
'strategy': 'distance',
|
||||
'max_distance': 1.0,
|
||||
},
|
||||
'config': {
|
||||
'similarity_threshold': 0.8,
|
||||
'auto_flush': 50,
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
</CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
Alright, let's dive into what each key means in the yaml config above:
|
||||
|
||||
1. `app` Section:
|
||||
- `config`:
|
||||
- `name` (String): The name of your full-stack application.
|
||||
- `id` (String): The id of your full-stack application.
|
||||
<Note>Only use this to reload already created apps. We recommend users to not create their own ids.</Note>
|
||||
- `collect_metrics` (Boolean): Indicates whether metrics should be collected for the app, defaults to `True`
|
||||
- `log_level` (String): The log level for the app, defaults to `WARNING`
|
||||
2. `llm` Section:
|
||||
- `provider` (String): The provider for the language model, which is set to 'openai'. You can find the full list of llm providers in [our docs](/components/llms).
|
||||
- `config`:
|
||||
- `model` (String): The specific model being used, 'gpt-3.5-turbo'.
|
||||
- `temperature` (Float): Controls the randomness of the model's output. A higher value (closer to 1) makes the output more random.
|
||||
- `max_tokens` (Integer): Controls how many tokens are used in the response.
|
||||
- `top_p` (Float): Controls the diversity of word selection. A higher value (closer to 1) makes word selection more diverse.
|
||||
- `stream` (Boolean): Controls if the response is streamed back to the user (set to false).
|
||||
- `online` (Boolean): Controls whether to use internet to get more context for answering query (set to false).
|
||||
- `token_usage` (Boolean): Controls whether to use token usage for the querying models (set to false).
|
||||
- `prompt` (String): A prompt for the model to follow when generating responses, requires `$context` and `$query` variables.
|
||||
- `system_prompt` (String): A system prompt for the model to follow when generating responses, in this case, it's set to the style of William Shakespeare.
|
||||
- `number_documents` (Integer): Number of documents to pull from the vectordb as context, defaults to 1
|
||||
- `api_key` (String): The API key for the language model.
|
||||
- `model_kwargs` (Dict): Keyword arguments to pass to the language model. Used for `aws_bedrock` provider, since it requires different arguments for each model.
|
||||
- `http_client_proxies` (Dict | String): The proxy server settings used to create `self.http_client` using `httpx.Client(proxies=http_client_proxies)`
|
||||
- `http_async_client_proxies` (Dict | String): The proxy server settings for async calls used to create `self.http_async_client` using `httpx.AsyncClient(proxies=http_async_client_proxies)`
|
||||
3. `vectordb` Section:
|
||||
- `provider` (String): The provider for the vector database, set to 'chroma'. You can find the full list of vector database providers in [our docs](/components/vector-databases).
|
||||
- `config`:
|
||||
- `collection_name` (String): The initial collection name for the vectordb, set to 'full-stack-app'.
|
||||
- `dir` (String): The directory for the local database, set to 'db'.
|
||||
- `allow_reset` (Boolean): Indicates whether resetting the vectordb is allowed, set to true.
|
||||
- `batch_size` (Integer): The batch size for docs insertion in vectordb, defaults to `100`
|
||||
<Note>We recommend you to checkout vectordb specific config [here](https://docs.embedchain.ai/components/vector-databases)</Note>
|
||||
4. `embedder` Section:
|
||||
- `provider` (String): The provider for the embedder, set to 'openai'. You can find the full list of embedding model providers in [our docs](/components/embedding-models).
|
||||
- `config`:
|
||||
- `model` (String): The specific model used for text embedding, 'text-embedding-ada-002'.
|
||||
- `vector_dimension` (Integer): The vector dimension of the embedding model. [Defaults](https://github.com/embedchain/embedchain/blob/main/embedchain/models/vector_dimensions.py)
|
||||
- `api_key` (String): The API key for the embedding model.
|
||||
- `endpoint` (String): The endpoint for the HuggingFace embedding model.
|
||||
- `deployment_name` (String): The deployment name for the embedding model.
|
||||
- `title` (String): The title for the embedding model for Google Embedder.
|
||||
- `task_type` (String): The task type for the embedding model for Google Embedder.
|
||||
- `model_kwargs` (Dict): Used to pass extra arguments to embedders.
|
||||
5. `chunker` Section:
|
||||
- `chunk_size` (Integer): The size of each chunk of text that is sent to the language model.
|
||||
- `chunk_overlap` (Integer): The amount of overlap between each chunk of text.
|
||||
- `length_function` (String): The function used to calculate the length of each chunk of text. In this case, it's set to 'len'. You can also use any function import directly as a string here.
|
||||
- `min_chunk_size` (Integer): The minimum size of each chunk of text that is sent to the language model. Must be less than `chunk_size`, and greater than `chunk_overlap`.
|
||||
6. `cache` Section: (Optional)
|
||||
- `similarity_evaluation` (Optional): The config for similarity evaluation strategy. If not provided, the default `distance` based similarity evaluation strategy is used.
|
||||
- `strategy` (String): The strategy to use for similarity evaluation. Currently, only `distance` and `exact` based similarity evaluation is supported. Defaults to `distance`.
|
||||
- `max_distance` (Float): The bound of maximum distance. Defaults to `1.0`.
|
||||
- `positive` (Boolean): If the larger distance indicates more similar of two entities, set it `True`, otherwise `False`. Defaults to `False`.
|
||||
- `config` (Optional): The config for initializing the cache. If not provided, sensible default values are used as mentioned below.
|
||||
- `similarity_threshold` (Float): The threshold for similarity evaluation. Defaults to `0.8`.
|
||||
- `auto_flush` (Integer): The number of queries after which the cache is flushed. Defaults to `20`.
|
||||
7. `memory` Section: (Optional)
|
||||
- `api_key` (String): The API key of mem0.
|
||||
- `top_k` (Integer): The number of top-k results to return. Defaults to `10`.
|
||||
<Note>
|
||||
If you provide a cache section, the app will automatically configure and use a cache to store the results of the language model. This is useful if you want to speed up the response time and save inference cost of your app.
|
||||
</Note>
|
||||
If you have questions about the configuration above, please feel free to reach out to us using one of the following methods:
|
||||
|
||||
<Snippet file="get-help.mdx" />
|
||||
44
embedchain/docs/api-reference/app/add.mdx
Normal file
44
embedchain/docs/api-reference/app/add.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,44 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: '📊 add'
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
`add()` method is used to load the data sources from different data sources to a RAG pipeline. You can find the signature below:
|
||||
|
||||
### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
<ParamField path="source" type="str">
|
||||
The data to embed, can be a URL, local file or raw content, depending on the data type.. You can find the full list of supported data sources [here](/components/data-sources/overview).
|
||||
</ParamField>
|
||||
<ParamField path="data_type" type="str" optional>
|
||||
Type of data source. It can be automatically detected but user can force what data type to load as.
|
||||
</ParamField>
|
||||
<ParamField path="metadata" type="dict" optional>
|
||||
Any metadata that you want to store with the data source. Metadata is generally really useful for doing metadata filtering on top of semantic search to yield faster search and better results.
|
||||
</ParamField>
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage
|
||||
|
||||
### Load data from webpage
|
||||
|
||||
```python Code example
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
|
||||
app = App()
|
||||
app.add("https://www.forbes.com/profile/elon-musk")
|
||||
# Inserting batches in chromadb: 100%|███████████████| 1/1 [00:00<00:00, 1.19it/s]
|
||||
# Successfully saved https://www.forbes.com/profile/elon-musk (DataType.WEB_PAGE). New chunks count: 4
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Load data from sitemap
|
||||
|
||||
```python Code example
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
|
||||
app = App()
|
||||
app.add("https://python.langchain.com/sitemap.xml", data_type="sitemap")
|
||||
# Loading pages: 100%|█████████████| 1108/1108 [00:47<00:00, 23.17it/s]
|
||||
# Inserting batches in chromadb: 100%|█████████| 111/111 [04:41<00:00, 2.54s/it]
|
||||
# Successfully saved https://python.langchain.com/sitemap.xml (DataType.SITEMAP). New chunks count: 11024
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can find complete list of supported data sources [here](/components/data-sources/overview).
|
||||
171
embedchain/docs/api-reference/app/chat.mdx
Normal file
171
embedchain/docs/api-reference/app/chat.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,171 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: '💬 chat'
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
`chat()` method allows you to chat over your data sources using a user-friendly chat API. You can find the signature below:
|
||||
|
||||
### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
<ParamField path="input_query" type="str">
|
||||
Question to ask
|
||||
</ParamField>
|
||||
<ParamField path="config" type="BaseLlmConfig" optional>
|
||||
Configure different llm settings such as prompt, temprature, number_documents etc.
|
||||
</ParamField>
|
||||
<ParamField path="dry_run" type="bool" optional>
|
||||
The purpose is to test the prompt structure without actually running LLM inference. Defaults to `False`
|
||||
</ParamField>
|
||||
<ParamField path="where" type="dict" optional>
|
||||
A dictionary of key-value pairs to filter the chunks from the vector database. Defaults to `None`
|
||||
</ParamField>
|
||||
<ParamField path="session_id" type="str" optional>
|
||||
Session ID of the chat. This can be used to maintain chat history of different user sessions. Default value: `default`
|
||||
</ParamField>
|
||||
<ParamField path="citations" type="bool" optional>
|
||||
Return citations along with the LLM answer. Defaults to `False`
|
||||
</ParamField>
|
||||
|
||||
### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
<ResponseField name="answer" type="str | tuple">
|
||||
If `citations=False`, return a stringified answer to the question asked. <br />
|
||||
If `citations=True`, returns a tuple with answer and citations respectively.
|
||||
</ResponseField>
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage
|
||||
|
||||
### With citations
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to get the answer to question and return both answer and citations, use the following code snippet:
|
||||
|
||||
```python With Citations
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
|
||||
# Initialize app
|
||||
app = App()
|
||||
|
||||
# Add data source
|
||||
app.add("https://www.forbes.com/profile/elon-musk")
|
||||
|
||||
# Get relevant answer for your query
|
||||
answer, sources = app.chat("What is the net worth of Elon?", citations=True)
|
||||
print(answer)
|
||||
# Answer: The net worth of Elon Musk is $221.9 billion.
|
||||
|
||||
print(sources)
|
||||
# [
|
||||
# (
|
||||
# 'Elon Musk PROFILEElon MuskCEO, Tesla$247.1B$2.3B (0.96%)Real Time Net Worthas of 12/7/23 ...',
|
||||
# {
|
||||
# 'url': 'https://www.forbes.com/profile/elon-musk',
|
||||
# 'score': 0.89,
|
||||
# ...
|
||||
# }
|
||||
# ),
|
||||
# (
|
||||
# '74% of the company, which is now called X.Wealth HistoryHOVER TO REVEAL NET WORTH BY YEARForbes ...',
|
||||
# {
|
||||
# 'url': 'https://www.forbes.com/profile/elon-musk',
|
||||
# 'score': 0.81,
|
||||
# ...
|
||||
# }
|
||||
# ),
|
||||
# (
|
||||
# 'founded in 2002, is worth nearly $150 billion after a $750 million tender offer in June 2023 ...',
|
||||
# {
|
||||
# 'url': 'https://www.forbes.com/profile/elon-musk',
|
||||
# 'score': 0.73,
|
||||
# ...
|
||||
# }
|
||||
# )
|
||||
# ]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Note>
|
||||
When `citations=True`, note that the returned `sources` are a list of tuples where each tuple has two elements (in the following order):
|
||||
1. source chunk
|
||||
2. dictionary with metadata about the source chunk
|
||||
- `url`: url of the source
|
||||
- `doc_id`: document id (used for book keeping purposes)
|
||||
- `score`: score of the source chunk with respect to the question
|
||||
- other metadata you might have added at the time of adding the source
|
||||
</Note>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Without citations
|
||||
|
||||
If you just want to return answers and don't want to return citations, you can use the following example:
|
||||
|
||||
```python Without Citations
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
|
||||
# Initialize app
|
||||
app = App()
|
||||
|
||||
# Add data source
|
||||
app.add("https://www.forbes.com/profile/elon-musk")
|
||||
|
||||
# Chat on your data using `.chat()`
|
||||
answer = app.chat("What is the net worth of Elon?")
|
||||
print(answer)
|
||||
# Answer: The net worth of Elon Musk is $221.9 billion.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### With session id
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to maintain chat sessions for different users, you can simply pass the `session_id` keyword argument. See the example below:
|
||||
|
||||
```python With session id
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
|
||||
app = App()
|
||||
app.add("https://www.forbes.com/profile/elon-musk")
|
||||
|
||||
# Chat on your data using `.chat()`
|
||||
app.chat("What is the net worth of Elon Musk?", session_id="user1")
|
||||
# 'The net worth of Elon Musk is $250.8 billion.'
|
||||
app.chat("What is the net worth of Bill Gates?", session_id="user2")
|
||||
# "I don't know the current net worth of Bill Gates."
|
||||
app.chat("What was my last question", session_id="user1")
|
||||
# 'Your last question was "What is the net worth of Elon Musk?"'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### With custom context window
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to customize the context window that you want to use during chat (default context window is 3 document chunks), you can do using the following code snippet:
|
||||
|
||||
```python with custom chunks size
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
from embedchain.config import BaseLlmConfig
|
||||
|
||||
app = App()
|
||||
app.add("https://www.forbes.com/profile/elon-musk")
|
||||
|
||||
query_config = BaseLlmConfig(number_documents=5)
|
||||
app.chat("What is the net worth of Elon Musk?", config=query_config)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### With Mem0 to store chat history
|
||||
|
||||
Mem0 is a cutting-edge long-term memory for LLMs to enable personalization for the GenAI stack. It enables LLMs to remember past interactions and provide more personalized responses.
|
||||
|
||||
Follow these steps to use Mem0 to enable memory for personalization in your apps:
|
||||
- Install the [`mem0`](https://docs.mem0.ai/) package using `pip install memzero`.
|
||||
- Get the api_key from [Mem0 Platform](https://app.mem0.ai/).
|
||||
- Provide api_key in config under `memory`, refer [Configurations](docs/api-reference/advanced/configuration.mdx).
|
||||
|
||||
```python with mem0
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
|
||||
config = {
|
||||
"memory": {
|
||||
"api_key": "m0-xxx",
|
||||
"top_k": 5
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
app = App.from_config(config=config)
|
||||
app.add("https://www.forbes.com/profile/elon-musk")
|
||||
|
||||
app.chat("What is the net worth of Elon Musk?")
|
||||
```
|
||||
48
embedchain/docs/api-reference/app/delete.mdx
Normal file
48
embedchain/docs/api-reference/app/delete.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,48 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: 🗑 delete
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## Delete Document
|
||||
|
||||
`delete()` method allows you to delete a document previously added to the app.
|
||||
|
||||
### Usage
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
|
||||
app = App()
|
||||
|
||||
forbes_doc_id = app.add("https://www.forbes.com/profile/elon-musk")
|
||||
wiki_doc_id = app.add("https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Elon_Musk")
|
||||
|
||||
app.delete(forbes_doc_id) # deletes the forbes document
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Note>
|
||||
If you do not have the document id, you can use `app.db.get()` method to get the document and extract the `hash` key from `metadatas` dictionary object, which serves as the document id.
|
||||
</Note>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Delete Chat Session History
|
||||
|
||||
`delete_session_chat_history()` method allows you to delete all previous messages in a chat history.
|
||||
|
||||
### Usage
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
|
||||
app = App()
|
||||
|
||||
app.add("https://www.forbes.com/profile/elon-musk")
|
||||
|
||||
app.chat("What is the net worth of Elon Musk?")
|
||||
|
||||
app.delete_session_chat_history()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Note>
|
||||
`delete_session_chat_history(session_id="session_1")` method also accepts `session_id` optional param for deleting chat history of a specific session.
|
||||
It assumes the default session if no `session_id` is provided.
|
||||
</Note>
|
||||
5
embedchain/docs/api-reference/app/deploy.mdx
Normal file
5
embedchain/docs/api-reference/app/deploy.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,5 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: 🚀 deploy
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
The `deploy()` method is currently available on an invitation-only basis. To request access, please submit your information via the provided [Google Form](https://forms.gle/vigN11h7b4Ywat668). We will review your request and respond promptly.
|
||||
41
embedchain/docs/api-reference/app/evaluate.mdx
Normal file
41
embedchain/docs/api-reference/app/evaluate.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,41 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: '📝 evaluate'
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
`evaluate()` method is used to evaluate the performance of a RAG app. You can find the signature below:
|
||||
|
||||
### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
<ParamField path="question" type="Union[str, list[str]]">
|
||||
A question or a list of questions to evaluate your app on.
|
||||
</ParamField>
|
||||
<ParamField path="metrics" type="Optional[list[Union[BaseMetric, str]]]" optional>
|
||||
The metrics to evaluate your app on. Defaults to all metrics: `["context_relevancy", "answer_relevancy", "groundedness"]`
|
||||
</ParamField>
|
||||
<ParamField path="num_workers" type="int" optional>
|
||||
Specify the number of threads to use for parallel processing.
|
||||
</ParamField>
|
||||
|
||||
### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
<ResponseField name="metrics" type="dict">
|
||||
Returns the metrics you have chosen to evaluate your app on as a dictionary.
|
||||
</ResponseField>
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
|
||||
app = App()
|
||||
|
||||
# add data source
|
||||
app.add("https://www.forbes.com/profile/elon-musk")
|
||||
|
||||
# run evaluation
|
||||
app.evaluate("what is the net worth of Elon Musk?")
|
||||
# {'answer_relevancy': 0.958019958036268, 'context_relevancy': 0.12903225806451613}
|
||||
|
||||
# or
|
||||
# app.evaluate(["what is the net worth of Elon Musk?", "which companies does Elon Musk own?"])
|
||||
```
|
||||
33
embedchain/docs/api-reference/app/get.mdx
Normal file
33
embedchain/docs/api-reference/app/get.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,33 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: 📄 get
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## Get data sources
|
||||
|
||||
`get_data_sources()` returns a list of all the data sources added in the app.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Usage
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
|
||||
app = App()
|
||||
|
||||
app.add("https://www.forbes.com/profile/elon-musk")
|
||||
app.add("https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Elon_Musk")
|
||||
|
||||
data_sources = app.get_data_sources()
|
||||
# [
|
||||
# {
|
||||
# 'data_type': 'web_page',
|
||||
# 'data_value': 'https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Elon_Musk',
|
||||
# 'metadata': 'null'
|
||||
# },
|
||||
# {
|
||||
# 'data_type': 'web_page',
|
||||
# 'data_value': 'https://www.forbes.com/profile/elon-musk',
|
||||
# 'metadata': 'null'
|
||||
# }
|
||||
# ]
|
||||
```
|
||||
130
embedchain/docs/api-reference/app/overview.mdx
Normal file
130
embedchain/docs/api-reference/app/overview.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,130 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: "App"
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Create a RAG app object on Embedchain. This is the main entrypoint for a developer to interact with Embedchain APIs. An app configures the llm, vector database, embedding model, and retrieval strategy of your choice.
|
||||
|
||||
### Attributes
|
||||
|
||||
<ParamField path="local_id" type="str">
|
||||
App ID
|
||||
</ParamField>
|
||||
<ParamField path="name" type="str" optional>
|
||||
Name of the app
|
||||
</ParamField>
|
||||
<ParamField path="config" type="BaseConfig">
|
||||
Configuration of the app
|
||||
</ParamField>
|
||||
<ParamField path="llm" type="BaseLlm">
|
||||
Configured LLM for the RAG app
|
||||
</ParamField>
|
||||
<ParamField path="db" type="BaseVectorDB">
|
||||
Configured vector database for the RAG app
|
||||
</ParamField>
|
||||
<ParamField path="embedding_model" type="BaseEmbedder">
|
||||
Configured embedding model for the RAG app
|
||||
</ParamField>
|
||||
<ParamField path="chunker" type="ChunkerConfig">
|
||||
Chunker configuration
|
||||
</ParamField>
|
||||
<ParamField path="client" type="Client" optional>
|
||||
Client object (used to deploy an app to Embedchain platform)
|
||||
</ParamField>
|
||||
<ParamField path="logger" type="logging.Logger">
|
||||
Logger object
|
||||
</ParamField>
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage
|
||||
|
||||
You can create an app instance using the following methods:
|
||||
|
||||
### Default setting
|
||||
|
||||
```python Code Example
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
app = App()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Python Dict
|
||||
|
||||
```python Code Example
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
|
||||
config_dict = {
|
||||
'llm': {
|
||||
'provider': 'gpt4all',
|
||||
'config': {
|
||||
'model': 'orca-mini-3b-gguf2-q4_0.gguf',
|
||||
'temperature': 0.5,
|
||||
'max_tokens': 1000,
|
||||
'top_p': 1,
|
||||
'stream': False
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
'embedder': {
|
||||
'provider': 'gpt4all'
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
# load llm configuration from config dict
|
||||
app = App.from_config(config=config_dict)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### YAML Config
|
||||
|
||||
<CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
```python main.py
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
|
||||
# load llm configuration from config.yaml file
|
||||
app = App.from_config(config_path="config.yaml")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml config.yaml
|
||||
llm:
|
||||
provider: gpt4all
|
||||
config:
|
||||
model: 'orca-mini-3b-gguf2-q4_0.gguf'
|
||||
temperature: 0.5
|
||||
max_tokens: 1000
|
||||
top_p: 1
|
||||
stream: false
|
||||
|
||||
embedder:
|
||||
provider: gpt4all
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
### JSON Config
|
||||
|
||||
<CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
```python main.py
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
|
||||
# load llm configuration from config.json file
|
||||
app = App.from_config(config_path="config.json")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```json config.json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"llm": {
|
||||
"provider": "gpt4all",
|
||||
"config": {
|
||||
"model": "orca-mini-3b-gguf2-q4_0.gguf",
|
||||
"temperature": 0.5,
|
||||
"max_tokens": 1000,
|
||||
"top_p": 1,
|
||||
"stream": false
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"embedder": {
|
||||
"provider": "gpt4all"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</CodeGroup>
|
||||
109
embedchain/docs/api-reference/app/query.mdx
Normal file
109
embedchain/docs/api-reference/app/query.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,109 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: '❓ query'
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
`.query()` method empowers developers to ask questions and receive relevant answers through a user-friendly query API. Function signature is given below:
|
||||
|
||||
### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
<ParamField path="input_query" type="str">
|
||||
Question to ask
|
||||
</ParamField>
|
||||
<ParamField path="config" type="BaseLlmConfig" optional>
|
||||
Configure different llm settings such as prompt, temprature, number_documents etc.
|
||||
</ParamField>
|
||||
<ParamField path="dry_run" type="bool" optional>
|
||||
The purpose is to test the prompt structure without actually running LLM inference. Defaults to `False`
|
||||
</ParamField>
|
||||
<ParamField path="where" type="dict" optional>
|
||||
A dictionary of key-value pairs to filter the chunks from the vector database. Defaults to `None`
|
||||
</ParamField>
|
||||
<ParamField path="citations" type="bool" optional>
|
||||
Return citations along with the LLM answer. Defaults to `False`
|
||||
</ParamField>
|
||||
|
||||
### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
<ResponseField name="answer" type="str | tuple">
|
||||
If `citations=False`, return a stringified answer to the question asked. <br />
|
||||
If `citations=True`, returns a tuple with answer and citations respectively.
|
||||
</ResponseField>
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage
|
||||
|
||||
### With citations
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to get the answer to question and return both answer and citations, use the following code snippet:
|
||||
|
||||
```python With Citations
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
|
||||
# Initialize app
|
||||
app = App()
|
||||
|
||||
# Add data source
|
||||
app.add("https://www.forbes.com/profile/elon-musk")
|
||||
|
||||
# Get relevant answer for your query
|
||||
answer, sources = app.query("What is the net worth of Elon?", citations=True)
|
||||
print(answer)
|
||||
# Answer: The net worth of Elon Musk is $221.9 billion.
|
||||
|
||||
print(sources)
|
||||
# [
|
||||
# (
|
||||
# 'Elon Musk PROFILEElon MuskCEO, Tesla$247.1B$2.3B (0.96%)Real Time Net Worthas of 12/7/23 ...',
|
||||
# {
|
||||
# 'url': 'https://www.forbes.com/profile/elon-musk',
|
||||
# 'score': 0.89,
|
||||
# ...
|
||||
# }
|
||||
# ),
|
||||
# (
|
||||
# '74% of the company, which is now called X.Wealth HistoryHOVER TO REVEAL NET WORTH BY YEARForbes ...',
|
||||
# {
|
||||
# 'url': 'https://www.forbes.com/profile/elon-musk',
|
||||
# 'score': 0.81,
|
||||
# ...
|
||||
# }
|
||||
# ),
|
||||
# (
|
||||
# 'founded in 2002, is worth nearly $150 billion after a $750 million tender offer in June 2023 ...',
|
||||
# {
|
||||
# 'url': 'https://www.forbes.com/profile/elon-musk',
|
||||
# 'score': 0.73,
|
||||
# ...
|
||||
# }
|
||||
# )
|
||||
# ]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Note>
|
||||
When `citations=True`, note that the returned `sources` are a list of tuples where each tuple has two elements (in the following order):
|
||||
1. source chunk
|
||||
2. dictionary with metadata about the source chunk
|
||||
- `url`: url of the source
|
||||
- `doc_id`: document id (used for book keeping purposes)
|
||||
- `score`: score of the source chunk with respect to the question
|
||||
- other metadata you might have added at the time of adding the source
|
||||
</Note>
|
||||
|
||||
### Without citations
|
||||
|
||||
If you just want to return answers and don't want to return citations, you can use the following example:
|
||||
|
||||
```python Without Citations
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
|
||||
# Initialize app
|
||||
app = App()
|
||||
|
||||
# Add data source
|
||||
app.add("https://www.forbes.com/profile/elon-musk")
|
||||
|
||||
# Get relevant answer for your query
|
||||
answer = app.query("What is the net worth of Elon?")
|
||||
print(answer)
|
||||
# Answer: The net worth of Elon Musk is $221.9 billion.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
17
embedchain/docs/api-reference/app/reset.mdx
Normal file
17
embedchain/docs/api-reference/app/reset.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: 🔄 reset
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
`reset()` method allows you to wipe the data from your RAG application and start from scratch.
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
|
||||
app = App()
|
||||
app.add("https://www.forbes.com/profile/elon-musk")
|
||||
|
||||
# Reset the app
|
||||
app.reset()
|
||||
```
|
||||
111
embedchain/docs/api-reference/app/search.mdx
Normal file
111
embedchain/docs/api-reference/app/search.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,111 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: '🔍 search'
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
`.search()` enables you to uncover the most pertinent context by performing a semantic search across your data sources based on a given query. Refer to the function signature below:
|
||||
|
||||
### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
<ParamField path="query" type="str">
|
||||
Question
|
||||
</ParamField>
|
||||
<ParamField path="num_documents" type="int" optional>
|
||||
Number of relevant documents to fetch. Defaults to `3`
|
||||
</ParamField>
|
||||
<ParamField path="where" type="dict" optional>
|
||||
Key value pair for metadata filtering.
|
||||
</ParamField>
|
||||
<ParamField path="raw_filter" type="dict" optional>
|
||||
Pass raw filter query based on your vector database.
|
||||
Currently, `raw_filter` param is only supported for Pinecone vector database.
|
||||
</ParamField>
|
||||
|
||||
### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
<ResponseField name="answer" type="dict">
|
||||
Return list of dictionaries that contain the relevant chunk and their source information.
|
||||
</ResponseField>
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage
|
||||
|
||||
### Basic
|
||||
|
||||
Refer to the following example on how to use the search api:
|
||||
|
||||
```python Code example
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
|
||||
app = App()
|
||||
app.add("https://www.forbes.com/profile/elon-musk")
|
||||
|
||||
context = app.search("What is the net worth of Elon?", num_documents=2)
|
||||
print(context)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Advanced
|
||||
|
||||
#### Metadata filtering using `where` params
|
||||
|
||||
Here is an advanced example of `search()` API with metadata filtering on pinecone database:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import os
|
||||
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
|
||||
os.environ["PINECONE_API_KEY"] = "xxx"
|
||||
|
||||
config = {
|
||||
"vectordb": {
|
||||
"provider": "pinecone",
|
||||
"config": {
|
||||
"metric": "dotproduct",
|
||||
"vector_dimension": 1536,
|
||||
"index_name": "ec-test",
|
||||
"serverless_config": {"cloud": "aws", "region": "us-west-2"},
|
||||
},
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
app = App.from_config(config=config)
|
||||
|
||||
app.add("https://www.forbes.com/profile/bill-gates", metadata={"type": "forbes", "person": "gates"})
|
||||
app.add("https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bill_Gates", metadata={"type": "wiki", "person": "gates"})
|
||||
|
||||
results = app.search("What is the net worth of Bill Gates?", where={"person": "gates"})
|
||||
print("Num of search results: ", len(results))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Metadata filtering using `raw_filter` params
|
||||
|
||||
Following is an example of metadata filtering by passing the raw filter query that pinecone vector database follows:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import os
|
||||
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
|
||||
os.environ["PINECONE_API_KEY"] = "xxx"
|
||||
|
||||
config = {
|
||||
"vectordb": {
|
||||
"provider": "pinecone",
|
||||
"config": {
|
||||
"metric": "dotproduct",
|
||||
"vector_dimension": 1536,
|
||||
"index_name": "ec-test",
|
||||
"serverless_config": {"cloud": "aws", "region": "us-west-2"},
|
||||
},
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
app = App.from_config(config=config)
|
||||
|
||||
app.add("https://www.forbes.com/profile/bill-gates", metadata={"year": 2022, "person": "gates"})
|
||||
app.add("https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bill_Gates", metadata={"year": 2024, "person": "gates"})
|
||||
|
||||
print("Filter with person: gates and year > 2023")
|
||||
raw_filter = {"$and": [{"person": "gates"}, {"year": {"$gt": 2023}}]}
|
||||
results = app.search("What is the net worth of Bill Gates?", raw_filter=raw_filter)
|
||||
print("Num of search results: ", len(results))
|
||||
```
|
||||
0
embedchain/docs/api-reference/overview.mdx
Normal file
0
embedchain/docs/api-reference/overview.mdx
Normal file
54
embedchain/docs/api-reference/store/ai-assistants.mdx
Normal file
54
embedchain/docs/api-reference/store/ai-assistants.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,54 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: 'AI Assistant'
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
The `AIAssistant` class, an alternative to the OpenAI Assistant API, is designed for those who prefer using large language models (LLMs) other than those provided by OpenAI. It facilitates the creation of AI Assistants with several key benefits:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Visibility into Citations**: It offers transparent access to the sources and citations used by the AI, enhancing the understanding and trustworthiness of its responses.
|
||||
|
||||
- **Debugging Capabilities**: Users have the ability to delve into and debug the AI's processes, allowing for a deeper understanding and fine-tuning of its performance.
|
||||
|
||||
- **Customizable Prompts**: The class provides the flexibility to modify and tailor prompts according to specific needs, enabling more precise and relevant interactions.
|
||||
|
||||
- **Chain of Thought Integration**: It supports the incorporation of a 'chain of thought' approach, which helps in breaking down complex queries into simpler, sequential steps, thereby improving the clarity and accuracy of responses.
|
||||
|
||||
It is ideal for those who value customization, transparency, and detailed control over their AI Assistant's functionalities.
|
||||
|
||||
### Arguments
|
||||
|
||||
<ParamField path="name" type="string" optional>
|
||||
Name for your AI assistant
|
||||
</ParamField>
|
||||
|
||||
<ParamField path="instructions" type="string" optional>
|
||||
How the Assistant and model should behave or respond
|
||||
</ParamField>
|
||||
|
||||
<ParamField path="assistant_id" type="string" optional>
|
||||
Load existing AI Assistant. If you pass this, you don't have to pass other arguments.
|
||||
</ParamField>
|
||||
|
||||
<ParamField path="thread_id" type="string" optional>
|
||||
Existing thread id if exists
|
||||
</ParamField>
|
||||
|
||||
<ParamField path="yaml_path" type="str" Optional>
|
||||
Embedchain pipeline config yaml path to use. This will define the configuration of the AI Assistant (such as configuring the LLM, vector database, and embedding model)
|
||||
</ParamField>
|
||||
|
||||
<ParamField path="data_sources" type="list" default="[]">
|
||||
Add data sources to your assistant. You can add in the following format: `[{"source": "https://example.com", "data_type": "web_page"}]`
|
||||
</ParamField>
|
||||
|
||||
<ParamField path="collect_metrics" type="boolean" default="True">
|
||||
Anonymous telemetry (doesn't collect any user information or user's files). Used to improve the Embedchain package utilization. Default is `True`.
|
||||
</ParamField>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage
|
||||
|
||||
For detailed guidance on creating your own AI Assistant, click the link below. It provides step-by-step instructions to help you through the process:
|
||||
|
||||
<Card title="Guide to Creating Your AI Assistant" icon="link" href="/examples/opensource-assistant">
|
||||
Learn how to build a customized AI Assistant using the `AIAssistant` class.
|
||||
</Card>
|
||||
45
embedchain/docs/api-reference/store/openai-assistant.mdx
Normal file
45
embedchain/docs/api-reference/store/openai-assistant.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,45 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: 'OpenAI Assistant'
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
### Arguments
|
||||
|
||||
<ParamField path="name" type="string">
|
||||
Name for your AI assistant
|
||||
</ParamField>
|
||||
|
||||
<ParamField path="instructions" type="string">
|
||||
how the Assistant and model should behave or respond
|
||||
</ParamField>
|
||||
|
||||
<ParamField path="assistant_id" type="string">
|
||||
Load existing OpenAI Assistant. If you pass this, you don't have to pass other arguments.
|
||||
</ParamField>
|
||||
|
||||
<ParamField path="thread_id" type="string">
|
||||
Existing OpenAI thread id if exists
|
||||
</ParamField>
|
||||
|
||||
<ParamField path="model" type="str" default="gpt-4-1106-preview">
|
||||
OpenAI model to use
|
||||
</ParamField>
|
||||
|
||||
<ParamField path="tools" type="list">
|
||||
OpenAI tools to use. Default set to `[{"type": "retrieval"}]`
|
||||
</ParamField>
|
||||
|
||||
<ParamField path="data_sources" type="list" default="[]">
|
||||
Add data sources to your assistant. You can add in the following format: `[{"source": "https://example.com", "data_type": "web_page"}]`
|
||||
</ParamField>
|
||||
|
||||
<ParamField path="telemetry" type="boolean" default="True">
|
||||
Anonymous telemetry (doesn't collect any user information or user's files). Used to improve the Embedchain package utilization. Default is `True`.
|
||||
</ParamField>
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage
|
||||
|
||||
For detailed guidance on creating your own OpenAI Assistant, click the link below. It provides step-by-step instructions to help you through the process:
|
||||
|
||||
<Card title="Guide to Creating Your OpenAI Assistant" icon="link" href="/examples/openai-assistant">
|
||||
Learn how to build an OpenAI Assistant using the `OpenAIAssistant` class.
|
||||
</Card>
|
||||
28
embedchain/docs/community/connect-with-us.mdx
Normal file
28
embedchain/docs/community/connect-with-us.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,28 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: 🤝 Connect with Us
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
We believe in building a vibrant and supportive community around embedchain. There are various channels through which you can connect with us, stay updated, and contribute to the ongoing discussions:
|
||||
|
||||
<CardGroup cols={3}>
|
||||
<Card title="Twitter" icon="twitter" href="https://twitter.com/embedchain">
|
||||
Follow us on Twitter
|
||||
</Card>
|
||||
<Card title="Slack" icon="slack" href="https://embedchain.ai/slack" color="#4A154B">
|
||||
Join our slack community
|
||||
</Card>
|
||||
<Card title="Discord" icon="discord" href="https://discord.gg/6PzXDgEjG5" color="#7289DA">
|
||||
Join our discord community
|
||||
</Card>
|
||||
<Card title="LinkedIn" icon="linkedin" href="https://www.linkedin.com/company/embedchain/">
|
||||
Connect with us on LinkedIn
|
||||
</Card>
|
||||
<Card title="Schedule a call" icon="calendar" href="https://cal.com/taranjeetio/ec">
|
||||
Schedule a call with Embedchain founder
|
||||
</Card>
|
||||
<Card title="Newsletter" icon="message" href="https://embedchain.substack.com/">
|
||||
Subscribe to our newsletter
|
||||
</Card>
|
||||
</CardGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
We look forward to connecting with you and seeing how we can create amazing things together!
|
||||
25
embedchain/docs/components/data-sources/audio.mdx
Normal file
25
embedchain/docs/components/data-sources/audio.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,25 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: "🎤 Audio"
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
To use an audio as data source, just add `data_type` as `audio` and pass in the path of the audio (local or hosted).
|
||||
|
||||
We use [Deepgram](https://developers.deepgram.com/docs/introduction) to transcribe the audiot to text, and then use the generated text as the data source.
|
||||
|
||||
You would require an Deepgram API key which is available [here](https://console.deepgram.com/signup?jump=keys) to use this feature.
|
||||
|
||||
### Without customization
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import os
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
|
||||
os.environ["DEEPGRAM_API_KEY"] = "153xxx"
|
||||
|
||||
app = App()
|
||||
app.add("introduction.wav", data_type="audio")
|
||||
response = app.query("What is my name and how old am I?")
|
||||
print(response)
|
||||
# Answer: Your name is Dave and you are 21 years old.
|
||||
```
|
||||
16
embedchain/docs/components/data-sources/beehiiv.mdx
Normal file
16
embedchain/docs/components/data-sources/beehiiv.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,16 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: "🐝 Beehiiv"
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
To add any Beehiiv data sources to your app, just add the base url as the source and set the data_type to `beehiiv`.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
|
||||
app = App()
|
||||
|
||||
# source: just add the base url and set the data_type to 'beehiiv'
|
||||
app.add('https://aibreakfast.beehiiv.com', data_type='beehiiv')
|
||||
app.query("How much is OpenAI paying developers?")
|
||||
# Answer: OpenAI is aggressively recruiting Google's top AI researchers with offers ranging between $5 to $10 million annually, primarily in stock options.
|
||||
```
|
||||
28
embedchain/docs/components/data-sources/csv.mdx
Normal file
28
embedchain/docs/components/data-sources/csv.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,28 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: '📊 CSV'
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
You can load any csv file from your local file system or through a URL. Headers are included for each line, so if you have an `age` column, `18` will be added as `age: 18`.
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage
|
||||
|
||||
### Load from a local file
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
app = App()
|
||||
app.add('/path/to/file.csv', data_type='csv')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Load from URL
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
app = App()
|
||||
app.add('https://people.sc.fsu.edu/~jburkardt/data/csv/airtravel.csv', data_type="csv")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Note>
|
||||
There is a size limit allowed for csv file beyond which it can throw error. This limit is set by the LLMs. Please consider chunking large csv files into smaller csv files.
|
||||
</Note>
|
||||
|
||||
42
embedchain/docs/components/data-sources/custom.mdx
Normal file
42
embedchain/docs/components/data-sources/custom.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,42 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: '⚙️ Custom'
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
When we say "custom", we mean that you can customize the loader and chunker to your needs. This is done by passing a custom loader and chunker to the `add` method.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
import your_loader
|
||||
from my_module import CustomLoader
|
||||
from my_module import CustomChunker
|
||||
|
||||
app = App()
|
||||
loader = CustomLoader()
|
||||
chunker = CustomChunker()
|
||||
|
||||
app.add("source", data_type="custom", loader=loader, chunker=chunker)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Note>
|
||||
The custom loader and chunker must be a class that inherits from the [`BaseLoader`](https://github.com/embedchain/embedchain/blob/main/embedchain/loaders/base_loader.py) and [`BaseChunker`](https://github.com/embedchain/embedchain/blob/main/embedchain/chunkers/base_chunker.py) classes respectively.
|
||||
</Note>
|
||||
|
||||
<Note>
|
||||
If the `data_type` is not a valid data type, the `add` method will fallback to the `custom` data type and expect a custom loader and chunker to be passed by the user.
|
||||
</Note>
|
||||
|
||||
Example:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
from embedchain.loaders.github import GithubLoader
|
||||
|
||||
app = App()
|
||||
|
||||
loader = GithubLoader(config={"token": "ghp_xxx"})
|
||||
|
||||
app.add("repo:embedchain/embedchain type:repo", data_type="github", loader=loader)
|
||||
|
||||
app.query("What is Embedchain?")
|
||||
# Answer: Embedchain is a Data Platform for Large Language Models (LLMs). It allows users to seamlessly load, index, retrieve, and sync unstructured data in order to build dynamic, LLM-powered applications. There is also a JavaScript implementation called embedchain-js available on GitHub.
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,85 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: 'Data type handling'
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## Automatic data type detection
|
||||
|
||||
The add method automatically tries to detect the data_type, based on your input for the source argument. So `app.add('https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dQw4w9WgXcQ')` is enough to embed a YouTube video.
|
||||
|
||||
This detection is implemented for all formats. It is based on factors such as whether it's a URL, a local file, the source data type, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
### Debugging automatic detection
|
||||
|
||||
Set `log_level: DEBUG` in the config yaml to debug if the data type detection is done right or not. Otherwise, you will not know when, for instance, an invalid filepath is interpreted as raw text instead.
|
||||
|
||||
### Forcing a data type
|
||||
|
||||
To omit any issues with the data type detection, you can **force** a data_type by adding it as a `add` method argument.
|
||||
The examples below show you the keyword to force the respective `data_type`.
|
||||
|
||||
Forcing can also be used for edge cases, such as interpreting a sitemap as a web_page, for reading its raw text instead of following links.
|
||||
|
||||
## Remote data types
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
**Use local files in remote data types**
|
||||
|
||||
Some data_types are meant for remote content and only work with URLs.
|
||||
You can pass local files by formatting the path using the `file:` [URI scheme](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File_URI_scheme), e.g. `file:///info.pdf`.
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
## Reusing a vector database
|
||||
|
||||
Default behavior is to create a persistent vector db in the directory **./db**. You can split your application into two Python scripts: one to create a local vector db and the other to reuse this local persistent vector db. This is useful when you want to index hundreds of documents and separately implement a chat interface.
|
||||
|
||||
Create a local index:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
|
||||
config = {
|
||||
"app": {
|
||||
"config": {
|
||||
"id": "app-1"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
naval_chat_bot = App.from_config(config=config)
|
||||
naval_chat_bot.add("https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3qHkcs3kG44")
|
||||
naval_chat_bot.add("https://navalmanack.s3.amazonaws.com/Eric-Jorgenson_The-Almanack-of-Naval-Ravikant_Final.pdf")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can reuse the local index with the same code, but without adding new documents:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
|
||||
config = {
|
||||
"app": {
|
||||
"config": {
|
||||
"id": "app-1"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
naval_chat_bot = App.from_config(config=config)
|
||||
print(naval_chat_bot.query("What unique capacity does Naval argue humans possess when it comes to understanding explanations or concepts?"))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Resetting an app and vector database
|
||||
|
||||
You can reset the app by simply calling the `reset` method. This will delete the vector database and all other app related files.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
|
||||
app = App()config = {
|
||||
"app": {
|
||||
"config": {
|
||||
"id": "app-1"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
naval_chat_bot = App.from_config(config=config)
|
||||
app.add("https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3qHkcs3kG44")
|
||||
app.reset()
|
||||
```
|
||||
41
embedchain/docs/components/data-sources/directory.mdx
Normal file
41
embedchain/docs/components/data-sources/directory.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,41 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: '📁 Directory/Folder'
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
To use an entire directory as data source, just add `data_type` as `directory` and pass in the path of the local directory.
|
||||
|
||||
### Without customization
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import os
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
|
||||
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = "sk-xxx"
|
||||
|
||||
app = App()
|
||||
app.add("./elon-musk", data_type="directory")
|
||||
response = app.query("list all files")
|
||||
print(response)
|
||||
# Answer: Files are elon-musk-1.txt, elon-musk-2.pdf.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Customization
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import os
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
from embedchain.loaders.directory_loader import DirectoryLoader
|
||||
|
||||
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = "sk-xxx"
|
||||
lconfig = {
|
||||
"recursive": True,
|
||||
"extensions": [".txt"]
|
||||
}
|
||||
loader = DirectoryLoader(config=lconfig)
|
||||
app = App()
|
||||
app.add("./elon-musk", loader=loader)
|
||||
response = app.query("what are all the files related to?")
|
||||
print(response)
|
||||
|
||||
# Answer: The files are related to Elon Musk.
|
||||
```
|
||||
28
embedchain/docs/components/data-sources/discord.mdx
Normal file
28
embedchain/docs/components/data-sources/discord.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,28 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: "💬 Discord"
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
To add any Discord channel messages to your app, just add the `channel_id` as the source and set the `data_type` to `discord`.
|
||||
|
||||
<Note>
|
||||
This loader requires a Discord bot token with read messages access.
|
||||
To obtain the token, follow the instructions provided in this tutorial:
|
||||
<a href="https://www.writebots.com/discord-bot-token/">How to Get a Discord Bot Token?</a>.
|
||||
</Note>
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import os
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
|
||||
# add your discord "BOT" token
|
||||
os.environ["DISCORD_TOKEN"] = "xxx"
|
||||
|
||||
app = App()
|
||||
|
||||
app.add("1177296711023075338", data_type="discord")
|
||||
|
||||
response = app.query("What is Joe saying about Elon Musk?")
|
||||
|
||||
print(response)
|
||||
# Answer: Joe is saying "Elon Musk is a genius".
|
||||
```
|
||||
44
embedchain/docs/components/data-sources/discourse.mdx
Normal file
44
embedchain/docs/components/data-sources/discourse.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,44 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: '🗨️ Discourse'
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
You can now easily load data from your community built with [Discourse](https://discourse.org/).
|
||||
|
||||
## Example
|
||||
|
||||
1. Setup the Discourse Loader with your community url.
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
from embedchain.loaders.discourse import DiscourseLoader
|
||||
|
||||
dicourse_loader = DiscourseLoader(config={"domain": "https://community.openai.com"})
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. Once you setup the loader, you can create an app and load data using the above discourse loader
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
import os
|
||||
from embedchain.pipeline import Pipeline as App
|
||||
|
||||
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = "sk-xxx"
|
||||
|
||||
app = App()
|
||||
|
||||
app.add("openai after:2023-10-1", data_type="discourse", loader=dicourse_loader)
|
||||
|
||||
question = "Where can I find the OpenAI API status page?"
|
||||
app.query(question)
|
||||
# Answer: You can find the OpenAI API status page at https:/status.openai.com/.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
NOTE: The `add` function of the app will accept any executable search query to load data. Refer [Discourse API Docs](https://docs.discourse.org/#tag/Search) to learn more about search queries.
|
||||
|
||||
3. We automatically create a chunker to chunk your discourse data, however if you wish to provide your own chunker class. Here is how you can do that:
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
|
||||
from embedchain.chunkers.discourse import DiscourseChunker
|
||||
from embedchain.config.add_config import ChunkerConfig
|
||||
|
||||
discourse_chunker_config = ChunkerConfig(chunk_size=1000, chunk_overlap=0, length_function=len)
|
||||
discourse_chunker = DiscourseChunker(config=discourse_chunker_config)
|
||||
|
||||
app.add("openai", data_type='discourse', loader=dicourse_loader, chunker=discourse_chunker)
|
||||
```
|
||||
14
embedchain/docs/components/data-sources/docs-site.mdx
Normal file
14
embedchain/docs/components/data-sources/docs-site.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,14 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: '📚 Code Docs website'
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
To add any code documentation website as a loader, use the data_type as `docs_site`. Eg:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
|
||||
app = App()
|
||||
app.add("https://docs.embedchain.ai/", data_type="docs_site")
|
||||
app.query("What is Embedchain?")
|
||||
# Answer: Embedchain is a platform that utilizes various components, including paid/proprietary ones, to provide what is believed to be the best configuration available. It uses LLM (Language Model) providers such as OpenAI, Anthpropic, Vertex_AI, GPT4ALL, Azure_OpenAI, LLAMA2, JINA, Ollama, Together and COHERE. Embedchain allows users to import and utilize these LLM providers for their applications.'
|
||||
```
|
||||
18
embedchain/docs/components/data-sources/docx.mdx
Normal file
18
embedchain/docs/components/data-sources/docx.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,18 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: '📄 Docx file'
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
### Docx file
|
||||
|
||||
To add any doc/docx file, use the data_type as `docx`. `docx` allows remote urls and conventional file paths. Eg:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
|
||||
app = App()
|
||||
app.add('https://example.com/content/intro.docx', data_type="docx")
|
||||
# Or add file using the local file path on your system
|
||||
# app.add('content/intro.docx', data_type="docx")
|
||||
|
||||
app.query("Summarize the docx data?")
|
||||
```
|
||||
37
embedchain/docs/components/data-sources/dropbox.mdx
Normal file
37
embedchain/docs/components/data-sources/dropbox.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,37 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: '💾 Dropbox'
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
To load folders or files from your Dropbox account, configure the `data_type` parameter as `dropbox` and specify the path to the desired file or folder, starting from the root directory of your Dropbox account.
|
||||
|
||||
For Dropbox access, an **access token** is required. Obtain this token by visiting [Dropbox Developer Apps](https://www.dropbox.com/developers/apps). There, create a new app and generate an access token for it.
|
||||
|
||||
Ensure your app has the following settings activated:
|
||||
|
||||
- In the Permissions section, enable `files.content.read` and `files.metadata.read`.
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage
|
||||
|
||||
Install the `dropbox` pypi package:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install dropbox
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Following is an example of how to use the dropbox loader:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import os
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
|
||||
os.environ["DROPBOX_ACCESS_TOKEN"] = "sl.xxx"
|
||||
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = "sk-xxx"
|
||||
|
||||
app = App()
|
||||
|
||||
# any path from the root of your dropbox account, you can leave it "" for the root folder
|
||||
app.add("/test", data_type="dropbox")
|
||||
|
||||
print(app.query("Which two celebrities are mentioned here?"))
|
||||
# The two celebrities mentioned in the given context are Elon Musk and Jeff Bezos.
|
||||
```
|
||||
18
embedchain/docs/components/data-sources/excel-file.mdx
Normal file
18
embedchain/docs/components/data-sources/excel-file.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,18 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: '📄 Excel file'
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
### Excel file
|
||||
|
||||
To add any xlsx/xls file, use the data_type as `excel_file`. `excel_file` allows remote urls and conventional file paths. Eg:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
|
||||
app = App()
|
||||
app.add('https://example.com/content/intro.xlsx', data_type="excel_file")
|
||||
# Or add file using the local file path on your system
|
||||
# app.add('content/intro.xls', data_type="excel_file")
|
||||
|
||||
app.query("Give brief information about data.")
|
||||
```
|
||||
52
embedchain/docs/components/data-sources/github.mdx
Normal file
52
embedchain/docs/components/data-sources/github.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,52 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: 📝 Github
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
1. Setup the Github loader by configuring the Github account with username and personal access token (PAT). Check out [this](https://docs.github.com/en/enterprise-server@3.6/authentication/keeping-your-account-and-data-secure/managing-your-personal-access-tokens#creating-a-personal-access-token) link to learn how to create a PAT.
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
from embedchain.loaders.github import GithubLoader
|
||||
|
||||
loader = GithubLoader(
|
||||
config={
|
||||
"token":"ghp_xxxx"
|
||||
}
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. Once you setup the loader, you can create an app and load data using the above Github loader
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
import os
|
||||
from embedchain.pipeline import Pipeline as App
|
||||
|
||||
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = "sk-xxxx"
|
||||
|
||||
app = App()
|
||||
|
||||
app.add("repo:embedchain/embedchain type:repo", data_type="github", loader=loader)
|
||||
|
||||
response = app.query("What is Embedchain?")
|
||||
# Answer: Embedchain is a Data Platform for Large Language Models (LLMs). It allows users to seamlessly load, index, retrieve, and sync unstructured data in order to build dynamic, LLM-powered applications. There is also a JavaScript implementation called embedchain-js available on GitHub.
|
||||
```
|
||||
The `add` function of the app will accept any valid github query with qualifiers. It only supports loading github code, repository, issues and pull-requests.
|
||||
<Note>
|
||||
You must provide qualifiers `type:` and `repo:` in the query. The `type:` qualifier can be a combination of `code`, `repo`, `pr`, `issue`, `branch`, `file`. The `repo:` qualifier must be a valid github repository name.
|
||||
</Note>
|
||||
|
||||
<Card title="Valid queries" icon="lightbulb" iconType="duotone" color="#ca8b04">
|
||||
- `repo:embedchain/embedchain type:repo` - to load the repository
|
||||
- `repo:embedchain/embedchain type:branch name:feature_test` - to load the branch of the repository
|
||||
- `repo:embedchain/embedchain type:file path:README.md` - to load the specific file of the repository
|
||||
- `repo:embedchain/embedchain type:issue,pr` - to load the issues and pull-requests of the repository
|
||||
- `repo:embedchain/embedchain type:issue state:closed` - to load the closed issues of the repository
|
||||
</Card>
|
||||
|
||||
3. We automatically create a chunker to chunk your GitHub data, however if you wish to provide your own chunker class. Here is how you can do that:
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
from embedchain.chunkers.common_chunker import CommonChunker
|
||||
from embedchain.config.add_config import ChunkerConfig
|
||||
|
||||
github_chunker_config = ChunkerConfig(chunk_size=2000, chunk_overlap=0, length_function=len)
|
||||
github_chunker = CommonChunker(config=github_chunker_config)
|
||||
|
||||
app.add(load_query, data_type="github", loader=loader, chunker=github_chunker)
|
||||
```
|
||||
34
embedchain/docs/components/data-sources/gmail.mdx
Normal file
34
embedchain/docs/components/data-sources/gmail.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,34 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: '📬 Gmail'
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
To use GmailLoader you must install the extra dependencies with `pip install --upgrade embedchain[gmail]`.
|
||||
|
||||
The `source` must be a valid Gmail search query, you can refer `https://support.google.com/mail/answer/7190?hl=en` to build a query.
|
||||
|
||||
To load Gmail messages, you MUST use the data_type as `gmail`. Otherwise the source will be detected as simple `text`.
|
||||
|
||||
To use this you need to save `credentials.json` in the directory from where you will run the loader. Follow these steps to get the credentials
|
||||
|
||||
1. Go to the [Google Cloud Console](https://console.cloud.google.com/apis/credentials).
|
||||
2. Create a project if you don't have one already.
|
||||
3. Create an `OAuth Consent Screen` in the project. You may need to select the `external` option.
|
||||
4. Make sure the consent screen is published.
|
||||
5. Enable the [Gmail API](https://console.cloud.google.com/apis/api/gmail.googleapis.com)
|
||||
6. Create credentials from the `Credentials` tab.
|
||||
7. Select the type `OAuth Client ID`.
|
||||
8. Choose the application type `Web application`. As a name you can choose `embedchain` or any other name as per your use case.
|
||||
9. Add an authorized redirect URI for `http://localhost:8080/`.
|
||||
10. You can leave everything else at default, finish the creation.
|
||||
11. When you are done, a modal opens where you can download the details in `json` format.
|
||||
12. Put the `.json` file in your current directory and rename it to `credentials.json`
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
|
||||
app = App()
|
||||
|
||||
gmail_filter = "to: me label:inbox"
|
||||
app.add(gmail_filter, data_type="gmail")
|
||||
app.query("Summarize my email conversations")
|
||||
```
|
||||
28
embedchain/docs/components/data-sources/google-drive.mdx
Normal file
28
embedchain/docs/components/data-sources/google-drive.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,28 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: 'Google Drive'
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
To use GoogleDriveLoader you must install the extra dependencies with `pip install --upgrade embedchain[googledrive]`.
|
||||
|
||||
The data_type must be `google_drive`. Otherwise, it will be considered a regular web page.
|
||||
|
||||
Google Drive requires the setup of credentials. This can be done by following the steps below:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Go to the [Google Cloud Console](https://console.cloud.google.com/apis/credentials).
|
||||
2. Create a project if you don't have one already.
|
||||
3. Enable the [Google Drive API](https://console.cloud.google.com/flows/enableapi?apiid=drive.googleapis.com)
|
||||
4. [Authorize credentials for desktop app](https://developers.google.com/drive/api/quickstart/python#authorize_credentials_for_a_desktop_application)
|
||||
5. When done, you will be able to download the credentials in `json` format. Rename the downloaded file to `credentials.json` and save it in `~/.credentials/credentials.json`
|
||||
6. Set the environment variable `GOOGLE_APPLICATION_CREDENTIALS=~/.credentials/credentials.json`
|
||||
|
||||
The first time you use the loader, you will be prompted to enter your Google account credentials.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
|
||||
app = App()
|
||||
|
||||
url = "https://drive.google.com/drive/u/0/folders/xxx-xxx"
|
||||
app.add(url, data_type="google_drive")
|
||||
```
|
||||
45
embedchain/docs/components/data-sources/image.mdx
Normal file
45
embedchain/docs/components/data-sources/image.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,45 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: "🖼️ Image"
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
To use an image as data source, just add `data_type` as `image` and pass in the path of the image (local or hosted).
|
||||
|
||||
We use [GPT4 Vision](https://platform.openai.com/docs/guides/vision) to generate meaning of the image using a custom prompt, and then use the generated text as the data source.
|
||||
|
||||
You would require an OpenAI API key with access to `gpt-4-vision-preview` model to use this feature.
|
||||
|
||||
### Without customization
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import os
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
|
||||
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = "sk-xxx"
|
||||
|
||||
app = App()
|
||||
app.add("./Elon-Musk.webp", data_type="image")
|
||||
response = app.query("Describe the man in the image.")
|
||||
print(response)
|
||||
# Answer: The man in the image is dressed in formal attire, wearing a dark suit jacket and a white collared shirt. He has short hair and is standing. He appears to be gazing off to the side with a reflective expression. The background is dark with faint, warm-toned vertical lines, possibly from a lit environment behind the individual or reflections. The overall atmosphere is somewhat moody and introspective.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Customization
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import os
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
from embedchain.loaders.image import ImageLoader
|
||||
|
||||
image_loader = ImageLoader(
|
||||
max_tokens=100,
|
||||
api_key="sk-xxx",
|
||||
prompt="Is the person looking wealthy? Structure your thoughts around what you see in the image.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
app = App()
|
||||
app.add("./Elon-Musk.webp", data_type="image", loader=image_loader)
|
||||
response = app.query("Describe the man in the image.")
|
||||
print(response)
|
||||
# Answer: The man in the image appears to be well-dressed in a suit and shirt, suggesting that he may be in a professional or formal setting. His composed demeanor and confident posture further indicate a sense of self-assurance. Based on these visual cues, one could infer that the man may have a certain level of economic or social status, possibly indicating wealth or professional success.
|
||||
```
|
||||
44
embedchain/docs/components/data-sources/json.mdx
Normal file
44
embedchain/docs/components/data-sources/json.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,44 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: '📃 JSON'
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
To add any json file, use the data_type as `json`. Headers are included for each line, so for example if you have a json like `{"age": 18}`, then it will be added as `age: 18`.
|
||||
|
||||
Here are the supported sources for loading `json`:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
1. URL - valid url to json file that ends with ".json" extension.
|
||||
2. Local file - valid url to local json file that ends with ".json" extension.
|
||||
3. String - valid json string (e.g. - app.add('{"foo": "bar"}'))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
If you would like to add other data structures (e.g. list, dict etc.), convert it to a valid json first using `json.dumps()` function.
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
## Example
|
||||
|
||||
<CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
```python python
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
|
||||
app = App()
|
||||
|
||||
# Add json file
|
||||
app.add("temp.json")
|
||||
|
||||
app.query("What is the net worth of Elon Musk as of October 2023?")
|
||||
# As of October 2023, Elon Musk's net worth is $255.2 billion.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```json temp.json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"question": "What is your net worth, Elon Musk?",
|
||||
"answer": "As of October 2023, Elon Musk's net worth is $255.2 billion, making him one of the wealthiest individuals in the world."
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
</CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
14
embedchain/docs/components/data-sources/mdx.mdx
Normal file
14
embedchain/docs/components/data-sources/mdx.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,14 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: '📝 Mdx file'
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
To add any `.mdx` file to your app, use the data_type (first argument to `.add()` method) as `mdx`. Note that this supports support mdx file present on machine, so this should be a file path. Eg:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
|
||||
app = App()
|
||||
app.add('path/to/file.mdx', data_type='mdx')
|
||||
|
||||
app.query("What are the docs about?")
|
||||
```
|
||||
47
embedchain/docs/components/data-sources/mysql.mdx
Normal file
47
embedchain/docs/components/data-sources/mysql.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,47 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: '🐬 MySQL'
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
1. Setup the MySQL loader by configuring the SQL db.
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
from embedchain.loaders.mysql import MySQLLoader
|
||||
|
||||
config = {
|
||||
"host": "host",
|
||||
"port": "port",
|
||||
"database": "database",
|
||||
"user": "username",
|
||||
"password": "password",
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
mysql_loader = MySQLLoader(config=config)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For more details on how to setup with valid config, check MySQL [documentation](https://dev.mysql.com/doc/connector-python/en/connector-python-connectargs.html).
|
||||
|
||||
2. Once you setup the loader, you can create an app and load data using the above MySQL loader
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
from embedchain.pipeline import Pipeline as App
|
||||
|
||||
app = App()
|
||||
|
||||
app.add("SELECT * FROM table_name;", data_type='mysql', loader=mysql_loader)
|
||||
# Adds `(1, 'What is your net worth, Elon Musk?', "As of October 2023, Elon Musk's net worth is $255.2 billion.")`
|
||||
|
||||
response = app.query(question)
|
||||
# Answer: As of October 2023, Elon Musk's net worth is $255.2 billion.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
NOTE: The `add` function of the app will accept any executable query to load data. DO NOT pass the `CREATE`, `INSERT` queries in `add` function.
|
||||
|
||||
3. We automatically create a chunker to chunk your SQL data, however if you wish to provide your own chunker class. Here is how you can do that:
|
||||
``Python
|
||||
|
||||
from embedchain.chunkers.mysql import MySQLChunker
|
||||
from embedchain.config.add_config import ChunkerConfig
|
||||
|
||||
mysql_chunker_config = ChunkerConfig(chunk_size=1000, chunk_overlap=0, length_function=len)
|
||||
mysql_chunker = MySQLChunker(config=mysql_chunker_config)
|
||||
|
||||
app.add("SELECT * FROM table_name;", data_type='mysql', loader=mysql_loader, chunker=mysql_chunker)
|
||||
```
|
||||
20
embedchain/docs/components/data-sources/notion.mdx
Normal file
20
embedchain/docs/components/data-sources/notion.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,20 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: '📓 Notion'
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
To use notion you must install the extra dependencies with `pip install --upgrade embedchain[community]`.
|
||||
|
||||
To load a notion page, use the data_type as `notion`. Since it is hard to automatically detect, it is advised to specify the `data_type` when adding a notion document.
|
||||
The next argument must **end** with the `notion page id`. The id is a 32-character string. Eg:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
|
||||
app = App()
|
||||
|
||||
app.add("cfbc134ca6464fc980d0391613959196", data_type="notion")
|
||||
app.add("my-page-cfbc134ca6464fc980d0391613959196", data_type="notion")
|
||||
app.add("https://www.notion.so/my-page-cfbc134ca6464fc980d0391613959196", data_type="notion")
|
||||
|
||||
app.query("Summarize the notion doc")
|
||||
```
|
||||
22
embedchain/docs/components/data-sources/openapi.mdx
Normal file
22
embedchain/docs/components/data-sources/openapi.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,22 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: 🙌 OpenAPI
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
To add any OpenAPI spec yaml file (currently the json file will be detected as JSON data type), use the data_type as 'openapi'. 'openapi' allows remote urls and conventional file paths.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
|
||||
app = App()
|
||||
|
||||
app.add("https://github.com/openai/openai-openapi/blob/master/openapi.yaml", data_type="openapi")
|
||||
# Or add using the local file path
|
||||
# app.add("configs/openai_openapi.yaml", data_type="openapi")
|
||||
|
||||
app.query("What can OpenAI API endpoint do? Can you list the things it can learn from?")
|
||||
# Answer: The OpenAI API endpoint allows users to interact with OpenAI's models and perform various tasks such as generating text, answering questions, summarizing documents, translating languages, and more. The specific capabilities and tasks that the API can learn from may vary depending on the models and features provided by OpenAI. For more detailed information, it is recommended to refer to the OpenAI API documentation at https://platform.openai.com/docs/api-reference.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Note>
|
||||
The yaml file added to the App must have the required OpenAPI fields otherwise the adding OpenAPI spec will fail. Please refer to [OpenAPI Spec Doc](https://spec.openapis.org/oas/v3.1.0)
|
||||
</Note>
|
||||
43
embedchain/docs/components/data-sources/overview.mdx
Normal file
43
embedchain/docs/components/data-sources/overview.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,43 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Overview
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Embedchain comes with built-in support for various data sources. We handle the complexity of loading unstructured data from these data sources, allowing you to easily customize your app through a user-friendly interface.
|
||||
|
||||
<CardGroup cols={4}>
|
||||
<Card title="PDF file" href="/components/data-sources/pdf-file"></Card>
|
||||
<Card title="CSV file" href="/components/data-sources/csv"></Card>
|
||||
<Card title="JSON file" href="/components/data-sources/json"></Card>
|
||||
<Card title="Text" href="/components/data-sources/text"></Card>
|
||||
<Card title="Text File" href="/components/data-sources/text-file"></Card>
|
||||
<Card title="Directory" href="/components/data-sources/directory"></Card>
|
||||
<Card title="Web page" href="/components/data-sources/web-page"></Card>
|
||||
<Card title="Youtube Channel" href="/components/data-sources/youtube-channel"></Card>
|
||||
<Card title="Youtube Video" href="/components/data-sources/youtube-video"></Card>
|
||||
<Card title="Docs website" href="/components/data-sources/docs-site"></Card>
|
||||
<Card title="MDX file" href="/components/data-sources/mdx"></Card>
|
||||
<Card title="DOCX file" href="/components/data-sources/docx"></Card>
|
||||
<Card title="Notion" href="/components/data-sources/notion"></Card>
|
||||
<Card title="Sitemap" href="/components/data-sources/sitemap"></Card>
|
||||
<Card title="XML file" href="/components/data-sources/xml"></Card>
|
||||
<Card title="Q&A pair" href="/components/data-sources/qna"></Card>
|
||||
<Card title="OpenAPI" href="/components/data-sources/openapi"></Card>
|
||||
<Card title="Gmail" href="/components/data-sources/gmail"></Card>
|
||||
<Card title="Google Drive" href="/components/data-sources/google-drive"></Card>
|
||||
<Card title="GitHub" href="/components/data-sources/github"></Card>
|
||||
<Card title="Postgres" href="/components/data-sources/postgres"></Card>
|
||||
<Card title="MySQL" href="/components/data-sources/mysql"></Card>
|
||||
<Card title="Slack" href="/components/data-sources/slack"></Card>
|
||||
<Card title="Discord" href="/components/data-sources/discord"></Card>
|
||||
<Card title="Discourse" href="/components/data-sources/discourse"></Card>
|
||||
<Card title="Substack" href="/components/data-sources/substack"></Card>
|
||||
<Card title="Beehiiv" href="/components/data-sources/beehiiv"></Card>
|
||||
<Card title="Dropbox" href="/components/data-sources/dropbox"></Card>
|
||||
<Card title="Image" href="/components/data-sources/image"></Card>
|
||||
<Card title="Audio" href="/components/data-sources/audio"></Card>
|
||||
<Card title="Custom" href="/components/data-sources/custom"></Card>
|
||||
</CardGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
<br/ >
|
||||
|
||||
<Snippet file="missing-data-source-tip.mdx" />
|
||||
43
embedchain/docs/components/data-sources/pdf-file.mdx
Normal file
43
embedchain/docs/components/data-sources/pdf-file.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,43 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: '📰 PDF'
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
You can load any pdf file from your local file system or through a URL.
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage
|
||||
|
||||
### Load from a local file
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
app = App()
|
||||
app.add('/path/to/file.pdf', data_type='pdf_file')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Load from URL
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
app = App()
|
||||
app.add('https://arxiv.org/pdf/1706.03762.pdf', data_type='pdf_file')
|
||||
app.query("What is the paper 'attention is all you need' about?", citations=True)
|
||||
# Answer: The paper "Attention Is All You Need" proposes a new network architecture called the Transformer, which is based solely on attention mechanisms. It suggests that complex recurrent or convolutional neural networks can be replaced with a simpler architecture that connects the encoder and decoder through attention. The paper discusses how this approach can improve sequence transduction models, such as neural machine translation.
|
||||
# Contexts:
|
||||
# [
|
||||
# (
|
||||
# 'Provided proper attribution is ...',
|
||||
# {
|
||||
# 'page': 0,
|
||||
# 'url': 'https://arxiv.org/pdf/1706.03762.pdf',
|
||||
# 'score': 0.3676220203221626,
|
||||
# ...
|
||||
# }
|
||||
# ),
|
||||
# ]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
We also store the page number under the key `page` with each chunk that helps understand where the answer is coming from. You can fetch the `page` key while during retrieval (refer to the example given above).
|
||||
|
||||
<Note>
|
||||
Note that we do not support password protected pdf files.
|
||||
</Note>
|
||||
64
embedchain/docs/components/data-sources/postgres.mdx
Normal file
64
embedchain/docs/components/data-sources/postgres.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,64 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: '🐘 Postgres'
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
1. Setup the Postgres loader by configuring the postgres db.
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
from embedchain.loaders.postgres import PostgresLoader
|
||||
|
||||
config = {
|
||||
"host": "host_address",
|
||||
"port": "port_number",
|
||||
"dbname": "database_name",
|
||||
"user": "username",
|
||||
"password": "password",
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
"""
|
||||
config = {
|
||||
"url": "your_postgres_url"
|
||||
}
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
postgres_loader = PostgresLoader(config=config)
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can either setup the loader by passing the postgresql url or by providing the config data.
|
||||
For more details on how to setup with valid url and config, check postgres [documentation](https://www.postgresql.org/docs/current/libpq-connect.html#LIBPQ-CONNSTRING:~:text=34.1.1.%C2%A0Connection%20Strings-,%23,-Several%20libpq%20functions).
|
||||
|
||||
NOTE: if you provide the `url` field in config, all other fields will be ignored.
|
||||
|
||||
2. Once you setup the loader, you can create an app and load data using the above postgres loader
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
import os
|
||||
from embedchain.pipeline import Pipeline as App
|
||||
|
||||
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = "sk-xxx"
|
||||
|
||||
app = App()
|
||||
|
||||
question = "What is Elon Musk's networth?"
|
||||
response = app.query(question)
|
||||
# Answer: As of September 2021, Elon Musk's net worth is estimated to be around $250 billion, making him one of the wealthiest individuals in the world. However, please note that net worth can fluctuate over time due to various factors such as stock market changes and business ventures.
|
||||
|
||||
app.add("SELECT * FROM table_name;", data_type='postgres', loader=postgres_loader)
|
||||
# Adds `(1, 'What is your net worth, Elon Musk?', "As of October 2023, Elon Musk's net worth is $255.2 billion.")`
|
||||
|
||||
response = app.query(question)
|
||||
# Answer: As of October 2023, Elon Musk's net worth is $255.2 billion.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
NOTE: The `add` function of the app will accept any executable query to load data. DO NOT pass the `CREATE`, `INSERT` queries in `add` function as they will result in not adding any data, so it is pointless.
|
||||
|
||||
3. We automatically create a chunker to chunk your postgres data, however if you wish to provide your own chunker class. Here is how you can do that:
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
|
||||
from embedchain.chunkers.postgres import PostgresChunker
|
||||
from embedchain.config.add_config import ChunkerConfig
|
||||
|
||||
postgres_chunker_config = ChunkerConfig(chunk_size=1000, chunk_overlap=0, length_function=len)
|
||||
postgres_chunker = PostgresChunker(config=postgres_chunker_config)
|
||||
|
||||
app.add("SELECT * FROM table_name;", data_type='postgres', loader=postgres_loader, chunker=postgres_chunker)
|
||||
```
|
||||
13
embedchain/docs/components/data-sources/qna.mdx
Normal file
13
embedchain/docs/components/data-sources/qna.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,13 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: '❓💬 Question and answer pair'
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
QnA pair is a local data type. To supply your own QnA pair, use the data_type as `qna_pair` and enter a tuple. Eg:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
|
||||
app = App()
|
||||
|
||||
app.add(("Question", "Answer"), data_type="qna_pair")
|
||||
```
|
||||
13
embedchain/docs/components/data-sources/sitemap.mdx
Normal file
13
embedchain/docs/components/data-sources/sitemap.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,13 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: '🗺️ Sitemap'
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Add all web pages from an xml-sitemap. Filters non-text files. Use the data_type as `sitemap`. Eg:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
|
||||
app = App()
|
||||
|
||||
app.add('https://example.com/sitemap.xml', data_type='sitemap')
|
||||
```
|
||||
71
embedchain/docs/components/data-sources/slack.mdx
Normal file
71
embedchain/docs/components/data-sources/slack.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,71 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: '🤖 Slack'
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## Pre-requisite
|
||||
- Download required packages by running `pip install --upgrade "embedchain[slack]"`.
|
||||
- Configure your slack bot token as environment variable `SLACK_USER_TOKEN`.
|
||||
- Find your user token on your [Slack Account](https://api.slack.com/authentication/token-types)
|
||||
- Make sure your slack user token includes [search](https://api.slack.com/scopes/search:read) scope.
|
||||
|
||||
## Example
|
||||
|
||||
### Get Started
|
||||
|
||||
This will automatically retrieve data from the workspace associated with the user's token.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import os
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
|
||||
os.environ["SLACK_USER_TOKEN"] = "xoxp-xxx"
|
||||
app = App()
|
||||
|
||||
app.add("in:general", data_type="slack")
|
||||
|
||||
result = app.query("what are the messages in general channel?")
|
||||
|
||||
print(result)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Customize your SlackLoader
|
||||
1. Setup the Slack loader by configuring the Slack Webclient.
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
from embedchain.loaders.slack import SlackLoader
|
||||
|
||||
os.environ["SLACK_USER_TOKEN"] = "xoxp-*"
|
||||
|
||||
config = {
|
||||
'base_url': slack_app_url,
|
||||
'headers': web_headers,
|
||||
'team_id': slack_team_id,
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
loader = SlackLoader(config)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
NOTE: you can also pass the `config` with `base_url`, `headers`, `team_id` to setup your SlackLoader.
|
||||
|
||||
2. Once you setup the loader, you can create an app and load data using the above slack loader
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
import os
|
||||
from embedchain.pipeline import Pipeline as App
|
||||
|
||||
app = App()
|
||||
|
||||
app.add("in:random", data_type="slack", loader=loader)
|
||||
question = "Which bots are available in the slack workspace's random channel?"
|
||||
# Answer: The available bot in the slack workspace's random channel is the Embedchain bot.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3. We automatically create a chunker to chunk your slack data, however if you wish to provide your own chunker class. Here is how you can do that:
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
from embedchain.chunkers.slack import SlackChunker
|
||||
from embedchain.config.add_config import ChunkerConfig
|
||||
|
||||
slack_chunker_config = ChunkerConfig(chunk_size=1000, chunk_overlap=0, length_function=len)
|
||||
slack_chunker = SlackChunker(config=slack_chunker_config)
|
||||
|
||||
app.add(slack_chunker, data_type="slack", loader=loader, chunker=slack_chunker)
|
||||
```
|
||||
16
embedchain/docs/components/data-sources/substack.mdx
Normal file
16
embedchain/docs/components/data-sources/substack.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,16 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: "📝 Substack"
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
To add any Substack data sources to your app, just add the main base url as the source and set the data_type to `substack`.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
|
||||
app = App()
|
||||
|
||||
# source: for any substack just add the root URL
|
||||
app.add('https://www.lennysnewsletter.com', data_type='substack')
|
||||
app.query("Who is Brian Chesky?")
|
||||
# Answer: Brian Chesky is the co-founder and CEO of Airbnb.
|
||||
```
|
||||
14
embedchain/docs/components/data-sources/text-file.mdx
Normal file
14
embedchain/docs/components/data-sources/text-file.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,14 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: '📄 Text file'
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
To add a .txt file, specify the data_type as `text_file`. The URL provided in the first parameter of the `add` function, should be a local path. Eg:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
|
||||
app = App()
|
||||
app.add('path/to/file.txt', data_type="text_file")
|
||||
|
||||
app.query("Summarize the information of the text file")
|
||||
```
|
||||
17
embedchain/docs/components/data-sources/text.mdx
Normal file
17
embedchain/docs/components/data-sources/text.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: '📝 Text'
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
### Text
|
||||
|
||||
Text is a local data type. To supply your own text, use the data_type as `text` and enter a string. The text is not processed, this can be very versatile. Eg:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
|
||||
app = App()
|
||||
|
||||
app.add('Seek wealth, not money or status. Wealth is having assets that earn while you sleep. Money is how we transfer time and wealth. Status is your place in the social hierarchy.', data_type='text')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Note: This is not used in the examples because in most cases you will supply a whole paragraph or file, which did not fit.
|
||||
13
embedchain/docs/components/data-sources/web-page.mdx
Normal file
13
embedchain/docs/components/data-sources/web-page.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,13 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: '🌐 HTML Web page'
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
To add any web page, use the data_type as `web_page`. Eg:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
|
||||
app = App()
|
||||
|
||||
app.add('a_valid_web_page_url', data_type='web_page')
|
||||
```
|
||||
17
embedchain/docs/components/data-sources/xml.mdx
Normal file
17
embedchain/docs/components/data-sources/xml.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: '🧾 XML file'
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
### XML file
|
||||
|
||||
To add any xml file, use the data_type as `xml`. Eg:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
|
||||
app = App()
|
||||
|
||||
app.add('content/data.xml')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Note: Only the text content of the xml file will be added to the app. The tags will be ignored.
|
||||
22
embedchain/docs/components/data-sources/youtube-channel.mdx
Normal file
22
embedchain/docs/components/data-sources/youtube-channel.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,22 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: '📽️ Youtube Channel'
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## Setup
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure you have all the required packages installed before using this data type. You can install them by running the following command in your terminal.
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install -U "embedchain[youtube]"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage
|
||||
|
||||
To add all the videos from a youtube channel to your app, use the data_type as `youtube_channel`.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
|
||||
app = App()
|
||||
app.add("@channel_name", data_type="youtube_channel")
|
||||
```
|
||||
22
embedchain/docs/components/data-sources/youtube-video.mdx
Normal file
22
embedchain/docs/components/data-sources/youtube-video.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,22 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: '📺 Youtube Video'
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## Setup
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure you have all the required packages installed before using this data type. You can install them by running the following command in your terminal.
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install -U "embedchain[youtube]"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage
|
||||
|
||||
To add any youtube video to your app, use the data_type as `youtube_video`. Eg:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
|
||||
app = App()
|
||||
app.add('a_valid_youtube_url_here', data_type='youtube_video')
|
||||
```
|
||||
438
embedchain/docs/components/embedding-models.mdx
Normal file
438
embedchain/docs/components/embedding-models.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,438 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: 🧩 Embedding models
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
Embedchain supports several embedding models from the following providers:
|
||||
|
||||
<CardGroup cols={4}>
|
||||
<Card title="OpenAI" href="#openai"></Card>
|
||||
<Card title="GoogleAI" href="#google-ai"></Card>
|
||||
<Card title="Azure OpenAI" href="#azure-openai"></Card>
|
||||
<Card title="GPT4All" href="#gpt4all"></Card>
|
||||
<Card title="Hugging Face" href="#hugging-face"></Card>
|
||||
<Card title="Vertex AI" href="#vertex-ai"></Card>
|
||||
<Card title="NVIDIA AI" href="#nvidia-ai"></Card>
|
||||
<Card title="Cohere" href="#cohere"></Card>
|
||||
<Card title="Ollama" href="#ollama"></Card>
|
||||
<Card title="Clarifai" href="#clarifai"></Card>
|
||||
</CardGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
## OpenAI
|
||||
|
||||
To use OpenAI embedding function, you have to set the `OPENAI_API_KEY` environment variable. You can obtain the OpenAI API key from the [OpenAI Platform](https://platform.openai.com/account/api-keys).
|
||||
|
||||
Once you have obtained the key, you can use it like this:
|
||||
|
||||
<CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
```python main.py
|
||||
import os
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
|
||||
os.environ['OPENAI_API_KEY'] = 'xxx'
|
||||
|
||||
# load embedding model configuration from config.yaml file
|
||||
app = App.from_config(config_path="config.yaml")
|
||||
|
||||
app.add("https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/OpenAI")
|
||||
app.query("What is OpenAI?")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml config.yaml
|
||||
embedder:
|
||||
provider: openai
|
||||
config:
|
||||
model: 'text-embedding-3-small'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
* OpenAI announced two new embedding models: `text-embedding-3-small` and `text-embedding-3-large`. Embedchain supports both these models. Below you can find YAML config for both:
|
||||
|
||||
<CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml text-embedding-3-small.yaml
|
||||
embedder:
|
||||
provider: openai
|
||||
config:
|
||||
model: 'text-embedding-3-small'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml text-embedding-3-large.yaml
|
||||
embedder:
|
||||
provider: openai
|
||||
config:
|
||||
model: 'text-embedding-3-large'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
## Google AI
|
||||
|
||||
To use Google AI embedding function, you have to set the `GOOGLE_API_KEY` environment variable. You can obtain the Google API key from the [Google Maker Suite](https://makersuite.google.com/app/apikey)
|
||||
|
||||
<CodeGroup>
|
||||
```python main.py
|
||||
import os
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
|
||||
os.environ["GOOGLE_API_KEY"] = "xxx"
|
||||
|
||||
app = App.from_config(config_path="config.yaml")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml config.yaml
|
||||
embedder:
|
||||
provider: google
|
||||
config:
|
||||
model: 'models/embedding-001'
|
||||
task_type: "retrieval_document"
|
||||
title: "Embeddings for Embedchain"
|
||||
```
|
||||
</CodeGroup>
|
||||
<br/>
|
||||
<Note>
|
||||
For more details regarding the Google AI embedding model, please refer to the [Google AI documentation](https://ai.google.dev/tutorials/python_quickstart#use_embeddings).
|
||||
</Note>
|
||||
|
||||
## Azure OpenAI
|
||||
|
||||
To use Azure OpenAI embedding model, you have to set some of the azure openai related environment variables as given in the code block below:
|
||||
|
||||
<CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
```python main.py
|
||||
import os
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
|
||||
os.environ["OPENAI_API_TYPE"] = "azure"
|
||||
os.environ["AZURE_OPENAI_ENDPOINT"] = "https://xxx.openai.azure.com/"
|
||||
os.environ["AZURE_OPENAI_API_KEY"] = "xxx"
|
||||
os.environ["OPENAI_API_VERSION"] = "xxx"
|
||||
|
||||
app = App.from_config(config_path="config.yaml")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml config.yaml
|
||||
llm:
|
||||
provider: azure_openai
|
||||
config:
|
||||
model: gpt-35-turbo
|
||||
deployment_name: your_llm_deployment_name
|
||||
temperature: 0.5
|
||||
max_tokens: 1000
|
||||
top_p: 1
|
||||
stream: false
|
||||
|
||||
embedder:
|
||||
provider: azure_openai
|
||||
config:
|
||||
model: text-embedding-ada-002
|
||||
deployment_name: you_embedding_model_deployment_name
|
||||
```
|
||||
</CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
You can find the list of models and deployment name on the [Azure OpenAI Platform](https://oai.azure.com/portal).
|
||||
|
||||
## GPT4ALL
|
||||
|
||||
GPT4All supports generating high quality embeddings of arbitrary length documents of text using a CPU optimized contrastively trained Sentence Transformer.
|
||||
|
||||
<CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
```python main.py
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
|
||||
# load embedding model configuration from config.yaml file
|
||||
app = App.from_config(config_path="config.yaml")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml config.yaml
|
||||
llm:
|
||||
provider: gpt4all
|
||||
config:
|
||||
model: 'orca-mini-3b-gguf2-q4_0.gguf'
|
||||
temperature: 0.5
|
||||
max_tokens: 1000
|
||||
top_p: 1
|
||||
stream: false
|
||||
|
||||
embedder:
|
||||
provider: gpt4all
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
## Hugging Face
|
||||
|
||||
Hugging Face supports generating embeddings of arbitrary length documents of text using Sentence Transformer library. Example of how to generate embeddings using hugging face is given below:
|
||||
|
||||
<CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
```python main.py
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
|
||||
# load embedding model configuration from config.yaml file
|
||||
app = App.from_config(config_path="config.yaml")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml config.yaml
|
||||
llm:
|
||||
provider: huggingface
|
||||
config:
|
||||
model: 'google/flan-t5-xxl'
|
||||
temperature: 0.5
|
||||
max_tokens: 1000
|
||||
top_p: 0.5
|
||||
stream: false
|
||||
|
||||
embedder:
|
||||
provider: huggingface
|
||||
config:
|
||||
model: 'sentence-transformers/all-mpnet-base-v2'
|
||||
model_kwargs:
|
||||
trust_remote_code: True # Only use if you trust your embedder
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
## Vertex AI
|
||||
|
||||
Embedchain supports Google's VertexAI embeddings model through a simple interface. You just have to pass the `model_name` in the config yaml and it would work out of the box.
|
||||
|
||||
<CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
```python main.py
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
|
||||
# load embedding model configuration from config.yaml file
|
||||
app = App.from_config(config_path="config.yaml")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml config.yaml
|
||||
llm:
|
||||
provider: vertexai
|
||||
config:
|
||||
model: 'chat-bison'
|
||||
temperature: 0.5
|
||||
top_p: 0.5
|
||||
|
||||
embedder:
|
||||
provider: vertexai
|
||||
config:
|
||||
model: 'textembedding-gecko'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
## NVIDIA AI
|
||||
|
||||
[NVIDIA AI Foundation Endpoints](https://www.nvidia.com/en-us/ai-data-science/foundation-models/) let you quickly use NVIDIA's AI models, such as Mixtral 8x7B, Llama 2 etc, through our API. These models are available in the [NVIDIA NGC catalog](https://catalog.ngc.nvidia.com/ai-foundation-models), fully optimized and ready to use on NVIDIA's AI platform. They are designed for high speed and easy customization, ensuring smooth performance on any accelerated setup.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Usage
|
||||
|
||||
In order to use embedding models and LLMs from NVIDIA AI, create an account on [NVIDIA NGC Service](https://catalog.ngc.nvidia.com/).
|
||||
|
||||
Generate an API key from their dashboard. Set the API key as `NVIDIA_API_KEY` environment variable. Note that the `NVIDIA_API_KEY` will start with `nvapi-`.
|
||||
|
||||
Below is an example of how to use LLM model and embedding model from NVIDIA AI:
|
||||
|
||||
<CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
```python main.py
|
||||
import os
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
|
||||
os.environ['NVIDIA_API_KEY'] = 'nvapi-xxxx'
|
||||
|
||||
config = {
|
||||
"app": {
|
||||
"config": {
|
||||
"id": "my-app",
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
"llm": {
|
||||
"provider": "nvidia",
|
||||
"config": {
|
||||
"model": "nemotron_steerlm_8b",
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
"embedder": {
|
||||
"provider": "nvidia",
|
||||
"config": {
|
||||
"model": "nvolveqa_40k",
|
||||
"vector_dimension": 1024,
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
app = App.from_config(config=config)
|
||||
|
||||
app.add("https://www.forbes.com/profile/elon-musk")
|
||||
answer = app.query("What is the net worth of Elon Musk today?")
|
||||
# Answer: The net worth of Elon Musk is subject to fluctuations based on the market value of his holdings in various companies.
|
||||
# As of March 1, 2024, his net worth is estimated to be approximately $210 billion. However, this figure can change rapidly due to stock market fluctuations and other factors.
|
||||
# Additionally, his net worth may include other assets such as real estate and art, which are not reflected in his stock portfolio.
|
||||
```
|
||||
</CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Cohere
|
||||
|
||||
To use embedding models and LLMs from COHERE, create an account on [COHERE](https://dashboard.cohere.com/welcome/login?redirect_uri=%2Fapi-keys).
|
||||
|
||||
Generate an API key from their dashboard. Set the API key as `COHERE_API_KEY` environment variable.
|
||||
|
||||
Once you have obtained the key, you can use it like this:
|
||||
|
||||
<CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
```python main.py
|
||||
import os
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
|
||||
os.environ['COHERE_API_KEY'] = 'xxx'
|
||||
|
||||
# load embedding model configuration from config.yaml file
|
||||
app = App.from_config(config_path="config.yaml")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml config.yaml
|
||||
embedder:
|
||||
provider: cohere
|
||||
config:
|
||||
model: 'embed-english-light-v3.0'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
* Cohere has few embedding models: `embed-english-v3.0`, `embed-multilingual-v3.0`, `embed-multilingual-light-v3.0`, `embed-english-v2.0`, `embed-english-light-v2.0` and `embed-multilingual-v2.0`. Embedchain supports all these models. Below you can find YAML config for all:
|
||||
|
||||
<CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml embed-english-v3.0.yaml
|
||||
embedder:
|
||||
provider: cohere
|
||||
config:
|
||||
model: 'embed-english-v3.0'
|
||||
vector_dimension: 1024
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml embed-multilingual-v3.0.yaml
|
||||
embedder:
|
||||
provider: cohere
|
||||
config:
|
||||
model: 'embed-multilingual-v3.0'
|
||||
vector_dimension: 1024
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml embed-multilingual-light-v3.0.yaml
|
||||
embedder:
|
||||
provider: cohere
|
||||
config:
|
||||
model: 'embed-multilingual-light-v3.0'
|
||||
vector_dimension: 384
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml embed-english-v2.0.yaml
|
||||
embedder:
|
||||
provider: cohere
|
||||
config:
|
||||
model: 'embed-english-v2.0'
|
||||
vector_dimension: 4096
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml embed-english-light-v2.0.yaml
|
||||
embedder:
|
||||
provider: cohere
|
||||
config:
|
||||
model: 'embed-english-light-v2.0'
|
||||
vector_dimension: 1024
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml embed-multilingual-v2.0.yaml
|
||||
embedder:
|
||||
provider: cohere
|
||||
config:
|
||||
model: 'embed-multilingual-v2.0'
|
||||
vector_dimension: 768
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
## Ollama
|
||||
|
||||
Ollama enables the use of embedding models, allowing you to generate high-quality embeddings directly on your local machine. Make sure to install [Ollama](https://ollama.com/download) and keep it running before using the embedding model.
|
||||
|
||||
You can find the list of models at [Ollama Embedding Models](https://ollama.com/blog/embedding-models).
|
||||
|
||||
Below is an example of how to use embedding model Ollama:
|
||||
|
||||
<CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
```python main.py
|
||||
import os
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
|
||||
# load embedding model configuration from config.yaml file
|
||||
app = App.from_config(config_path="config.yaml")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml config.yaml
|
||||
embedder:
|
||||
provider: ollama
|
||||
config:
|
||||
model: 'all-minilm:latest'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
## Clarifai
|
||||
|
||||
Install related dependencies using the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install --upgrade 'embedchain[clarifai]'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
set the `CLARIFAI_PAT` as environment variable which you can find in the [security page](https://clarifai.com/settings/security). Optionally you can also pass the PAT key as parameters in LLM/Embedder class.
|
||||
|
||||
Now you are all set with exploring Embedchain.
|
||||
|
||||
<CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
```python main.py
|
||||
import os
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
|
||||
os.environ["CLARIFAI_PAT"] = "XXX"
|
||||
|
||||
# load llm and embedder configuration from config.yaml file
|
||||
app = App.from_config(config_path="config.yaml")
|
||||
|
||||
#Now let's add some data.
|
||||
app.add("https://www.forbes.com/profile/elon-musk")
|
||||
|
||||
#Query the app
|
||||
response = app.query("what college degrees does elon musk have?")
|
||||
```
|
||||
Head to [Clarifai Platform](https://clarifai.com/explore/models?page=1&perPage=24&filterData=%5B%7B%22field%22%3A%22output_fields%22%2C%22value%22%3A%5B%22embeddings%22%5D%7D%5D) to explore all the State of the Art embedding models available to use.
|
||||
For passing LLM model inference parameters use `model_kwargs` argument in the config file. Also you can use `api_key` argument to pass `CLARIFAI_PAT` in the config.
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml config.yaml
|
||||
llm:
|
||||
provider: clarifai
|
||||
config:
|
||||
model: "https://clarifai.com/mistralai/completion/models/mistral-7B-Instruct"
|
||||
model_kwargs:
|
||||
temperature: 0.5
|
||||
max_tokens: 1000
|
||||
embedder:
|
||||
provider: clarifai
|
||||
config:
|
||||
model: "https://clarifai.com/clarifai/main/models/BAAI-bge-base-en-v15"
|
||||
```
|
||||
</CodeGroup>
|
||||
275
embedchain/docs/components/evaluation.mdx
Normal file
275
embedchain/docs/components/evaluation.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,275 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: 🔬 Evaluation
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
We provide out-of-the-box evaluation metrics for your RAG application. You can use them to evaluate your RAG applications and compare against different settings of your production RAG application.
|
||||
|
||||
Currently, we provide support for following evaluation metrics:
|
||||
|
||||
<CardGroup cols={3}>
|
||||
<Card title="Context Relevancy" href="#context_relevancy"></Card>
|
||||
<Card title="Answer Relevancy" href="#answer_relevancy"></Card>
|
||||
<Card title="Groundedness" href="#groundedness"></Card>
|
||||
<Card title="Custom Metric" href="#custom_metric"></Card>
|
||||
</CardGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
## Quickstart
|
||||
|
||||
Here is a basic example of running evaluation:
|
||||
|
||||
```python example.py
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
|
||||
app = App()
|
||||
|
||||
# Add data sources
|
||||
app.add("https://www.forbes.com/profile/elon-musk")
|
||||
|
||||
# Run evaluation
|
||||
app.evaluate(["What is the net worth of Elon Musk?", "How many companies Elon Musk owns?"])
|
||||
# {'answer_relevancy': 0.9987286412340826, 'groundedness': 1.0, 'context_relevancy': 0.3571428571428571}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Under the hood, Embedchain does the following:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Runs semantic search in the vector database and fetches context
|
||||
2. LLM call with question, context to fetch the answer
|
||||
3. Run evaluation on following metrics: `context relevancy`, `groundedness`, and `answer relevancy` and return result
|
||||
|
||||
## Advanced Usage
|
||||
|
||||
We use OpenAI's `gpt-4` model as default LLM model for automatic evaluation. Hence, we require you to set `OPENAI_API_KEY` as an environment variable.
|
||||
|
||||
### Step-1: Create dataset
|
||||
|
||||
In order to evaluate your RAG application, you have to setup a dataset. A data point in the dataset consists of `questions`, `contexts`, `answer`. Here is an example of how to create a dataset for evaluation:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from embedchain.utils.eval import EvalData
|
||||
|
||||
data = [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"question": "What is the net worth of Elon Musk?",
|
||||
"contexts": [
|
||||
"Elon Musk PROFILEElon MuskCEO, ...",
|
||||
"a Twitter poll on whether the journalists' ...",
|
||||
"2016 and run by Jared Birchall.[335]...",
|
||||
],
|
||||
"answer": "As of the information provided, Elon Musk's net worth is $241.6 billion.",
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"question": "which companies does Elon Musk own?",
|
||||
"contexts": [
|
||||
"of December 2023[update], ...",
|
||||
"ThielCofounderView ProfileTeslaHolds ...",
|
||||
"Elon Musk PROFILEElon MuskCEO, ...",
|
||||
],
|
||||
"answer": "Elon Musk owns several companies, including Tesla, SpaceX, Neuralink, and The Boring Company.",
|
||||
},
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
dataset = []
|
||||
|
||||
for d in data:
|
||||
eval_data = EvalData(question=d["question"], contexts=d["contexts"], answer=d["answer"])
|
||||
dataset.append(eval_data)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Step-2: Run evaluation
|
||||
|
||||
Once you have created your dataset, you can run evaluation on the dataset by picking the metric you want to run evaluation on.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, you can run evaluation on context relevancy metric using the following code:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from embedchain.evaluation.metrics import ContextRelevance
|
||||
metric = ContextRelevance()
|
||||
score = metric.evaluate(dataset)
|
||||
print(score)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can choose a different metric or write your own to run evaluation on. You can check the following links:
|
||||
|
||||
- [Context Relevancy](#context_relevancy)
|
||||
- [Answer relenvancy](#answer_relevancy)
|
||||
- [Groundedness](#groundedness)
|
||||
- [Build your own metric](#custom_metric)
|
||||
|
||||
## Metrics
|
||||
|
||||
### Context Relevancy <a id="context_relevancy"></a>
|
||||
|
||||
Context relevancy is a metric to determine "how relevant the context is to the question". We use OpenAI's `gpt-4` model to determine the relevancy of the context. We achieve this by prompting the model with the question and the context and asking it to return relevant sentences from the context. We then use the following formula to determine the score:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
context_relevance_score = num_relevant_sentences_in_context / num_of_sentences_in_context
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Examples
|
||||
|
||||
You can run the context relevancy evaluation with the following simple code:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from embedchain.evaluation.metrics import ContextRelevance
|
||||
|
||||
metric = ContextRelevance()
|
||||
score = metric.evaluate(dataset) # 'dataset' is definted in the create dataset section
|
||||
print(score)
|
||||
# 0.27975528364849833
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
In the above example, we used sensible defaults for the evaluation. However, you can also configure the evaluation metric as per your needs using the `ContextRelevanceConfig` class.
|
||||
|
||||
Here is a more advanced example of how to pass a custom evaluation config for evaluating on context relevance metric:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from embedchain.config.evaluation.base import ContextRelevanceConfig
|
||||
from embedchain.evaluation.metrics import ContextRelevance
|
||||
|
||||
eval_config = ContextRelevanceConfig(model="gpt-4", api_key="sk-xxx", language="en")
|
||||
metric = ContextRelevance(config=eval_config)
|
||||
metric.evaluate(dataset)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### `ContextRelevanceConfig`
|
||||
|
||||
<ParamField path="model" type="str" optional>
|
||||
The model to use for the evaluation. Defaults to `gpt-4`. We only support openai's models for now.
|
||||
</ParamField>
|
||||
<ParamField path="api_key" type="str" optional>
|
||||
The openai api key to use for the evaluation. Defaults to `None`. If not provided, we will use the `OPENAI_API_KEY` environment variable.
|
||||
</ParamField>
|
||||
<ParamField path="language" type="str" optional>
|
||||
The language of the dataset being evaluated. We need this to determine the understand the context provided in the dataset. Defaults to `en`.
|
||||
</ParamField>
|
||||
<ParamField path="prompt" type="str" optional>
|
||||
The prompt to extract the relevant sentences from the context. Defaults to `CONTEXT_RELEVANCY_PROMPT`, which can be found at `embedchain.config.evaluation.base` path.
|
||||
</ParamField>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Answer Relevancy <a id="answer_relevancy"></a>
|
||||
|
||||
Answer relevancy is a metric to determine how relevant the answer is to the question. We prompt the model with the answer and asking it to generate questions from the answer. We then use the cosine similarity between the generated questions and the original question to determine the score.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
answer_relevancy_score = mean(cosine_similarity(generated_questions, original_question))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Examples
|
||||
|
||||
You can run the answer relevancy evaluation with the following simple code:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from embedchain.evaluation.metrics import AnswerRelevance
|
||||
|
||||
metric = AnswerRelevance()
|
||||
score = metric.evaluate(dataset)
|
||||
print(score)
|
||||
# 0.9505334177461916
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
In the above example, we used sensible defaults for the evaluation. However, you can also configure the evaluation metric as per your needs using the `AnswerRelevanceConfig` class. Here is a more advanced example where you can provide your own evaluation config:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from embedchain.config.evaluation.base import AnswerRelevanceConfig
|
||||
from embedchain.evaluation.metrics import AnswerRelevance
|
||||
|
||||
eval_config = AnswerRelevanceConfig(
|
||||
model='gpt-4',
|
||||
embedder="text-embedding-ada-002",
|
||||
api_key="sk-xxx",
|
||||
num_gen_questions=2
|
||||
)
|
||||
metric = AnswerRelevance(config=eval_config)
|
||||
score = metric.evaluate(dataset)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### `AnswerRelevanceConfig`
|
||||
|
||||
<ParamField path="model" type="str" optional>
|
||||
The model to use for the evaluation. Defaults to `gpt-4`. We only support openai's models for now.
|
||||
</ParamField>
|
||||
<ParamField path="embedder" type="str" optional>
|
||||
The embedder to use for embedding the text. Defaults to `text-embedding-ada-002`. We only support openai's embedders for now.
|
||||
</ParamField>
|
||||
<ParamField path="api_key" type="str" optional>
|
||||
The openai api key to use for the evaluation. Defaults to `None`. If not provided, we will use the `OPENAI_API_KEY` environment variable.
|
||||
</ParamField>
|
||||
<ParamField path="num_gen_questions" type="int" optional>
|
||||
The number of questions to generate for each answer. We use the generated questions to compare the similarity with the original question to determine the score. Defaults to `1`.
|
||||
</ParamField>
|
||||
<ParamField path="prompt" type="str" optional>
|
||||
The prompt to extract the `num_gen_questions` number of questions from the provided answer. Defaults to `ANSWER_RELEVANCY_PROMPT`, which can be found at `embedchain.config.evaluation.base` path.
|
||||
</ParamField>
|
||||
|
||||
## Groundedness <a id="groundedness"></a>
|
||||
|
||||
Groundedness is a metric to determine how grounded the answer is to the context. We use OpenAI's `gpt-4` model to determine the groundedness of the answer. We achieve this by prompting the model with the answer and asking it to generate claims from the answer. We then again prompt the model with the context and the generated claims to determine the verdict on the claims. We then use the following formula to determine the score:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
groundedness_score = (sum of all verdicts) / (total # of claims)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can run the groundedness evaluation with the following simple code:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from embedchain.evaluation.metrics import Groundedness
|
||||
metric = Groundedness()
|
||||
score = metric.evaluate(dataset) # dataset from above
|
||||
print(score)
|
||||
# 1.0
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
In the above example, we used sensible defaults for the evaluation. However, you can also configure the evaluation metric as per your needs using the `GroundednessConfig` class. Here is a more advanced example where you can configure the evaluation config:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from embedchain.config.evaluation.base import GroundednessConfig
|
||||
from embedchain.evaluation.metrics import Groundedness
|
||||
|
||||
eval_config = GroundednessConfig(model='gpt-4', api_key="sk-xxx")
|
||||
metric = Groundedness(config=eval_config)
|
||||
score = metric.evaluate(dataset)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### `GroundednessConfig`
|
||||
|
||||
<ParamField path="model" type="str" optional>
|
||||
The model to use for the evaluation. Defaults to `gpt-4`. We only support openai's models for now.
|
||||
</ParamField>
|
||||
<ParamField path="api_key" type="str" optional>
|
||||
The openai api key to use for the evaluation. Defaults to `None`. If not provided, we will use the `OPENAI_API_KEY` environment variable.
|
||||
</ParamField>
|
||||
<ParamField path="answer_claims_prompt" type="str" optional>
|
||||
The prompt to extract the claims from the provided answer. Defaults to `GROUNDEDNESS_ANSWER_CLAIMS_PROMPT`, which can be found at `embedchain.config.evaluation.base` path.
|
||||
</ParamField>
|
||||
<ParamField path="claims_inference_prompt" type="str" optional>
|
||||
The prompt to get verdicts on the claims from the answer from the given context. Defaults to `GROUNDEDNESS_CLAIMS_INFERENCE_PROMPT`, which can be found at `embedchain.config.evaluation.base` path.
|
||||
</ParamField>
|
||||
|
||||
## Custom <a id="custom_metric"></a>
|
||||
|
||||
You can also create your own evaluation metric by extending the `BaseMetric` class. You can find the source code for the existing metrics at `embedchain.evaluation.metrics` path.
|
||||
|
||||
<Note>
|
||||
You must provide the `name` of your custom metric in the `__init__` method of your class. This name will be used to identify your metric in the evaluation report.
|
||||
</Note>
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from typing import Optional
|
||||
|
||||
from embedchain.config.base_config import BaseConfig
|
||||
from embedchain.evaluation.metrics import BaseMetric
|
||||
from embedchain.utils.eval import EvalData
|
||||
|
||||
class MyCustomMetric(BaseMetric):
|
||||
def __init__(self, config: Optional[BaseConfig] = None):
|
||||
super().__init__(name="my_custom_metric")
|
||||
|
||||
def evaluate(self, dataset: list[EvalData]):
|
||||
score = 0.0
|
||||
# write your evaluation logic here
|
||||
return score
|
||||
```
|
||||
13
embedchain/docs/components/introduction.mdx
Normal file
13
embedchain/docs/components/introduction.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,13 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: 🧩 Introduction
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
You can configure following components
|
||||
|
||||
* [Data Source](/components/data-sources/overview)
|
||||
* [LLM](/components/llms)
|
||||
* [Embedding Model](/components/embedding-models)
|
||||
* [Vector Database](/components/vector-databases)
|
||||
* [Evaluation](/components/evaluation)
|
||||
901
embedchain/docs/components/llms.mdx
Normal file
901
embedchain/docs/components/llms.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,901 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: 🤖 Large language models (LLMs)
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
Embedchain comes with built-in support for various popular large language models. We handle the complexity of integrating these models for you, allowing you to easily customize your language model interactions through a user-friendly interface.
|
||||
|
||||
<CardGroup cols={4}>
|
||||
<Card title="OpenAI" href="#openai"></Card>
|
||||
<Card title="Google AI" href="#google-ai"></Card>
|
||||
<Card title="Azure OpenAI" href="#azure-openai"></Card>
|
||||
<Card title="Anthropic" href="#anthropic"></Card>
|
||||
<Card title="Cohere" href="#cohere"></Card>
|
||||
<Card title="Together" href="#together"></Card>
|
||||
<Card title="Ollama" href="#ollama"></Card>
|
||||
<Card title="vLLM" href="#vllm"></Card>
|
||||
<Card title="Clarifai" href="#clarifai"></Card>
|
||||
<Card title="GPT4All" href="#gpt4all"></Card>
|
||||
<Card title="JinaChat" href="#jinachat"></Card>
|
||||
<Card title="Hugging Face" href="#hugging-face"></Card>
|
||||
<Card title="Llama2" href="#llama2"></Card>
|
||||
<Card title="Vertex AI" href="#vertex-ai"></Card>
|
||||
<Card title="Mistral AI" href="#mistral-ai"></Card>
|
||||
<Card title="AWS Bedrock" href="#aws-bedrock"></Card>
|
||||
<Card title="Groq" href="#groq"></Card>
|
||||
<Card title="NVIDIA AI" href="#nvidia-ai"></Card>
|
||||
</CardGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
## OpenAI
|
||||
|
||||
To use OpenAI LLM models, you have to set the `OPENAI_API_KEY` environment variable. You can obtain the OpenAI API key from the [OpenAI Platform](https://platform.openai.com/account/api-keys).
|
||||
|
||||
Once you have obtained the key, you can use it like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import os
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
|
||||
os.environ['OPENAI_API_KEY'] = 'xxx'
|
||||
|
||||
app = App()
|
||||
app.add("https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/OpenAI")
|
||||
app.query("What is OpenAI?")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If you are looking to configure the different parameters of the LLM, you can do so by loading the app using a [yaml config](https://github.com/embedchain/embedchain/blob/main/configs/chroma.yaml) file.
|
||||
|
||||
<CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
```python main.py
|
||||
import os
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
|
||||
os.environ['OPENAI_API_KEY'] = 'xxx'
|
||||
|
||||
# load llm configuration from config.yaml file
|
||||
app = App.from_config(config_path="config.yaml")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml config.yaml
|
||||
llm:
|
||||
provider: openai
|
||||
config:
|
||||
model: 'gpt-3.5-turbo'
|
||||
temperature: 0.5
|
||||
max_tokens: 1000
|
||||
top_p: 1
|
||||
stream: false
|
||||
```
|
||||
</CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
### Function Calling
|
||||
Embedchain supports OpenAI [Function calling](https://platform.openai.com/docs/guides/function-calling) with a single function. It accepts inputs in accordance with the [Langchain interface](https://python.langchain.com/docs/modules/model_io/chat/function_calling#legacy-args-functions-and-function_call).
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="Pydantic Model">
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from pydantic import BaseModel
|
||||
|
||||
class multiply(BaseModel):
|
||||
"""Multiply two integers together."""
|
||||
|
||||
a: int = Field(..., description="First integer")
|
||||
b: int = Field(..., description="Second integer")
|
||||
```
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
<Accordion title="Python function">
|
||||
```python
|
||||
def multiply(a: int, b: int) -> int:
|
||||
"""Multiply two integers together.
|
||||
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
a: First integer
|
||||
b: Second integer
|
||||
"""
|
||||
return a * b
|
||||
```
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
<Accordion title="OpenAI tool dictionary">
|
||||
```python
|
||||
multiply = {
|
||||
"type": "function",
|
||||
"function": {
|
||||
"name": "multiply",
|
||||
"description": "Multiply two integers together.",
|
||||
"parameters": {
|
||||
"type": "object",
|
||||
"properties": {
|
||||
"a": {
|
||||
"description": "First integer",
|
||||
"type": "integer"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"b": {
|
||||
"description": "Second integer",
|
||||
"type": "integer"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"required": [
|
||||
"a",
|
||||
"b"
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
|
||||
With any of the previous inputs, the OpenAI LLM can be queried to provide the appropriate arguments for the function.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import os
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
from embedchain.llm.openai import OpenAILlm
|
||||
|
||||
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = "sk-xxx"
|
||||
|
||||
llm = OpenAILlm(tools=multiply)
|
||||
app = App(llm=llm)
|
||||
|
||||
result = app.query("What is the result of 125 multiplied by fifteen?")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Google AI
|
||||
|
||||
To use Google AI model, you have to set the `GOOGLE_API_KEY` environment variable. You can obtain the Google API key from the [Google Maker Suite](https://makersuite.google.com/app/apikey)
|
||||
|
||||
<CodeGroup>
|
||||
```python main.py
|
||||
import os
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
|
||||
os.environ["GOOGLE_API_KEY"] = "xxx"
|
||||
|
||||
app = App.from_config(config_path="config.yaml")
|
||||
|
||||
app.add("https://www.forbes.com/profile/elon-musk")
|
||||
|
||||
response = app.query("What is the net worth of Elon Musk?")
|
||||
if app.llm.config.stream: # if stream is enabled, response is a generator
|
||||
for chunk in response:
|
||||
print(chunk)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
print(response)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml config.yaml
|
||||
llm:
|
||||
provider: google
|
||||
config:
|
||||
model: gemini-pro
|
||||
max_tokens: 1000
|
||||
temperature: 0.5
|
||||
top_p: 1
|
||||
stream: false
|
||||
|
||||
embedder:
|
||||
provider: google
|
||||
config:
|
||||
model: 'models/embedding-001'
|
||||
task_type: "retrieval_document"
|
||||
title: "Embeddings for Embedchain"
|
||||
```
|
||||
</CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
## Azure OpenAI
|
||||
|
||||
To use Azure OpenAI model, you have to set some of the azure openai related environment variables as given in the code block below:
|
||||
|
||||
<CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
```python main.py
|
||||
import os
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
|
||||
os.environ["OPENAI_API_TYPE"] = "azure"
|
||||
os.environ["AZURE_OPENAI_ENDPOINT"] = "https://xxx.openai.azure.com/"
|
||||
os.environ["AZURE_OPENAI_KEY"] = "xxx"
|
||||
os.environ["OPENAI_API_VERSION"] = "xxx"
|
||||
|
||||
app = App.from_config(config_path="config.yaml")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml config.yaml
|
||||
llm:
|
||||
provider: azure_openai
|
||||
config:
|
||||
model: gpt-3.5-turbo
|
||||
deployment_name: your_llm_deployment_name
|
||||
temperature: 0.5
|
||||
max_tokens: 1000
|
||||
top_p: 1
|
||||
stream: false
|
||||
|
||||
embedder:
|
||||
provider: azure_openai
|
||||
config:
|
||||
model: text-embedding-ada-002
|
||||
deployment_name: you_embedding_model_deployment_name
|
||||
```
|
||||
</CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
You can find the list of models and deployment name on the [Azure OpenAI Platform](https://oai.azure.com/portal).
|
||||
|
||||
## Anthropic
|
||||
|
||||
To use anthropic's model, please set the `ANTHROPIC_API_KEY` which you find on their [Account Settings Page](https://console.anthropic.com/account/keys).
|
||||
|
||||
<CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
```python main.py
|
||||
import os
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
|
||||
os.environ["ANTHROPIC_API_KEY"] = "xxx"
|
||||
|
||||
# load llm configuration from config.yaml file
|
||||
app = App.from_config(config_path="config.yaml")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml config.yaml
|
||||
llm:
|
||||
provider: anthropic
|
||||
config:
|
||||
model: 'claude-instant-1'
|
||||
temperature: 0.5
|
||||
max_tokens: 1000
|
||||
top_p: 1
|
||||
stream: false
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
## Cohere
|
||||
|
||||
Install related dependencies using the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install --upgrade 'embedchain[cohere]'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Set the `COHERE_API_KEY` as environment variable which you can find on their [Account settings page](https://dashboard.cohere.com/api-keys).
|
||||
|
||||
Once you have the API key, you are all set to use it with Embedchain.
|
||||
|
||||
<CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
```python main.py
|
||||
import os
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
|
||||
os.environ["COHERE_API_KEY"] = "xxx"
|
||||
|
||||
# load llm configuration from config.yaml file
|
||||
app = App.from_config(config_path="config.yaml")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml config.yaml
|
||||
llm:
|
||||
provider: cohere
|
||||
config:
|
||||
model: large
|
||||
temperature: 0.5
|
||||
max_tokens: 1000
|
||||
top_p: 1
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
## Together
|
||||
|
||||
Install related dependencies using the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install --upgrade 'embedchain[together]'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Set the `TOGETHER_API_KEY` as environment variable which you can find on their [Account settings page](https://api.together.xyz/settings/api-keys).
|
||||
|
||||
Once you have the API key, you are all set to use it with Embedchain.
|
||||
|
||||
<CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
```python main.py
|
||||
import os
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
|
||||
os.environ["TOGETHER_API_KEY"] = "xxx"
|
||||
|
||||
# load llm configuration from config.yaml file
|
||||
app = App.from_config(config_path="config.yaml")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml config.yaml
|
||||
llm:
|
||||
provider: together
|
||||
config:
|
||||
model: togethercomputer/RedPajama-INCITE-7B-Base
|
||||
temperature: 0.5
|
||||
max_tokens: 1000
|
||||
top_p: 1
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
## Ollama
|
||||
|
||||
Setup Ollama using https://github.com/jmorganca/ollama
|
||||
|
||||
<CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
```python main.py
|
||||
import os
|
||||
os.environ["OLLAMA_HOST"] = "http://127.0.0.1:11434"
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
|
||||
# load llm configuration from config.yaml file
|
||||
app = App.from_config(config_path="config.yaml")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml config.yaml
|
||||
llm:
|
||||
provider: ollama
|
||||
config:
|
||||
model: 'llama2'
|
||||
temperature: 0.5
|
||||
top_p: 1
|
||||
stream: true
|
||||
base_url: 'http://localhost:11434'
|
||||
embedder:
|
||||
provider: ollama
|
||||
config:
|
||||
model: znbang/bge:small-en-v1.5-q8_0
|
||||
base_url: http://localhost:11434
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## vLLM
|
||||
|
||||
Setup vLLM by following instructions given in [their docs](https://docs.vllm.ai/en/latest/getting_started/installation.html).
|
||||
|
||||
<CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
```python main.py
|
||||
import os
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
|
||||
# load llm configuration from config.yaml file
|
||||
app = App.from_config(config_path="config.yaml")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml config.yaml
|
||||
llm:
|
||||
provider: vllm
|
||||
config:
|
||||
model: 'meta-llama/Llama-2-70b-hf'
|
||||
temperature: 0.5
|
||||
top_p: 1
|
||||
top_k: 10
|
||||
stream: true
|
||||
trust_remote_code: true
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
## Clarifai
|
||||
|
||||
Install related dependencies using the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install --upgrade 'embedchain[clarifai]'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
set the `CLARIFAI_PAT` as environment variable which you can find in the [security page](https://clarifai.com/settings/security). Optionally you can also pass the PAT key as parameters in LLM/Embedder class.
|
||||
|
||||
Now you are all set with exploring Embedchain.
|
||||
|
||||
<CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
```python main.py
|
||||
import os
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
|
||||
os.environ["CLARIFAI_PAT"] = "XXX"
|
||||
|
||||
# load llm configuration from config.yaml file
|
||||
app = App.from_config(config_path="config.yaml")
|
||||
|
||||
#Now let's add some data.
|
||||
app.add("https://www.forbes.com/profile/elon-musk")
|
||||
|
||||
#Query the app
|
||||
response = app.query("what college degrees does elon musk have?")
|
||||
```
|
||||
Head to [Clarifai Platform](https://clarifai.com/explore/models?page=1&perPage=24&filterData=%5B%7B%22field%22%3A%22use_cases%22%2C%22value%22%3A%5B%22llm%22%5D%7D%5D) to browse various State-of-the-Art LLM models for your use case.
|
||||
For passing model inference parameters use `model_kwargs` argument in the config file. Also you can use `api_key` argument to pass `CLARIFAI_PAT` in the config.
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml config.yaml
|
||||
llm:
|
||||
provider: clarifai
|
||||
config:
|
||||
model: "https://clarifai.com/mistralai/completion/models/mistral-7B-Instruct"
|
||||
model_kwargs:
|
||||
temperature: 0.5
|
||||
max_tokens: 1000
|
||||
embedder:
|
||||
provider: clarifai
|
||||
config:
|
||||
model: "https://clarifai.com/clarifai/main/models/BAAI-bge-base-en-v15"
|
||||
```
|
||||
</CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## GPT4ALL
|
||||
|
||||
Install related dependencies using the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install --upgrade 'embedchain[opensource]'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
GPT4all is a free-to-use, locally running, privacy-aware chatbot. No GPU or internet required. You can use this with Embedchain using the following code:
|
||||
|
||||
<CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
```python main.py
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
|
||||
# load llm configuration from config.yaml file
|
||||
app = App.from_config(config_path="config.yaml")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml config.yaml
|
||||
llm:
|
||||
provider: gpt4all
|
||||
config:
|
||||
model: 'orca-mini-3b-gguf2-q4_0.gguf'
|
||||
temperature: 0.5
|
||||
max_tokens: 1000
|
||||
top_p: 1
|
||||
stream: false
|
||||
|
||||
embedder:
|
||||
provider: gpt4all
|
||||
```
|
||||
</CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## JinaChat
|
||||
|
||||
First, set `JINACHAT_API_KEY` in environment variable which you can obtain from [their platform](https://chat.jina.ai/api).
|
||||
|
||||
Once you have the key, load the app using the config yaml file:
|
||||
|
||||
<CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
```python main.py
|
||||
import os
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
|
||||
os.environ["JINACHAT_API_KEY"] = "xxx"
|
||||
# load llm configuration from config.yaml file
|
||||
app = App.from_config(config_path="config.yaml")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml config.yaml
|
||||
llm:
|
||||
provider: jina
|
||||
config:
|
||||
temperature: 0.5
|
||||
max_tokens: 1000
|
||||
top_p: 1
|
||||
stream: false
|
||||
```
|
||||
</CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Hugging Face
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Install related dependencies using the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install --upgrade 'embedchain[huggingface-hub]'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
First, set `HUGGINGFACE_ACCESS_TOKEN` in environment variable which you can obtain from [their platform](https://huggingface.co/settings/tokens).
|
||||
|
||||
You can load the LLMs from Hugging Face using three ways:
|
||||
|
||||
- [Hugging Face Hub](#hugging-face-hub)
|
||||
- [Hugging Face Local Pipelines](#hugging-face-local-pipelines)
|
||||
- [Hugging Face Inference Endpoint](#hugging-face-inference-endpoint)
|
||||
|
||||
### Hugging Face Hub
|
||||
|
||||
To load the model from Hugging Face Hub, use the following code:
|
||||
|
||||
<CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
```python main.py
|
||||
import os
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
|
||||
os.environ["HUGGINGFACE_ACCESS_TOKEN"] = "xxx"
|
||||
|
||||
config = {
|
||||
"app": {"config": {"id": "my-app"}},
|
||||
"llm": {
|
||||
"provider": "huggingface",
|
||||
"config": {
|
||||
"model": "bigscience/bloom-1b7",
|
||||
"top_p": 0.5,
|
||||
"max_length": 200,
|
||||
"temperature": 0.1,
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
app = App.from_config(config=config)
|
||||
```
|
||||
</CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
### Hugging Face Local Pipelines
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to load the locally downloaded model from Hugging Face, you can do so by following the code provided below:
|
||||
|
||||
<CodeGroup>
|
||||
```python main.py
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
|
||||
config = {
|
||||
"app": {"config": {"id": "my-app"}},
|
||||
"llm": {
|
||||
"provider": "huggingface",
|
||||
"config": {
|
||||
"model": "Trendyol/Trendyol-LLM-7b-chat-v0.1",
|
||||
"local": True, # Necessary if you want to run model locally
|
||||
"top_p": 0.5,
|
||||
"max_tokens": 1000,
|
||||
"temperature": 0.1,
|
||||
},
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
app = App.from_config(config=config)
|
||||
```
|
||||
</CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
### Hugging Face Inference Endpoint
|
||||
|
||||
You can also use [Hugging Face Inference Endpoints](https://huggingface.co/docs/inference-endpoints/index#-inference-endpoints) to access custom endpoints. First, set the `HUGGINGFACE_ACCESS_TOKEN` as above.
|
||||
|
||||
Then, load the app using the config yaml file:
|
||||
|
||||
<CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
```python main.py
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
|
||||
config = {
|
||||
"app": {"config": {"id": "my-app"}},
|
||||
"llm": {
|
||||
"provider": "huggingface",
|
||||
"config": {
|
||||
"endpoint": "https://api-inference.huggingface.co/models/gpt2",
|
||||
"model_params": {"temprature": 0.1, "max_new_tokens": 100}
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
}
|
||||
app = App.from_config(config=config)
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
</CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
Currently only supports `text-generation` and `text2text-generation` for now [[ref](https://api.python.langchain.com/en/latest/llms/langchain_community.llms.huggingface_endpoint.HuggingFaceEndpoint.html?highlight=huggingfaceendpoint#)].
|
||||
|
||||
See langchain's [hugging face endpoint](https://python.langchain.com/docs/integrations/chat/huggingface#huggingfaceendpoint) for more information.
|
||||
|
||||
## Llama2
|
||||
|
||||
Llama2 is integrated through [Replicate](https://replicate.com/). Set `REPLICATE_API_TOKEN` in environment variable which you can obtain from [their platform](https://replicate.com/account/api-tokens).
|
||||
|
||||
Once you have the token, load the app using the config yaml file:
|
||||
|
||||
<CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
```python main.py
|
||||
import os
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
|
||||
os.environ["REPLICATE_API_TOKEN"] = "xxx"
|
||||
|
||||
# load llm configuration from config.yaml file
|
||||
app = App.from_config(config_path="config.yaml")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml config.yaml
|
||||
llm:
|
||||
provider: llama2
|
||||
config:
|
||||
model: 'a16z-infra/llama13b-v2-chat:df7690f1994d94e96ad9d568eac121aecf50684a0b0963b25a41cc40061269e5'
|
||||
temperature: 0.5
|
||||
max_tokens: 1000
|
||||
top_p: 0.5
|
||||
stream: false
|
||||
```
|
||||
</CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
## Vertex AI
|
||||
|
||||
Setup Google Cloud Platform application credentials by following the instruction on [GCP](https://cloud.google.com/docs/authentication/external/set-up-adc). Once setup is done, use the following code to create an app using VertexAI as provider:
|
||||
|
||||
<CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
```python main.py
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
|
||||
# load llm configuration from config.yaml file
|
||||
app = App.from_config(config_path="config.yaml")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml config.yaml
|
||||
llm:
|
||||
provider: vertexai
|
||||
config:
|
||||
model: 'chat-bison'
|
||||
temperature: 0.5
|
||||
top_p: 0.5
|
||||
```
|
||||
</CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Mistral AI
|
||||
|
||||
Obtain the Mistral AI api key from their [console](https://console.mistral.ai/).
|
||||
|
||||
<CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
```python main.py
|
||||
os.environ["MISTRAL_API_KEY"] = "xxx"
|
||||
|
||||
app = App.from_config(config_path="config.yaml")
|
||||
|
||||
app.add("https://www.forbes.com/profile/elon-musk")
|
||||
|
||||
response = app.query("what is the net worth of Elon Musk?")
|
||||
# As of January 16, 2024, Elon Musk's net worth is $225.4 billion.
|
||||
|
||||
response = app.chat("which companies does elon own?")
|
||||
# Elon Musk owns Tesla, SpaceX, Boring Company, Twitter, and X.
|
||||
|
||||
response = app.chat("what question did I ask you already?")
|
||||
# You have asked me several times already which companies Elon Musk owns, specifically Tesla, SpaceX, Boring Company, Twitter, and X.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml config.yaml
|
||||
llm:
|
||||
provider: mistralai
|
||||
config:
|
||||
model: mistral-tiny
|
||||
temperature: 0.5
|
||||
max_tokens: 1000
|
||||
top_p: 1
|
||||
embedder:
|
||||
provider: mistralai
|
||||
config:
|
||||
model: mistral-embed
|
||||
```
|
||||
</CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## AWS Bedrock
|
||||
|
||||
### Setup
|
||||
- Before using the AWS Bedrock LLM, make sure you have the appropriate model access from [Bedrock Console](https://us-east-1.console.aws.amazon.com/bedrock/home?region=us-east-1#/modelaccess).
|
||||
- You will also need to authenticate the `boto3` client by using a method in the [AWS documentation](https://boto3.amazonaws.com/v1/documentation/api/latest/guide/credentials.html#configuring-credentials)
|
||||
- You can optionally export an `AWS_REGION`
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Usage
|
||||
|
||||
<CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
```python main.py
|
||||
import os
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
|
||||
os.environ["AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID"] = "xxx"
|
||||
os.environ["AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY"] = "xxx"
|
||||
os.environ["AWS_REGION"] = "us-west-2"
|
||||
|
||||
app = App.from_config(config_path="config.yaml")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml config.yaml
|
||||
llm:
|
||||
provider: aws_bedrock
|
||||
config:
|
||||
model: amazon.titan-text-express-v1
|
||||
# check notes below for model_kwargs
|
||||
model_kwargs:
|
||||
temperature: 0.5
|
||||
topP: 1
|
||||
maxTokenCount: 1000
|
||||
```
|
||||
</CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
<br />
|
||||
<Note>
|
||||
The model arguments are different for each providers. Please refer to the [AWS Bedrock Documentation](https://us-east-1.console.aws.amazon.com/bedrock/home?region=us-east-1#/providers) to find the appropriate arguments for your model.
|
||||
</Note>
|
||||
|
||||
<br/ >
|
||||
|
||||
## Groq
|
||||
|
||||
[Groq](https://groq.com/) is the creator of the world's first Language Processing Unit (LPU), providing exceptional speed performance for AI workloads running on their LPU Inference Engine.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Usage
|
||||
|
||||
In order to use LLMs from Groq, go to their [platform](https://console.groq.com/keys) and get the API key.
|
||||
|
||||
Set the API key as `GROQ_API_KEY` environment variable or pass in your app configuration to use the model as given below in the example.
|
||||
|
||||
<CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
```python main.py
|
||||
import os
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
|
||||
# Set your API key here or pass as the environment variable
|
||||
groq_api_key = "gsk_xxxx"
|
||||
|
||||
config = {
|
||||
"llm": {
|
||||
"provider": "groq",
|
||||
"config": {
|
||||
"model": "mixtral-8x7b-32768",
|
||||
"api_key": groq_api_key,
|
||||
"stream": True
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
app = App.from_config(config=config)
|
||||
# Add your data source here
|
||||
app.add("https://docs.embedchain.ai/sitemap.xml", data_type="sitemap")
|
||||
app.query("Write a poem about Embedchain")
|
||||
|
||||
# In the realm of data, vast and wide,
|
||||
# Embedchain stands with knowledge as its guide.
|
||||
# A platform open, for all to try,
|
||||
# Building bots that can truly fly.
|
||||
|
||||
# With REST API, data in reach,
|
||||
# Deployment a breeze, as easy as a speech.
|
||||
# Updating data sources, anytime, anyday,
|
||||
# Embedchain's power, never sway.
|
||||
|
||||
# A knowledge base, an assistant so grand,
|
||||
# Connecting to platforms, near and far.
|
||||
# Discord, WhatsApp, Slack, and more,
|
||||
# Embedchain's potential, never a bore.
|
||||
```
|
||||
</CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
## NVIDIA AI
|
||||
|
||||
[NVIDIA AI Foundation Endpoints](https://www.nvidia.com/en-us/ai-data-science/foundation-models/) let you quickly use NVIDIA's AI models, such as Mixtral 8x7B, Llama 2 etc, through our API. These models are available in the [NVIDIA NGC catalog](https://catalog.ngc.nvidia.com/ai-foundation-models), fully optimized and ready to use on NVIDIA's AI platform. They are designed for high speed and easy customization, ensuring smooth performance on any accelerated setup.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Usage
|
||||
|
||||
In order to use LLMs from NVIDIA AI, create an account on [NVIDIA NGC Service](https://catalog.ngc.nvidia.com/).
|
||||
|
||||
Generate an API key from their dashboard. Set the API key as `NVIDIA_API_KEY` environment variable. Note that the `NVIDIA_API_KEY` will start with `nvapi-`.
|
||||
|
||||
Below is an example of how to use LLM model and embedding model from NVIDIA AI:
|
||||
|
||||
<CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
```python main.py
|
||||
import os
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
|
||||
os.environ['NVIDIA_API_KEY'] = 'nvapi-xxxx'
|
||||
|
||||
config = {
|
||||
"app": {
|
||||
"config": {
|
||||
"id": "my-app",
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
"llm": {
|
||||
"provider": "nvidia",
|
||||
"config": {
|
||||
"model": "nemotron_steerlm_8b",
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
"embedder": {
|
||||
"provider": "nvidia",
|
||||
"config": {
|
||||
"model": "nvolveqa_40k",
|
||||
"vector_dimension": 1024,
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
app = App.from_config(config=config)
|
||||
|
||||
app.add("https://www.forbes.com/profile/elon-musk")
|
||||
answer = app.query("What is the net worth of Elon Musk today?")
|
||||
# Answer: The net worth of Elon Musk is subject to fluctuations based on the market value of his holdings in various companies.
|
||||
# As of March 1, 2024, his net worth is estimated to be approximately $210 billion. However, this figure can change rapidly due to stock market fluctuations and other factors.
|
||||
# Additionally, his net worth may include other assets such as real estate and art, which are not reflected in his stock portfolio.
|
||||
```
|
||||
</CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
## Token Usage
|
||||
|
||||
You can get the cost of the query by setting `token_usage` to `True` in the config file. This will return the token details: `prompt_tokens`, `completion_tokens`, `total_tokens`, `total_cost`, `cost_currency`.
|
||||
The list of paid LLMs that support token usage are:
|
||||
- OpenAI
|
||||
- Vertex AI
|
||||
- Anthropic
|
||||
- Cohere
|
||||
- Together
|
||||
- Groq
|
||||
- Mistral AI
|
||||
- NVIDIA AI
|
||||
|
||||
Here is an example of how to use token usage:
|
||||
<CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
```python main.py
|
||||
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = "xxx"
|
||||
|
||||
app = App.from_config(config_path="config.yaml")
|
||||
|
||||
app.add("https://www.forbes.com/profile/elon-musk")
|
||||
|
||||
response = app.query("what is the net worth of Elon Musk?")
|
||||
# {'answer': 'Elon Musk's net worth is $209.9 billion as of 6/9/24.',
|
||||
# 'usage': {'prompt_tokens': 1228,
|
||||
# 'completion_tokens': 21,
|
||||
# 'total_tokens': 1249,
|
||||
# 'total_cost': 0.001884,
|
||||
# 'cost_currency': 'USD'}
|
||||
# }
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
response = app.chat("Which companies did Elon Musk found?")
|
||||
# {'answer': 'Elon Musk founded six companies, including Tesla, which is an electric car maker, SpaceX, a rocket producer, and the Boring Company, a tunneling startup.',
|
||||
# 'usage': {'prompt_tokens': 1616,
|
||||
# 'completion_tokens': 34,
|
||||
# 'total_tokens': 1650,
|
||||
# 'total_cost': 0.002492,
|
||||
# 'cost_currency': 'USD'}
|
||||
# }
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml config.yaml
|
||||
llm:
|
||||
provider: openai
|
||||
config:
|
||||
model: gpt-3.5-turbo
|
||||
temperature: 0.5
|
||||
max_tokens: 1000
|
||||
token_usage: true
|
||||
```
|
||||
</CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
If a model is missing and you'd like to add it to `model_prices_and_context_window.json`, please feel free to open a PR.
|
||||
|
||||
<br/ >
|
||||
|
||||
<Snippet file="missing-llm-tip.mdx" />
|
||||
0
embedchain/docs/components/retrieval-methods.mdx
Normal file
0
embedchain/docs/components/retrieval-methods.mdx
Normal file
20
embedchain/docs/components/vector-databases.mdx
Normal file
20
embedchain/docs/components/vector-databases.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,20 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: 🗄️ Vector databases
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
Utilizing a vector database alongside Embedchain is a seamless process. All you need to do is configure it within the YAML configuration file. We've provided examples for each supported database below:
|
||||
|
||||
<CardGroup cols={4}>
|
||||
<Card title="ChromaDB" href="#chromadb"></Card>
|
||||
<Card title="Elasticsearch" href="#elasticsearch"></Card>
|
||||
<Card title="OpenSearch" href="#opensearch"></Card>
|
||||
<Card title="Zilliz" href="#zilliz"></Card>
|
||||
<Card title="LanceDB" href="#lancedb"></Card>
|
||||
<Card title="Pinecone" href="#pinecone"></Card>
|
||||
<Card title="Qdrant" href="#qdrant"></Card>
|
||||
<Card title="Weaviate" href="#weaviate"></Card>
|
||||
</CardGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
<Snippet file="missing-vector-db-tip.mdx" />
|
||||
35
embedchain/docs/components/vector-databases/chromadb.mdx
Normal file
35
embedchain/docs/components/vector-databases/chromadb.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,35 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: ChromaDB
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
```python main.py
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
|
||||
# load chroma configuration from yaml file
|
||||
app = App.from_config(config_path="config1.yaml")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml config1.yaml
|
||||
vectordb:
|
||||
provider: chroma
|
||||
config:
|
||||
collection_name: 'my-collection'
|
||||
dir: db
|
||||
allow_reset: true
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml config2.yaml
|
||||
vectordb:
|
||||
provider: chroma
|
||||
config:
|
||||
collection_name: 'my-collection'
|
||||
host: localhost
|
||||
port: 5200
|
||||
allow_reset: true
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
<Snippet file="missing-vector-db-tip.mdx" />
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,39 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Elasticsearch
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Install related dependencies using the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install --upgrade 'embedchain[elasticsearch]'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Note>
|
||||
You can configure the Elasticsearch connection by providing either `es_url` or `cloud_id`. If you are using the Elasticsearch Service on Elastic Cloud, you can find the `cloud_id` on the [Elastic Cloud dashboard](https://cloud.elastic.co/deployments).
|
||||
</Note>
|
||||
|
||||
You can authorize the connection to Elasticsearch by providing either `basic_auth`, `api_key`, or `bearer_auth`.
|
||||
|
||||
<CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
```python main.py
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
|
||||
# load elasticsearch configuration from yaml file
|
||||
app = App.from_config(config_path="config.yaml")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml config.yaml
|
||||
vectordb:
|
||||
provider: elasticsearch
|
||||
config:
|
||||
collection_name: 'es-index'
|
||||
cloud_id: 'deployment-name:xxxx'
|
||||
basic_auth:
|
||||
- elastic
|
||||
- <your_password>
|
||||
verify_certs: false
|
||||
```
|
||||
</CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
<Snippet file="missing-vector-db-tip.mdx" />
|
||||
100
embedchain/docs/components/vector-databases/lancedb.mdx
Normal file
100
embedchain/docs/components/vector-databases/lancedb.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,100 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: LanceDB
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## Install Embedchain with LanceDB
|
||||
|
||||
Install Embedchain, LanceDB and related dependencies using the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install "embedchain[lancedb]"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
LanceDB is a developer-friendly, open source database for AI. From hyper scalable vector search and advanced retrieval for RAG, to streaming training data and interactive exploration of large scale AI datasets.
|
||||
In order to use LanceDB as vector database, not need to set any key for local use.
|
||||
|
||||
### With OPENAI
|
||||
<CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
```python main.py
|
||||
import os
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
|
||||
# set OPENAI_API_KEY as env variable
|
||||
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = "sk-xxx"
|
||||
|
||||
# create Embedchain App and set config
|
||||
app = App.from_config(config={
|
||||
"vectordb": {
|
||||
"provider": "lancedb",
|
||||
"config": {
|
||||
"collection_name": "lancedb-index"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# add data source and start query in
|
||||
app.add("https://www.forbes.com/profile/elon-musk")
|
||||
|
||||
# query continuously
|
||||
while(True):
|
||||
question = input("Enter question: ")
|
||||
if question in ['q', 'exit', 'quit']:
|
||||
break
|
||||
answer = app.query(question)
|
||||
print(answer)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
### With Local LLM
|
||||
<CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
```python main.py
|
||||
from embedchain import Pipeline as App
|
||||
|
||||
# config for Embedchain App
|
||||
config = {
|
||||
'llm': {
|
||||
'provider': 'huggingface',
|
||||
'config': {
|
||||
'model': 'mistralai/Mistral-7B-v0.1',
|
||||
'temperature': 0.1,
|
||||
'max_tokens': 250,
|
||||
'top_p': 0.1,
|
||||
'stream': True
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
'embedder': {
|
||||
'provider': 'huggingface',
|
||||
'config': {
|
||||
'model': 'sentence-transformers/all-mpnet-base-v2'
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
'vectordb': {
|
||||
'provider': 'lancedb',
|
||||
'config': {
|
||||
'collection_name': 'lancedb-index'
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
app = App.from_config(config=config)
|
||||
|
||||
# add data source and start query in
|
||||
app.add("https://www.tesla.com/ns_videos/2022-tesla-impact-report.pdf")
|
||||
|
||||
# query continuously
|
||||
while(True):
|
||||
question = input("Enter question: ")
|
||||
if question in ['q', 'exit', 'quit']:
|
||||
break
|
||||
answer = app.query(question)
|
||||
print(answer)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<Snippet file="missing-vector-db-tip.mdx" />
|
||||
36
embedchain/docs/components/vector-databases/opensearch.mdx
Normal file
36
embedchain/docs/components/vector-databases/opensearch.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,36 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: OpenSearch
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Install related dependencies using the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install --upgrade 'embedchain[opensearch]'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
```python main.py
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
|
||||
# load opensearch configuration from yaml file
|
||||
app = App.from_config(config_path="config.yaml")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml config.yaml
|
||||
vectordb:
|
||||
provider: opensearch
|
||||
config:
|
||||
collection_name: 'my-app'
|
||||
opensearch_url: 'https://localhost:9200'
|
||||
http_auth:
|
||||
- admin
|
||||
- admin
|
||||
vector_dimension: 1536
|
||||
use_ssl: false
|
||||
verify_certs: false
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
<Snippet file="missing-vector-db-tip.mdx" />
|
||||
109
embedchain/docs/components/vector-databases/pinecone.mdx
Normal file
109
embedchain/docs/components/vector-databases/pinecone.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,109 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Pinecone
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
Install pinecone related dependencies using the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install --upgrade 'pinecone-client pinecone-text'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
In order to use Pinecone as vector database, set the environment variable `PINECONE_API_KEY` which you can find on [Pinecone dashboard](https://app.pinecone.io/).
|
||||
|
||||
<CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
```python main.py
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
|
||||
# Load pinecone configuration from yaml file
|
||||
app = App.from_config(config_path="pod_config.yaml")
|
||||
# Or
|
||||
app = App.from_config(config_path="serverless_config.yaml")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml pod_config.yaml
|
||||
vectordb:
|
||||
provider: pinecone
|
||||
config:
|
||||
metric: cosine
|
||||
vector_dimension: 1536
|
||||
index_name: my-pinecone-index
|
||||
pod_config:
|
||||
environment: gcp-starter
|
||||
metadata_config:
|
||||
indexed:
|
||||
- "url"
|
||||
- "hash"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml serverless_config.yaml
|
||||
vectordb:
|
||||
provider: pinecone
|
||||
config:
|
||||
metric: cosine
|
||||
vector_dimension: 1536
|
||||
index_name: my-pinecone-index
|
||||
serverless_config:
|
||||
cloud: aws
|
||||
region: us-west-2
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
<br />
|
||||
<Note>
|
||||
You can find more information about Pinecone configuration [here](https://docs.pinecone.io/docs/manage-indexes#create-a-pod-based-index).
|
||||
You can also optionally provide `index_name` as a config param in yaml file to specify the index name. If not provided, the index name will be `{collection_name}-{vector_dimension}`.
|
||||
</Note>
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage
|
||||
|
||||
### Hybrid search
|
||||
|
||||
Here is an example of how you can do hybrid search using Pinecone as a vector database through Embedchain.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import os
|
||||
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
|
||||
config = {
|
||||
'app': {
|
||||
"config": {
|
||||
"id": "ec-docs-hybrid-search"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
'vectordb': {
|
||||
'provider': 'pinecone',
|
||||
'config': {
|
||||
'metric': 'dotproduct',
|
||||
'vector_dimension': 1536,
|
||||
'index_name': 'my-index',
|
||||
'serverless_config': {
|
||||
'cloud': 'aws',
|
||||
'region': 'us-west-2'
|
||||
},
|
||||
'hybrid_search': True, # Remember to set this for hybrid search
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
# Initialize app
|
||||
app = App.from_config(config=config)
|
||||
|
||||
# Add documents
|
||||
app.add("/path/to/file.pdf", data_type="pdf_file", namespace="my-namespace")
|
||||
|
||||
# Query
|
||||
app.query("<YOUR QUESTION HERE>", namespace="my-namespace")
|
||||
|
||||
# Chat
|
||||
app.chat("<YOUR QUESTION HERE>", namespace="my-namespace")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Under the hood, Embedchain fetches the relevant chunks from the documents you added by doing hybrid search on the pinecone index.
|
||||
If you have questions on how pinecone hybrid search works, please refer to their [offical documentation here](https://docs.pinecone.io/docs/hybrid-search).
|
||||
|
||||
<Snippet file="missing-vector-db-tip.mdx" />
|
||||
23
embedchain/docs/components/vector-databases/qdrant.mdx
Normal file
23
embedchain/docs/components/vector-databases/qdrant.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,23 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Qdrant
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
In order to use Qdrant as a vector database, set the environment variables `QDRANT_URL` and `QDRANT_API_KEY` which you can find on [Qdrant Dashboard](https://cloud.qdrant.io/).
|
||||
|
||||
<CodeGroup>
|
||||
```python main.py
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
|
||||
# load qdrant configuration from yaml file
|
||||
app = App.from_config(config_path="config.yaml")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml config.yaml
|
||||
vectordb:
|
||||
provider: qdrant
|
||||
config:
|
||||
collection_name: my_qdrant_index
|
||||
```
|
||||
</CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
<Snippet file="missing-vector-db-tip.mdx" />
|
||||
24
embedchain/docs/components/vector-databases/weaviate.mdx
Normal file
24
embedchain/docs/components/vector-databases/weaviate.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,24 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Weaviate
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
In order to use Weaviate as a vector database, set the environment variables `WEAVIATE_ENDPOINT` and `WEAVIATE_API_KEY` which you can find on [Weaviate dashboard](https://console.weaviate.cloud/dashboard).
|
||||
|
||||
<CodeGroup>
|
||||
```python main.py
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
|
||||
# load weaviate configuration from yaml file
|
||||
app = App.from_config(config_path="config.yaml")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml config.yaml
|
||||
vectordb:
|
||||
provider: weaviate
|
||||
config:
|
||||
collection_name: my_weaviate_index
|
||||
```
|
||||
</CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
<Snippet file="missing-vector-db-tip.mdx" />
|
||||
39
embedchain/docs/components/vector-databases/zilliz.mdx
Normal file
39
embedchain/docs/components/vector-databases/zilliz.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,39 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Zilliz
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Install related dependencies using the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install --upgrade 'embedchain[milvus]'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Set the Zilliz environment variables `ZILLIZ_CLOUD_URI` and `ZILLIZ_CLOUD_TOKEN` which you can find it on their [cloud platform](https://cloud.zilliz.com/).
|
||||
|
||||
<CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
```python main.py
|
||||
import os
|
||||
from embedchain import App
|
||||
|
||||
os.environ['ZILLIZ_CLOUD_URI'] = 'https://xxx.zillizcloud.com'
|
||||
os.environ['ZILLIZ_CLOUD_TOKEN'] = 'xxx'
|
||||
|
||||
# load zilliz configuration from yaml file
|
||||
app = App.from_config(config_path="config.yaml")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml config.yaml
|
||||
vectordb:
|
||||
provider: zilliz
|
||||
config:
|
||||
collection_name: 'zilliz_app'
|
||||
uri: https://xxxx.api.gcp-region.zillizcloud.com
|
||||
token: xxx
|
||||
vector_dim: 1536
|
||||
metric_type: L2
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
<Snippet file="missing-vector-db-tip.mdx" />
|
||||
45
embedchain/docs/contribution/dev.mdx
Normal file
45
embedchain/docs/contribution/dev.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,45 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: '👨💻 Development'
|
||||
description: 'Contribute to Embedchain framework development'
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Thank you for your interest in contributing to the EmbedChain project! We welcome your ideas and contributions to help improve the project. Please follow the instructions below to get started:
|
||||
|
||||
1. **Fork the repository**: Click on the "Fork" button at the top right corner of this repository page. This will create a copy of the repository in your own GitHub account.
|
||||
|
||||
2. **Install the required dependencies**: Ensure that you have the necessary dependencies installed in your Python environment. You can do this by running the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
make install
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3. **Make changes in the code**: Create a new branch in your forked repository and make your desired changes in the codebase.
|
||||
4. **Format code**: Before creating a pull request, it's important to ensure that your code follows our formatting guidelines. Run the following commands to format the code:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
make lint format
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
5. **Create a pull request**: When you are ready to contribute your changes, submit a pull request to the EmbedChain repository. Provide a clear and descriptive title for your pull request, along with a detailed description of the changes you have made.
|
||||
|
||||
## Team
|
||||
|
||||
### Authors
|
||||
|
||||
- Taranjeet Singh ([@taranjeetio](https://twitter.com/taranjeetio))
|
||||
- Deshraj Yadav ([@deshrajdry](https://twitter.com/deshrajdry))
|
||||
|
||||
### Citation
|
||||
|
||||
If you utilize this repository, please consider citing it with:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
@misc{embedchain,
|
||||
author = {Taranjeet Singh, Deshraj Yadav},
|
||||
title = {Embechain: The Open Source RAG Framework},
|
||||
year = {2023},
|
||||
publisher = {GitHub},
|
||||
journal = {GitHub repository},
|
||||
howpublished = {\url{https://github.com/embedchain/embedchain}},
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
61
embedchain/docs/contribution/docs.mdx
Normal file
61
embedchain/docs/contribution/docs.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,61 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: '📝 Documentation'
|
||||
description: 'Contribute to Embedchain docs'
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<Info>
|
||||
**Prerequisite** You should have installed Node.js (version 18.10.0 or
|
||||
higher).
|
||||
</Info>
|
||||
|
||||
Step 1. Install Mintlify on your OS:
|
||||
|
||||
<CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
```bash npm
|
||||
npm i -g mintlify
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```bash yarn
|
||||
yarn global add mintlify
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
Step 2. Go to the `docs/` directory (where you can find `mint.json`) and run the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
mintlify dev
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The documentation website is now available at `http://localhost:3000`.
|
||||
|
||||
### Custom Ports
|
||||
|
||||
Mintlify uses port 3000 by default. You can use the `--port` flag to customize the port Mintlify runs on. For example, use this command to run in port 3333:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
mintlify dev --port 3333
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You will see an error like this if you try to run Mintlify in a port that's already taken:
|
||||
|
||||
```md
|
||||
Error: listen EADDRINUSE: address already in use :::3000
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Mintlify Versions
|
||||
|
||||
Each CLI is linked to a specific version of Mintlify. Please update the CLI if your local website looks different than production.
|
||||
|
||||
<CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
```bash npm
|
||||
npm i -g mintlify@latest
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```bash yarn
|
||||
yarn global upgrade mintlify
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</CodeGroup>
|
||||
4
embedchain/docs/contribution/guidelines.mdx
Normal file
4
embedchain/docs/contribution/guidelines.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,4 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: '📋 Guidelines'
|
||||
url: https://github.com/embedchain/embedchain/blob/main/CONTRIBUTING.md
|
||||
---
|
||||
4
embedchain/docs/contribution/python.mdx
Normal file
4
embedchain/docs/contribution/python.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,4 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: '🐍 Python'
|
||||
url: https://github.com/embedchain/embedchain
|
||||
---
|
||||
101
embedchain/docs/deployment/fly_io.mdx
Normal file
101
embedchain/docs/deployment/fly_io.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,101 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: 'Fly.io'
|
||||
description: 'Deploy your RAG application to fly.io platform'
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Embedchain has a nice and simple abstraction on top of the [Fly.io](https://fly.io/) tools to let developers deploy RAG application to fly.io platform seamlessly.
|
||||
|
||||
Follow the instructions given below to deploy your first application quickly:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Step-1: Install flyctl command line
|
||||
|
||||
<CodeGroup>
|
||||
```bash OSX
|
||||
brew install flyctl
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```bash Linux
|
||||
curl -L https://fly.io/install.sh | sh
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```bash Windows
|
||||
pwsh -Command "iwr https://fly.io/install.ps1 -useb | iex"
|
||||
```
|
||||
</CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
Once you have installed the fly.io cli tool, signup/login to their platform using the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
<CodeGroup>
|
||||
```bash Sign up
|
||||
fly auth signup
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```bash Sign in
|
||||
fly auth login
|
||||
```
|
||||
</CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
In case you run into issues, refer to official [fly.io docs](https://fly.io/docs/hands-on/install-flyctl/).
|
||||
|
||||
## Step-2: Create RAG app
|
||||
|
||||
We provide a command line utility called `ec` in embedchain that inherits the template for `fly.io` platform and help you deploy the app. Follow the instructions to create a fly.io app using the template provided:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash Install embedchain
|
||||
pip install embedchain
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```bash Create application
|
||||
mkdir my-rag-app
|
||||
ec create --template=fly.io
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This will generate a directory structure like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
├── Dockerfile
|
||||
├── app.py
|
||||
├── fly.toml
|
||||
├── .env
|
||||
├── .env.example
|
||||
├── embedchain.json
|
||||
└── requirements.txt
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Feel free to edit the files as required.
|
||||
- `Dockerfile`: Defines the steps to setup the application
|
||||
- `app.py`: Contains API app code
|
||||
- `fly.toml`: fly.io config file
|
||||
- `.env`: Contains environment variables for production
|
||||
- `.env.example`: Contains dummy environment variables (can ignore this file)
|
||||
- `embedchain.json`: Contains embedchain specific configuration for deployment (you don't need to configure this)
|
||||
- `requirements.txt`: Contains python dependencies for your application
|
||||
|
||||
## Step-3: Test app locally
|
||||
|
||||
You can run the app locally by simply doing:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash Run locally
|
||||
pip install -r requirements.txt
|
||||
ec dev
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Step-4: Deploy to fly.io
|
||||
|
||||
You can deploy to fly.io using the following command:
|
||||
```bash Deploy app
|
||||
ec deploy
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Once this step finished, it will provide you with the deployment endpoint where you can access the app live. It will look something like this (Swagger docs):
|
||||
|
||||
You can also check the logs, monitor app status etc on their dashboard by running command `fly dashboard`.
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="/images/fly_io.png" />
|
||||
|
||||
## Seeking help?
|
||||
|
||||
If you run into issues with deployment, please feel free to reach out to us via any of the following methods:
|
||||
|
||||
<Snippet file="get-help.mdx" />
|
||||
59
embedchain/docs/deployment/gradio_app.mdx
Normal file
59
embedchain/docs/deployment/gradio_app.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,59 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: 'Gradio.app'
|
||||
description: 'Deploy your RAG application to gradio.app platform'
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Embedchain offers a Streamlit template to facilitate the development of RAG chatbot applications in just three easy steps.
|
||||
|
||||
Follow the instructions given below to deploy your first application quickly:
|
||||
|
||||
## Step-1: Create RAG app
|
||||
|
||||
We provide a command line utility called `ec` in embedchain that inherits the template for `gradio.app` platform and help you deploy the app. Follow the instructions to create a gradio.app app using the template provided:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash Install embedchain
|
||||
pip install embedchain
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```bash Create application
|
||||
mkdir my-rag-app
|
||||
ec create --template=gradio.app
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This will generate a directory structure like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
├── app.py
|
||||
├── embedchain.json
|
||||
└── requirements.txt
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Feel free to edit the files as required.
|
||||
- `app.py`: Contains API app code
|
||||
- `embedchain.json`: Contains embedchain specific configuration for deployment (you don't need to configure this)
|
||||
- `requirements.txt`: Contains python dependencies for your application
|
||||
|
||||
## Step-2: Test app locally
|
||||
|
||||
You can run the app locally by simply doing:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash Run locally
|
||||
pip install -r requirements.txt
|
||||
ec dev
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Step-3: Deploy to gradio.app
|
||||
|
||||
```bash Deploy to gradio.app
|
||||
ec deploy
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This will run `gradio deploy` which will prompt you questions and deploy your app directly to huggingface spaces.
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="/images/gradio_app.png" alt="gradio app" />
|
||||
|
||||
## Seeking help?
|
||||
|
||||
If you run into issues with deployment, please feel free to reach out to us via any of the following methods:
|
||||
|
||||
<Snippet file="get-help.mdx" />
|
||||
103
embedchain/docs/deployment/huggingface_spaces.mdx
Normal file
103
embedchain/docs/deployment/huggingface_spaces.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,103 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: 'Huggingface.co'
|
||||
description: 'Deploy your RAG application to huggingface.co platform'
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
With Embedchain, you can directly host your apps in just three steps to huggingface spaces where you can view and deploy your app to the world.
|
||||
|
||||
We support two types of deployment to huggingface spaces:
|
||||
|
||||
<CardGroup cols={2}>
|
||||
<Card title="" href="#using-streamlit-io">
|
||||
Streamlit.io
|
||||
</Card>
|
||||
<Card title="" href="#using-gradio-app">
|
||||
Gradio.app
|
||||
</Card>
|
||||
</CardGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
## Using streamlit.io
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 1: Create a new RAG app
|
||||
|
||||
Create a new RAG app using the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
mkdir my-rag-app
|
||||
ec create --template=hf/streamlit.io # inside my-rag-app directory
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
When you run this for the first time, you'll be asked to login to huggingface.co. Once you login, you'll need to create a **write** token. You can create a write token by going to [huggingface.co settings](https://huggingface.co/settings/token). Once you create a token, you'll be asked to enter the token in the terminal.
|
||||
|
||||
This will also create an `embedchain.json` file in your app directory. Add a `name` key into the `embedchain.json` file. This will be the "repo-name" of your app in huggingface spaces.
|
||||
|
||||
```json embedchain.json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "my-rag-app",
|
||||
"provider": "hf/streamlit.io"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Step-2: Test app locally
|
||||
|
||||
You can run the app locally by simply doing:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash Run locally
|
||||
pip install -r requirements.txt
|
||||
ec dev
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Step-3: Deploy to huggingface spaces
|
||||
|
||||
```bash Deploy to huggingface spaces
|
||||
ec deploy
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This will deploy your app to huggingface spaces. You can view your app at `https://huggingface.co/spaces/<your-username>/my-rag-app`. This will get prompted in the terminal once the app is deployed.
|
||||
|
||||
## Using gradio.app
|
||||
|
||||
Similar to streamlit.io, you can deploy your app to gradio.app in just three steps.
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 1: Create a new RAG app
|
||||
|
||||
Create a new RAG app using the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
mkdir my-rag-app
|
||||
ec create --template=hf/gradio.app # inside my-rag-app directory
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
When you run this for the first time, you'll be asked to login to huggingface.co. Once you login, you'll need to create a **write** token. You can create a write token by going to [huggingface.co settings](https://huggingface.co/settings/token). Once you create a token, you'll be asked to enter the token in the terminal.
|
||||
|
||||
This will also create an `embedchain.json` file in your app directory. Add a `name` key into the `embedchain.json` file. This will be the "repo-name" of your app in huggingface spaces.
|
||||
|
||||
```json embedchain.json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "my-rag-app",
|
||||
"provider": "hf/gradio.app"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Step-2: Test app locally
|
||||
|
||||
You can run the app locally by simply doing:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash Run locally
|
||||
pip install -r requirements.txt
|
||||
ec dev
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Step-3: Deploy to huggingface spaces
|
||||
|
||||
```bash Deploy to huggingface spaces
|
||||
ec deploy
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This will deploy your app to huggingface spaces. You can view your app at `https://huggingface.co/spaces/<your-username>/my-rag-app`. This will get prompted in the terminal once the app is deployed.
|
||||
|
||||
## Seeking help?
|
||||
|
||||
If you run into issues with deployment, please feel free to reach out to us via any of the following methods:
|
||||
|
||||
<Snippet file="get-help.mdx" />
|
||||
63
embedchain/docs/deployment/modal_com.mdx
Normal file
63
embedchain/docs/deployment/modal_com.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,63 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: 'Modal.com'
|
||||
description: 'Deploy your RAG application to modal.com platform'
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Embedchain has a nice and simple abstraction on top of the [Modal.com](https://modal.com/) tools to let developers deploy RAG application to modal.com platform seamlessly.
|
||||
|
||||
Follow the instructions given below to deploy your first application quickly:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Step-1 Create RAG application:
|
||||
|
||||
We provide a command line utility called `ec` in embedchain that inherits the template for `modal.com` platform and help you deploy the app. Follow the instructions to create a modal.com app using the template provided:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```bash Create application
|
||||
pip install embedchain[modal]
|
||||
mkdir my-rag-app
|
||||
ec create --template=modal.com
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This `create` command will open a browser window and ask you to login to your modal.com account and will generate a directory structure like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
├── app.py
|
||||
├── .env
|
||||
├── .env.example
|
||||
├── embedchain.json
|
||||
└── requirements.txt
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Feel free to edit the files as required.
|
||||
- `app.py`: Contains API app code
|
||||
- `.env`: Contains environment variables for production
|
||||
- `.env.example`: Contains dummy environment variables (can ignore this file)
|
||||
- `embedchain.json`: Contains embedchain specific configuration for deployment (you don't need to configure this)
|
||||
- `requirements.txt`: Contains python dependencies for your FastAPI application
|
||||
|
||||
## Step-2: Test app locally
|
||||
|
||||
You can run the app locally by simply doing:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash Run locally
|
||||
pip install -r requirements.txt
|
||||
ec dev
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Step-3: Deploy to modal.com
|
||||
|
||||
You can deploy to modal.com using the following command:
|
||||
```bash Deploy app
|
||||
ec deploy
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Once this step finished, it will provide you with the deployment endpoint where you can access the app live. It will look something like this (Swagger docs):
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="/images/fly_io.png" />
|
||||
|
||||
## Seeking help?
|
||||
|
||||
If you run into issues with deployment, please feel free to reach out to us via any of the following methods:
|
||||
|
||||
<Snippet file="get-help.mdx" />
|
||||
86
embedchain/docs/deployment/railway.mdx
Normal file
86
embedchain/docs/deployment/railway.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,86 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: 'Railway.app'
|
||||
description: 'Deploy your RAG application to railway.app'
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
It's easy to host your Embedchain-powered apps and APIs on railway.
|
||||
|
||||
Follow the instructions given below to deploy your first application quickly:
|
||||
|
||||
## Step-1: Create RAG app
|
||||
|
||||
```bash Install embedchain
|
||||
pip install embedchain
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
**Create a full stack app using Embedchain CLI**
|
||||
|
||||
To use your hosted embedchain RAG app, you can easily set up a FastAPI server that can be used anywhere.
|
||||
To easily set up a FastAPI server, check out [Get started with Full stack](https://docs.embedchain.ai/get-started/full-stack) page.
|
||||
|
||||
Hosting this server on railway is super easy!
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
## Step-2: Set up your project
|
||||
|
||||
### With Docker
|
||||
|
||||
You can create a `Dockerfile` in the root of the project, with all the instructions. However, this method is sometimes slower in deployment.
|
||||
|
||||
### Without Docker
|
||||
|
||||
By default, Railway uses Python 3.7. Embedchain requires the python version to be >3.9 in order to install.
|
||||
|
||||
To fix this, create a `.python-version` file in the root directory of your project and specify the correct version
|
||||
|
||||
```bash .python-version
|
||||
3.10
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You also need to create a `requirements.txt` file to specify the requirements.
|
||||
|
||||
```bash requirements.txt
|
||||
python-dotenv
|
||||
embedchain
|
||||
fastapi==0.108.0
|
||||
uvicorn==0.25.0
|
||||
embedchain
|
||||
beautifulsoup4
|
||||
sentence-transformers
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Step-3: Deploy to Railway 🚀
|
||||
|
||||
1. Go to https://railway.app and create an account.
|
||||
2. Create a project by clicking on the "Start a new project" button
|
||||
|
||||
### With Github
|
||||
|
||||
Select `Empty Project` or `Deploy from Github Repo`.
|
||||
|
||||
You should be all set!
|
||||
|
||||
### Without Github
|
||||
|
||||
You can also use the railway CLI to deploy your apps from the terminal, if you don't want to connect a git repository.
|
||||
|
||||
To do this, just run this command in your terminal
|
||||
|
||||
```bash Install and set up railway CLI
|
||||
npm i -g @railway/cli
|
||||
railway login
|
||||
railway link [projectID]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, run `railway up` to deploy your app.
|
||||
```bash Deploy
|
||||
railway up
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Seeking help?
|
||||
|
||||
If you run into issues with deployment, please feel free to reach out to us via any of the following methods:
|
||||
|
||||
<Snippet file="get-help.mdx" />
|
||||
93
embedchain/docs/deployment/render_com.mdx
Normal file
93
embedchain/docs/deployment/render_com.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,93 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: 'Render.com'
|
||||
description: 'Deploy your RAG application to render.com platform'
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Embedchain has a nice and simple abstraction on top of the [render.com](https://render.com/) tools to let developers deploy RAG application to render.com platform seamlessly.
|
||||
|
||||
Follow the instructions given below to deploy your first application quickly:
|
||||
|
||||
## Step-1: Install `render` command line
|
||||
|
||||
<CodeGroup>
|
||||
```bash OSX
|
||||
brew tap render-oss/render
|
||||
brew install render
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```bash Linux
|
||||
# Make sure you have deno installed -> https://docs.render.com/docs/cli#from-source-unsupported-operating-systems
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/render-oss/render-cli
|
||||
cd render-cli
|
||||
make deps
|
||||
deno task run
|
||||
deno compile
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```bash Windows
|
||||
choco install rendercli
|
||||
```
|
||||
</CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
In case you run into issues, refer to official [render.com docs](https://docs.render.com/docs/cli).
|
||||
|
||||
## Step-2 Create RAG application:
|
||||
|
||||
We provide a command line utility called `ec` in embedchain that inherits the template for `render.com` platform and help you deploy the app. Follow the instructions to create a render.com app using the template provided:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```bash Create application
|
||||
pip install embedchain
|
||||
mkdir my-rag-app
|
||||
ec create --template=render.com
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This `create` command will open a browser window and ask you to login to your render.com account and will generate a directory structure like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
├── app.py
|
||||
├── .env
|
||||
├── render.yaml
|
||||
├── embedchain.json
|
||||
└── requirements.txt
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Feel free to edit the files as required.
|
||||
- `app.py`: Contains API app code
|
||||
- `.env`: Contains environment variables for production
|
||||
- `render.yaml`: Contains render.com specific configuration for deployment (configure this according to your needs, follow [this](https://docs.render.com/docs/blueprint-spec) for more info)
|
||||
- `embedchain.json`: Contains embedchain specific configuration for deployment (you don't need to configure this)
|
||||
- `requirements.txt`: Contains python dependencies for your application
|
||||
|
||||
## Step-3: Test app locally
|
||||
|
||||
You can run the app locally by simply doing:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash Run locally
|
||||
pip install -r requirements.txt
|
||||
ec dev
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Step-4: Deploy to render.com
|
||||
|
||||
Before deploying to render.com, you only have to set up one thing.
|
||||
|
||||
In the render.yaml file, make sure to modify the repo key by inserting the URL of your Git repository where your application will be hosted. You can create a repository from [GitHub](https://github.com) or [GitLab](https://gitlab.com/users/sign_in).
|
||||
|
||||
After that, you're ready to deploy on render.com.
|
||||
|
||||
```bash Deploy app
|
||||
ec deploy
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
When you run this, it should open up your render dashboard and you can see the app being deployed. You can find your hosted link over there only.
|
||||
|
||||
You can also check the logs, monitor app status etc on their dashboard by running command `render dashboard`.
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="/images/fly_io.png" />
|
||||
|
||||
## Seeking help?
|
||||
|
||||
If you run into issues with deployment, please feel free to reach out to us via any of the following methods:
|
||||
|
||||
<Snippet file="get-help.mdx" />
|
||||
62
embedchain/docs/deployment/streamlit_io.mdx
Normal file
62
embedchain/docs/deployment/streamlit_io.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,62 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: 'Streamlit.io'
|
||||
description: 'Deploy your RAG application to streamlit.io platform'
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Embedchain offers a Streamlit template to facilitate the development of RAG chatbot applications in just three easy steps.
|
||||
|
||||
Follow the instructions given below to deploy your first application quickly:
|
||||
|
||||
## Step-1: Create RAG app
|
||||
|
||||
We provide a command line utility called `ec` in embedchain that inherits the template for `streamlit.io` platform and help you deploy the app. Follow the instructions to create a streamlit.io app using the template provided:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash Install embedchain
|
||||
pip install embedchain
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```bash Create application
|
||||
mkdir my-rag-app
|
||||
ec create --template=streamlit.io
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This will generate a directory structure like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
├── .streamlit
|
||||
│ └── secrets.toml
|
||||
├── app.py
|
||||
├── embedchain.json
|
||||
└── requirements.txt
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Feel free to edit the files as required.
|
||||
- `app.py`: Contains API app code
|
||||
- `.streamlit/secrets.toml`: Contains secrets for your application
|
||||
- `embedchain.json`: Contains embedchain specific configuration for deployment (you don't need to configure this)
|
||||
- `requirements.txt`: Contains python dependencies for your application
|
||||
|
||||
Add your `OPENAI_API_KEY` in `.streamlit/secrets.toml` file to run and deploy the app.
|
||||
|
||||
## Step-2: Test app locally
|
||||
|
||||
You can run the app locally by simply doing:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash Run locally
|
||||
pip install -r requirements.txt
|
||||
ec dev
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Step-3: Deploy to streamlit.io
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Use the deploy button from the streamlit website to deploy your app.
|
||||
|
||||
You can refer this [guide](https://docs.streamlit.io/streamlit-community-cloud/deploy-your-app) if you run into any problems.
|
||||
|
||||
## Seeking help?
|
||||
|
||||
If you run into issues with deployment, please feel free to reach out to us via any of the following methods:
|
||||
|
||||
<Snippet file="get-help.mdx" />
|
||||
98
embedchain/docs/development.mdx
Normal file
98
embedchain/docs/development.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,98 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: 'Development'
|
||||
description: 'Learn how to preview changes locally'
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<Info>
|
||||
**Prerequisite** You should have installed Node.js (version 18.10.0 or
|
||||
higher).
|
||||
</Info>
|
||||
|
||||
Step 1. Install Mintlify on your OS:
|
||||
|
||||
<CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
```bash npm
|
||||
npm i -g mintlify
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```bash yarn
|
||||
yarn global add mintlify
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
Step 2. Go to the docs are located (where you can find `mint.json`) and run the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
mintlify dev
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The documentation website is now available at `http://localhost:3000`.
|
||||
|
||||
### Custom Ports
|
||||
|
||||
Mintlify uses port 3000 by default. You can use the `--port` flag to customize the port Mintlify runs on. For example, use this command to run in port 3333:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
mintlify dev --port 3333
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You will see an error like this if you try to run Mintlify in a port that's already taken:
|
||||
|
||||
```md
|
||||
Error: listen EADDRINUSE: address already in use :::3000
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Mintlify Versions
|
||||
|
||||
Each CLI is linked to a specific version of Mintlify. Please update the CLI if your local website looks different than production.
|
||||
|
||||
<CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
```bash npm
|
||||
npm i -g mintlify@latest
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```bash yarn
|
||||
yarn global upgrade mintlify
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</CodeGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
## Deployment
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
Unlimited editors available under the [Startup
|
||||
Plan](https://mintlify.com/pricing)
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
You should see the following if the deploy successfully went through:
|
||||
|
||||
<Frame>
|
||||
<img src="/images/checks-passed.png" style={{ borderRadius: '0.5rem' }} />
|
||||
</Frame>
|
||||
|
||||
## Troubleshooting
|
||||
|
||||
Here's how to solve some common problems when working with the CLI.
|
||||
|
||||
<AccordionGroup>
|
||||
<Accordion title="Mintlify is not loading">
|
||||
Update to Node v18. Run `mintlify install` and try again.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
<Accordion title="No such file or directory on Windows">
|
||||
Go to the `C:/Users/Username/.mintlify/` directory and remove the `mint`
|
||||
folder. Then Open the Git Bash in this location and run `git clone
|
||||
https://github.com/mintlify/mint.git`.
|
||||
|
||||
Repeat step 3.
|
||||
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
<Accordion title="Getting an unknown error">
|
||||
Try navigating to the root of your device and delete the ~/.mintlify folder.
|
||||
Then run `mintlify dev` again.
|
||||
</Accordion>
|
||||
</AccordionGroup>
|
||||
|
||||
Curious about what changed in a CLI version? [Check out the CLI changelog.](/changelog/command-line)
|
||||
32
embedchain/docs/examples/chat-with-PDF.mdx
Normal file
32
embedchain/docs/examples/chat-with-PDF.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,32 @@
|
||||
### Embedchain Chat with PDF App
|
||||
|
||||
You can easily create and deploy your own `chat-pdf` App using Embedchain.
|
||||
|
||||
Here are few simple steps for you to create and deploy your app:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Fork the embedchain repo from [Github](https://github.com/embedchain/embedchain).
|
||||
|
||||
<Note>
|
||||
If you run into problems with forking, please refer to [github docs](https://docs.github.com/en/pull-requests/collaborating-with-pull-requests/working-with-forks/fork-a-repo) for forking a repo.
|
||||
</Note>
|
||||
|
||||
2. Navigate to `chat-pdf` example app from your forked repo:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
cd <your_fork_repo>/examples/chat-pdf
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3. Run your app in development environment with simple commands
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install -r requirements.txt
|
||||
ec dev
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Feel free to improve our simple `chat-pdf` streamlit app and create pull request to showcase your app [here](https://docs.embedchain.ai/examples/showcase)
|
||||
|
||||
4. You can easily deploy your app using Streamlit interface
|
||||
|
||||
Connect your Github account with Streamlit and refer this [guide](https://docs.streamlit.io/streamlit-community-cloud/deploy-your-app) to deploy your app.
|
||||
|
||||
You can also use the deploy button from your streamlit website you see when running `ec dev` command.
|
||||
115
embedchain/docs/examples/community/showcase.mdx
Normal file
115
embedchain/docs/examples/community/showcase.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,115 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: '🎪 Community showcase'
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Embedchain community has been super active in creating demos on top of Embedchain. On this page, we showcase all the apps, blogs, videos, and tutorials created by the community. ❤️
|
||||
|
||||
## Apps
|
||||
|
||||
### Open Source
|
||||
|
||||
- [My GSoC23 bot- Streamlit chat](https://github.com/lucifertrj/EmbedChain_GSoC23_BOT) by Tarun Jain
|
||||
- [Discord Bot for LLM chat](https://github.com/Reidond/discord_bots_playground/tree/c8b0c36541e4b393782ee506804c4b6962426dd6/python/chat-channel-bot) by Reidond
|
||||
- [EmbedChain-Streamlit-Docker App](https://github.com/amjadraza/embedchain-streamlit-app) by amjadraza
|
||||
- [Harry Potter Philosphers Stone Bot](https://github.com/vinayak-kempawad/Harry_Potter_Philosphers_Stone_Bot/) by Vinayak Kempawad, ([LinkedIn post](https://www.linkedin.com/feed/update/urn:li:activity:7080907532155686912/))
|
||||
- [LLM bot trained on own messages](https://github.com/Harin329/harinBot) by Hao Wu
|
||||
|
||||
### Closed Source
|
||||
|
||||
- [Taobot.io](https://taobot.io) - chatbot & knowledgebase hybrid by [cachho](https://github.com/cachho)
|
||||
- [Create Instant ChatBot 🤖 using embedchain](https://databutton.com/v/h3e680h9) by Avra, ([Tweet](https://twitter.com/Avra_b/status/1674704745154641920/))
|
||||
- [JOBO 🤖 — The AI-driven sidekick to craft your resume](https://try-jobo.com/) by Enrico Willemse, ([LinkedIn Post](https://www.linkedin.com/posts/enrico-willemse_jobai-gptfun-embedchain-activity-7090340080879374336-ueLB/))
|
||||
- [Explore Your Knowledge Base: Interactive chats over various forms of documents](https://chatdocs.dkedar.com/) by Kedar Dabhadkar, ([LinkedIn Post](https://www.linkedin.com/posts/dkedar7_machinelearning-llmops-activity-7092524836639424513-2O3L/))
|
||||
- [Chatbot trained on 1000+ videos of Ester hicks the co-author behind the famous book Secret](https://ask-abraham.thoughtseed.repl.co) by Mohan Kumar
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Templates
|
||||
|
||||
### Replit
|
||||
- [Embedchain Chat Bot](https://replit.com/@taranjeet1/Embedchain-Chat-Bot) by taranjeetio
|
||||
- [Embedchain Memory Chat Bot Template](https://replit.com/@taranjeetio/Embedchain-Memory-Chat-Bot-Template) by taranjeetio
|
||||
- [Chatbot app to demonstrate question-answering using retrieved information](https://replit.com/@AllisonMorrell/EmbedChainlitPublic) by Allison Morrell, ([LinkedIn Post](https://www.linkedin.com/posts/allison-morrell-2889275a_retrievalbot-screenshots-activity-7080339991754649600-wihZ/))
|
||||
|
||||
## Posts
|
||||
|
||||
### Blogs
|
||||
|
||||
- [Customer Service LINE Bot](https://www.evanlin.com/langchain-embedchain/) by Evan Lin
|
||||
- [Chatbot in Under 5 mins using Embedchain](https://medium.com/@ayush.wattal/chatbot-in-under-5-mins-using-embedchain-a4f161fcf9c5) by Ayush Wattal
|
||||
- [Understanding what the LLM framework embedchain does](https://zenn.dev/hijikix/articles/4bc8d60156a436) by Daisuke Hashimoto
|
||||
- [In bed with GPT and Node.js](https://dev.to/worldlinetech/in-bed-with-gpt-and-nodejs-4kh2) by Raphaël Semeteys, ([LinkedIn Post](https://www.linkedin.com/posts/raphaelsemeteys_in-bed-with-gpt-and-nodejs-activity-7088113552326029313-nn87/))
|
||||
- [Using Embedchain — A powerful LangChain Python wrapper to build Chat Bots even faster!⚡](https://medium.com/@avra42/using-embedchain-a-powerful-langchain-python-wrapper-to-build-chat-bots-even-faster-35c12994a360) by Avra, ([Tweet](https://twitter.com/Avra_b/status/1686767751560310784/))
|
||||
- [What is the Embedchain library?](https://jahaniwww.com/%da%a9%d8%aa%d8%a7%d8%a8%d8%ae%d8%a7%d9%86%d9%87-embedchain/) by Ali Jahani, ([LinkedIn Post](https://www.linkedin.com/posts/ajahani_aepaetaeqaexaggahyaeu-aetaexaesabraeaaeqaepaeu-activity-7097605202135904256-ppU-/))
|
||||
- [LangChain is Nice, But Have You Tried EmbedChain ?](https://medium.com/thoughts-on-machine-learning/langchain-is-nice-but-have-you-tried-embedchain-215a34421cde) by FS Ndzomga, ([Tweet](https://twitter.com/ndzfs/status/1695583640372035951/))
|
||||
- [Simplest Method to Build a Custom Chatbot with GPT-3.5 (via Embedchain)](https://www.ainewsletter.today/p/simplest-method-to-build-a-custom) by Arjun, ([Tweet](https://twitter.com/aiguy_arjun/status/1696393808467091758/))
|
||||
|
||||
### LinkedIn
|
||||
|
||||
- [What is embedchain](https://www.linkedin.com/posts/activity-7079393104423698432-wRyi/) by Rithesh Sreenivasan
|
||||
- [Building a chatbot with EmbedChain](https://www.linkedin.com/posts/activity-7078434598984060928-Zdso/) by Lior Sinclair
|
||||
- [Making chatbot without vs with embedchain](https://www.linkedin.com/posts/kalyanksnlp_llms-chatbots-langchain-activity-7077453416221863936-7N1L/) by Kalyan KS
|
||||
- [EmbedChain - very intuitive, first you index your data and then query!](https://www.linkedin.com/posts/shubhamsaboo_embedchain-a-framework-to-easily-create-activity-7079535460699557888-ad1X/) by Shubham Saboo
|
||||
- [EmbedChain - Harnessing power of LLM](https://www.linkedin.com/posts/uditsaini_chatbotrevolution-llmpoweredbots-embedchainframework-activity-7077520356827181056-FjTK/) by Udit S.
|
||||
- [AI assistant for ABBYY Vantage](https://www.linkedin.com/posts/maximevermeir_llm-github-abbyy-activity-7081658972071424000-fXfZ/) by Maxime V.
|
||||
- [About embedchain](https://www.linkedin.com/feed/update/urn:li:activity:7080984218914189312/) by Morris Lee
|
||||
- [How to use Embedchain](https://www.linkedin.com/posts/nehaabansal_github-embedchainembedchain-framework-activity-7085830340136595456-kbW5/) by Neha Bansal
|
||||
- [Youtube/Webpage summary for Energy Study](https://www.linkedin.com/posts/bar%C4%B1%C5%9F-sanl%C4%B1-34b82715_enerji-python-activity-7082735341563977730-Js0U/) by Barış Sanlı, ([Tweet](https://twitter.com/barissanli/status/1676968784979193857/))
|
||||
- [Demo: How to use Embedchain? (Contains Collab Notebook link)](https://www.linkedin.com/posts/liorsinclair_embedchain-is-getting-a-lot-of-traction-because-activity-7103044695995424768-RckT/) by Lior Sinclair
|
||||
|
||||
### Twitter
|
||||
|
||||
- [What is embedchain](https://twitter.com/AlphaSignalAI/status/1672668574450847745) by Lior
|
||||
- [Building a chatbot with Embedchain](https://twitter.com/Saboo_Shubham_/status/1673537044419686401) by Shubham Saboo
|
||||
- [Chatbot docker image behind an API with yaml configs with Embedchain](https://twitter.com/tricalt/status/1678411430192730113/) by Vasilije
|
||||
- [Build AI powered PDF chatbot with just five lines of Python code with Embedchain!](https://twitter.com/Saboo_Shubham_/status/1676627104866156544/) by Shubham Saboo
|
||||
- [Chatbot against a youtube video using embedchain](https://twitter.com/smaameri/status/1675201443043704834/) by Sami Maameri
|
||||
- [Highlights of EmbedChain](https://twitter.com/carl_AIwarts/status/1673542204328120321/) by carl_AIwarts
|
||||
- [Build Llama-2 chatbot in less than 5 minutes](https://twitter.com/Saboo_Shubham_/status/1682168956918833152/) by Shubham Saboo
|
||||
- [All cool features of embedchain](https://twitter.com/DhravyaShah/status/1683497882438217728/) by Dhravya Shah, ([LinkedIn Post](https://www.linkedin.com/posts/dhravyashah_what-if-i-tell-you-that-you-can-make-an-ai-activity-7089459599287726080-ZIYm/))
|
||||
- [Read paid Medium articles for Free using embedchain](https://twitter.com/kumarkaushal_/status/1688952961622585344) by Kaushal Kumar
|
||||
|
||||
## Videos
|
||||
|
||||
- [Embedchain in one shot](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vIhDh7H73Ww&t=82s) by AI with Tarun
|
||||
- [embedChain Create LLM powered bots over any dataset Python Demo Tesla Neurallink Chatbot Example](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bJqAn22a6Gc) by Rithesh Sreenivasan
|
||||
- [Embedchain - NEW 🔥 Langchain BABY to build LLM Bots](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qj_GNQ06I8o) by 1littlecoder
|
||||
- [EmbedChain -- NEW!: Build LLM-Powered Bots with Any Dataset](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XmaBezzGHu4) by DataInsightEdge
|
||||
- [Chat With Your PDFs in less than 10 lines of code! EMBEDCHAIN tutorial](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1ugkcsAcw44) by Phani Reddy
|
||||
- [How To Create A Custom Knowledge AI Powered Bot | Install + How To Use](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VfCrIiAst-c) by The Ai Solopreneur
|
||||
- [Build Custom Chatbot in 6 min with this Framework [Beginner Friendly]](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-8HxOpaFySM) by Maya Akim
|
||||
- [embedchain-streamlit-app](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3-9GVd-3v74) by Amjad Raza
|
||||
- [🤖CHAT with ANY ONLINE RESOURCES using EMBEDCHAIN - a LangChain wrapper, in few lines of code !](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Mp7zJe4TIdM) by Avra
|
||||
- [Building resource-driven LLM-powered bots with Embedchain](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IVfcAgxTO4I) by BugBytes
|
||||
- [embedchain-streamlit-demo](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yJAWB13FhYQ) by Amjad Raza
|
||||
- [Embedchain - create your own AI chatbots using open source models](https://www.youtube.com/shorts/O3rJWKwSrWE) by Dhravya Shah
|
||||
- [AI ChatBot in 5 lines Python Code](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zjWvLJLksv8) by Data Engineering
|
||||
- [Interview with Karl Marx](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5Y4Tscwj1xk) by Alexander Ray Williams
|
||||
- [Vlog where we try to build a bot based on our content on the internet](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=I2w8CWM3bx4) by DV, ([Tweet](https://twitter.com/dvcoolster/status/1688387017544261632))
|
||||
- [CHAT with ANY ONLINE RESOURCES using EMBEDCHAIN|STREAMLIT with MEMORY |All OPENSOURCE](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TqQIHWoWTDQ&pp=ygUKZW1iZWRjaGFpbg%3D%3D) by DataInsightEdge
|
||||
- [Build POWERFUL LLM Bots EASILY with Your Own Data - Embedchain - Langchain 2.0? (Tutorial)](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jE24Y_GasE8) by WorldofAI, ([Tweet](https://twitter.com/intheworldofai/status/1696229166922780737))
|
||||
- [Embedchain: An AI knowledge base assistant for customizing enterprise private data, which can be connected to discord, whatsapp, slack, tele and other terminals (with gradio to build a request interface) in Chinese](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5RZzCJRk-d0) by AIGC LINK
|
||||
- [Embedchain Introduction](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Jet9zAqyggI) by Fahd Mirza
|
||||
|
||||
## Mentions
|
||||
|
||||
### Github repos
|
||||
|
||||
- [Awesome-LLM](https://github.com/Hannibal046/Awesome-LLM)
|
||||
- [awesome-chatgpt-api](https://github.com/reorx/awesome-chatgpt-api)
|
||||
- [awesome-langchain](https://github.com/kyrolabs/awesome-langchain)
|
||||
- [Awesome-Prompt-Engineering](https://github.com/promptslab/Awesome-Prompt-Engineering)
|
||||
- [awesome-chatgpt](https://github.com/eon01/awesome-chatgpt)
|
||||
- [Awesome-LLMOps](https://github.com/tensorchord/Awesome-LLMOps)
|
||||
- [awesome-generative-ai](https://github.com/filipecalegario/awesome-generative-ai)
|
||||
- [awesome-gpt](https://github.com/formulahendry/awesome-gpt)
|
||||
- [awesome-ChatGPT-repositories](https://github.com/taishi-i/awesome-ChatGPT-repositories)
|
||||
- [awesome-gpt-prompt-engineering](https://github.com/snwfdhmp/awesome-gpt-prompt-engineering)
|
||||
- [awesome-chatgpt](https://github.com/awesome-chatgpt/awesome-chatgpt)
|
||||
- [awesome-llm-and-aigc](https://github.com/sjinzh/awesome-llm-and-aigc)
|
||||
- [awesome-compbio-chatgpt](https://github.com/csbl-br/awesome-compbio-chatgpt)
|
||||
- [Awesome-LLM4Tool](https://github.com/OpenGVLab/Awesome-LLM4Tool)
|
||||
|
||||
## Meetups
|
||||
|
||||
- [Dash and ChatGPT: Future of AI-enabled apps 30/08/23](https://go.plotly.com/dash-chatgpt)
|
||||
- [Pie & AI: Bangalore - Build end-to-end LLM app using Embedchain 01/09/23](https://www.eventbrite.com/e/pie-ai-bangalore-build-end-to-end-llm-app-using-embedchain-tickets-698045722547)
|
||||
70
embedchain/docs/examples/discord_bot.mdx
Normal file
70
embedchain/docs/examples/discord_bot.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,70 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: "🤖 Discord Bot"
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
### 🔑 Keys Setup
|
||||
|
||||
- Set your `OPENAI_API_KEY` in your variables.env file.
|
||||
- Go to [https://discord.com/developers/applications/](https://discord.com/developers/applications/) and click on `New Application`.
|
||||
- Enter the name for your bot, accept the terms and click on `Create`. On the resulting page, enter the details of your bot as you like.
|
||||
- On the left sidebar, click on `Bot`. Under the heading `Privileged Gateway Intents`, toggle all 3 options to ON position. Save your changes.
|
||||
- Now click on `Reset Token` and copy the token value. Set it as `DISCORD_BOT_TOKEN` in .env file.
|
||||
- On the left sidebar, click on `OAuth2` and go to `General`.
|
||||
- Set `Authorization Method` to `In-app Authorization`. Under `Scopes` select `bot`.
|
||||
- Under `Bot Permissions` allow the following and then click on `Save Changes`.
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
Send Messages (under Text Permissions)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- Now under `OAuth2` and go to `URL Generator`. Under `Scopes` select `bot`.
|
||||
- Under `Bot Permissions` set the same permissions as above.
|
||||
- Now scroll down and copy the `Generated URL`. Paste it in a browser window and select the Server where you want to add the bot.
|
||||
- Click on `Continue` and authorize the bot.
|
||||
- 🎉 The bot has been successfully added to your server. But it's still offline.
|
||||
|
||||
### Take the bot online
|
||||
|
||||
<Tabs>
|
||||
<Tab title="docker">
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
docker run --name discord-bot -e OPENAI_API_KEY=sk-xxx -e DISCORD_BOT_TOKEN=xxx -p 8080:8080 embedchain/discord-bot:latest
|
||||
```
|
||||
</Tab>
|
||||
<Tab title="python">
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install --upgrade "embedchain[discord]"
|
||||
|
||||
python -m embedchain.bots.discord
|
||||
|
||||
# or if you prefer to see the question and not only the answer, run it with
|
||||
python -m embedchain.bots.discord --include-question
|
||||
```
|
||||
</Tab>
|
||||
</Tabs>
|
||||
|
||||
### 🚀 Usage Instructions
|
||||
|
||||
- Go to the server where you have added your bot.
|
||||
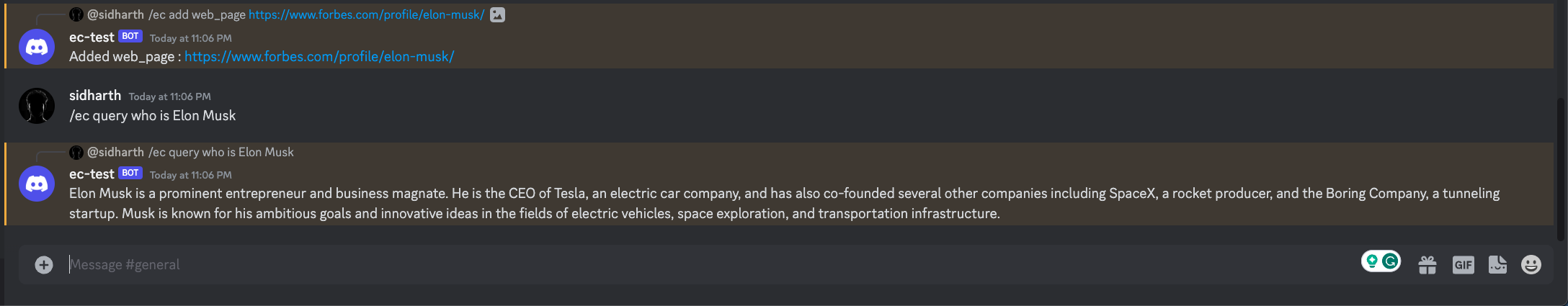
|
||||
- You can add data sources to the bot using the slash command:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
/ec add <data_type> <url_or_text>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- You can ask your queries from the bot using the slash command:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
/ec query <question>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- You can chat with the bot using the slash command:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
/ec chat <question>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
📝 Note: To use the bot privately, you can message the bot directly by right clicking the bot and selecting `Message`.
|
||||
|
||||
🎉 Happy Chatting! 🎉
|
||||
57
embedchain/docs/examples/full_stack.mdx
Normal file
57
embedchain/docs/examples/full_stack.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,57 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: 'Full Stack'
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
The Full Stack app example can be found [here](https://github.com/embedchain/embedchain/tree/main/examples/full_stack).
|
||||
|
||||
This guide will help you setup the full stack app on your local machine.
|
||||
|
||||
### 🐳 Docker Setup
|
||||
|
||||
- Create a `docker-compose.yml` file and paste the following code in it.
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
version: "3.9"
|
||||
|
||||
services:
|
||||
backend:
|
||||
container_name: embedchain-backend
|
||||
restart: unless-stopped
|
||||
build:
|
||||
context: backend
|
||||
dockerfile: Dockerfile
|
||||
image: embedchain/backend
|
||||
ports:
|
||||
- "8000:8000"
|
||||
|
||||
frontend:
|
||||
container_name: embedchain-frontend
|
||||
restart: unless-stopped
|
||||
build:
|
||||
context: frontend
|
||||
dockerfile: Dockerfile
|
||||
image: embedchain/frontend
|
||||
ports:
|
||||
- "3000:3000"
|
||||
depends_on:
|
||||
- "backend"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- Run the following command,
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
docker-compose up
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
📝 Note: The build command might take a while to install all the packages depending on your system resources.
|
||||
|
||||
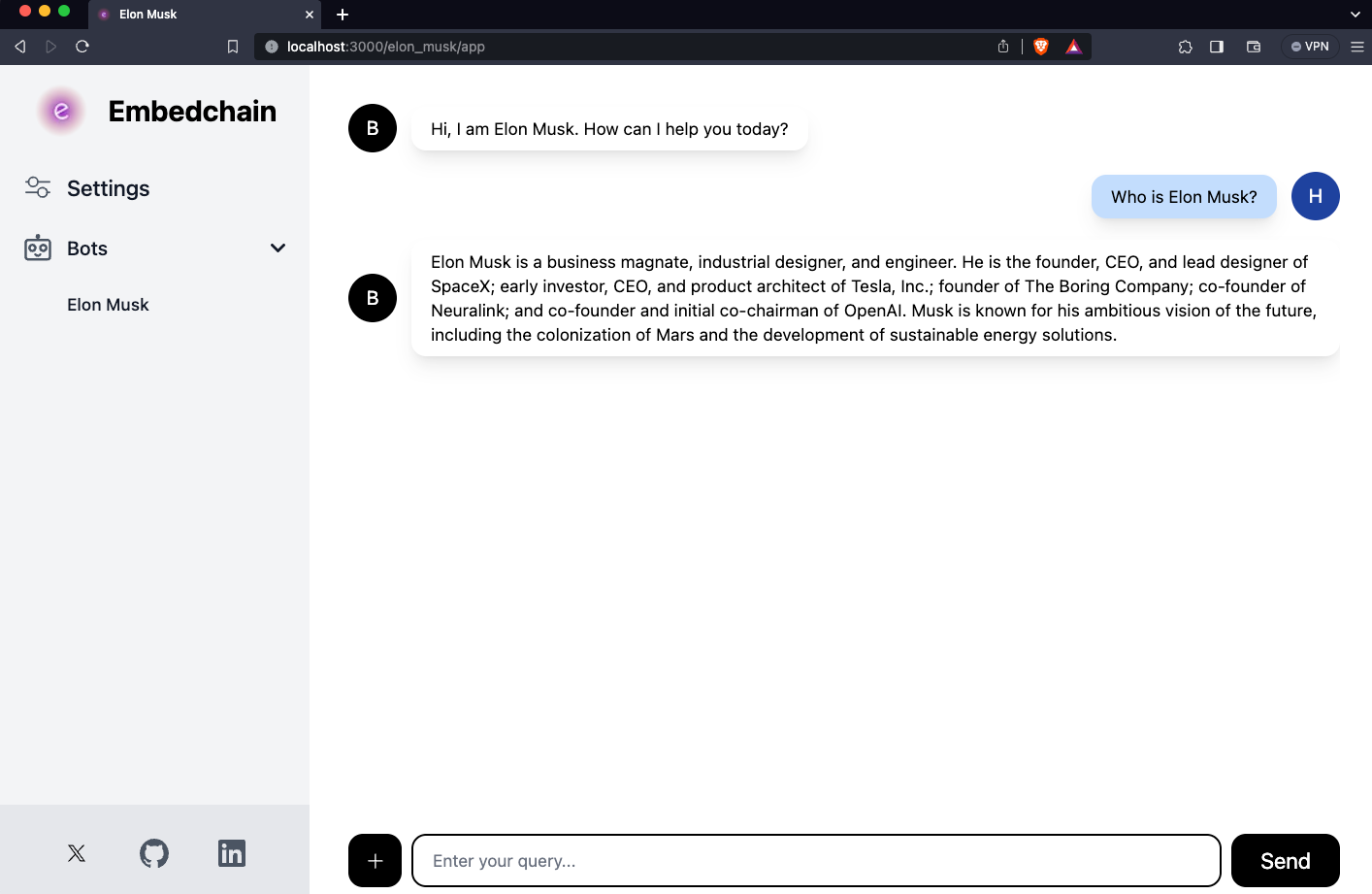
|
||||
|
||||
### 🚀 Usage Instructions
|
||||
|
||||
- Go to [http://localhost:3000/](http://localhost:3000/) in your browser to view the dashboard.
|
||||
- Add your `OpenAI API key` 🔑 in the Settings.
|
||||
- Create a new bot and you'll be navigated to its page.
|
||||
- Here you can add your data sources and then chat with the bot.
|
||||
|
||||
🎉 Happy Chatting! 🎉
|
||||
124
embedchain/docs/examples/nextjs-assistant.mdx
Normal file
124
embedchain/docs/examples/nextjs-assistant.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,124 @@
|
||||
Fork the Embedchain repo on [Github](https://github.com/embedchain/embedchain) to create your own NextJS discord and slack bot powered by Embedchain.
|
||||
|
||||
If you run into problems with forking, please refer to [github docs](https://docs.github.com/en/pull-requests/collaborating-with-pull-requests/working-with-forks/fork-a-repo) for forking a repo.
|
||||
|
||||
We will work from the `examples/nextjs` folder so change your current working directory by running the command - `cd <your_forked_repo>/examples/nextjs`
|
||||
|
||||
# Installation
|
||||
|
||||
First, lets start by install all the required packages and dependencies.
|
||||
|
||||
- Install all the required python packages by running ```pip install -r requirements.txt```
|
||||
|
||||
- We will use [Fly.io](https://fly.io/) to deploy our embedchain app, discord and slack bot. Follow the step one to install [Fly.io CLI](https://docs.embedchain.ai/deployment/fly_io#step-1-install-flyctl-command-line)
|
||||
|
||||
# Developement
|
||||
|
||||
## Embedchain App
|
||||
|
||||
First, we need an Embedchain app powered with the knowledge of NextJS. We have already created an embedchain app using FastAPI in `ec_app` folder for you. Feel free to ingest data of your choice to power the App.
|
||||
|
||||
<Note>
|
||||
Navigate to `ec_app` folder and create `.env` file in this folder and set your OpenAI API key as shown in `.env.example` file. If you want to use other open-source models, feel free to use the app config in `app.py`. More details for using custom configuration for Embedchain app is [available here](https://docs.embedchain.ai/api-reference/advanced/configuration).
|
||||
</Note>
|
||||
|
||||
Before running the ec commands to develope the app, open `fly.toml` file and update the `name` variable to something unique. This is important as `fly.io` requires users to provide a globally unique deployment app names.
|
||||
|
||||
Now, we need to launch this application with fly.io. You can see your app on [fly.io dashboard](https://fly.io/dashboard). Run the following command to launch your app on fly.io:
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
fly launch --no-deploy
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
To run the app in development, run the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
ec dev
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Run `ec deploy` to deploy your app on Fly.io. Once you deploy your app, save the endpoint on which our discord and slack bot will send requests.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Discord bot
|
||||
|
||||
For discord bot, you will need to create the bot on discord developer portal and get the discord bot token and your discord bot name.
|
||||
|
||||
While keeping in mind the following note, create the discord bot by following the instructions from our [discord bot docs](https://docs.embedchain.ai/examples/discord_bot) and get discord bot token.
|
||||
|
||||
<Note>
|
||||
You do not need to set `OPENAI_API_KEY` to run this discord bot. Follow the remaining instructions to create a discord bot app. We recommend you to give the following sets of bot permissions to run the discord bot without errors:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
(General Permissions)
|
||||
Read Message/View Channels
|
||||
|
||||
(Text Permissions)
|
||||
Send Messages
|
||||
Create Public Thread
|
||||
Create Private Thread
|
||||
Send Messages in Thread
|
||||
Manage Threads
|
||||
Embed Links
|
||||
Read Message History
|
||||
```
|
||||
</Note>
|
||||
|
||||
Once you have your discord bot token and discord app name. Navigate to `nextjs_discord` folder and create `.env` file and define your discord bot token, discord bot name and endpoint of your embedchain app as shown in `.env.example` file.
|
||||
|
||||
To run the app in development:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python app.py
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Before deploying the app, open `fly.toml` file and update the `name` variable to something unique. This is important as `fly.io` requires users to provide a globally unique deployment app names.
|
||||
|
||||
Now, we need to launch this application with fly.io. You can see your app on [fly.io dashboard](https://fly.io/dashboard). Run the following command to launch your app on fly.io:
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
fly launch --no-deploy
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Run `ec deploy` to deploy your app on Fly.io. Once you deploy your app, your discord bot will be live!
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Slack bot
|
||||
|
||||
For Slack bot, you will need to create the bot on slack developer portal and get the slack bot token and slack app token.
|
||||
|
||||
### Setup
|
||||
|
||||
- Create a workspace on Slack if you don't have one already by clicking [here](https://slack.com/intl/en-in/).
|
||||
- Create a new App on your Slack account by going [here](https://api.slack.com/apps).
|
||||
- Select `From Scratch`, then enter the Bot Name and select your workspace.
|
||||
- Go to `App Credentials` section on the `Basic Information` tab from the left sidebar, create your app token and save it in your `.env` file as `SLACK_APP_TOKEN`.
|
||||
- Go to `Socket Mode` tab from the left sidebar and enable the socket mode to listen to slack message from your workspace.
|
||||
- (Optional) Under the `App Home` tab you can change your App display name and default name.
|
||||
- Navigate to `Event Subscription` tab, and enable the event subscription so that we can listen to slack events.
|
||||
- Once you enable the event subscription, you will need to subscribe to bot events to authorize the bot to listen to app mention events of the bot. Do that by tapping on `Add Bot User Event` button and select `app_mention`.
|
||||
- On the left Sidebar, go to `OAuth and Permissions` and add the following scopes under `Bot Token Scopes`:
|
||||
```text
|
||||
app_mentions:read
|
||||
channels:history
|
||||
channels:read
|
||||
chat:write
|
||||
emoji:read
|
||||
reactions:write
|
||||
reactions:read
|
||||
```
|
||||
- Now select the option `Install to Workspace` and after it's done, copy the `Bot User OAuth Token` and set it in your `.env` file as `SLACK_BOT_TOKEN`.
|
||||
|
||||
Once you have your slack bot token and slack app token. Navigate to `nextjs_slack` folder and create `.env` file and define your slack bot token, slack app token and endpoint of your embedchain app as shown in `.env.example` file.
|
||||
|
||||
To run the app in development:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python app.py
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Before deploying the app, open `fly.toml` file and update the `name` variable to something unique. This is important as `fly.io` requires users to provide a globally unique deployment app names.
|
||||
|
||||
Now, we need to launch this application with fly.io. You can see your app on [fly.io dashboard](https://fly.io/dashboard). Run the following command to launch your app on fly.io:
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
fly launch --no-deploy
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Run `ec deploy` to deploy your app on Fly.io. Once you deploy your app, your slack bot will be live!
|
||||
138
embedchain/docs/examples/notebooks-and-replits.mdx
Normal file
138
embedchain/docs/examples/notebooks-and-replits.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,138 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Notebooks & Replits
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# Explore awesome apps
|
||||
|
||||
Check out the remarkable work accomplished using [Embedchain](https://app.embedchain.ai/custom-gpts/).
|
||||
|
||||
## Collection of Google colab notebook and Replit links for users
|
||||
|
||||
Get started with Embedchain by trying out the examples below. You can run the examples in your browser using Google Colab or Replit.
|
||||
|
||||
<table>
|
||||
<thead>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<th>LLM</th>
|
||||
<th>Google Colab</th>
|
||||
<th>Replit</th>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</thead>
|
||||
<tbody>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td className="align-middle">OpenAI</td>
|
||||
<td className="align-middle"><a target="_blank" href="https://colab.research.google.com/github/embedchain/embedchain/blob/main/notebooks/openai.ipynb"><img src="https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg" noZoom alt="Open In Colab"/></a></td>
|
||||
<td className="align-middle"><a target="_blank" href="https://replit.com/@taranjeetio/openai#main.py"><img src="https://replit.com/badge?caption=Try%20with%20Replit&variant=small" noZoom alt="Try with Replit Badge"/></a></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td className="align-middle">Anthropic</td>
|
||||
<td className="align-middle"><a target="_blank" href="https://colab.research.google.com/github/embedchain/embedchain/blob/main/notebooks/anthropic.ipynb"><img src="https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg" noZoom alt="Open In Colab"/></a></td>
|
||||
<td className="align-middle"><a target="_blank" href="https://replit.com/@taranjeetio/anthropic#main.py"><img src="https://replit.com/badge?caption=Try%20with%20Replit&variant=small" noZoom alt="Try with Replit Badge"/></a></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td className="align-middle">Azure OpenAI</td>
|
||||
<td className="align-middle"><a target="_blank" href="https://colab.research.google.com/github/embedchain/embedchain/blob/main/notebooks/azure-openai.ipynb"><img src="https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg" noZoom alt="Open In Colab"/></a></td>
|
||||
<td className="align-middle"><a target="_blank" href="https://replit.com/@taranjeetio/azureopenai#main.py"><img src="https://replit.com/badge?caption=Try%20with%20Replit&variant=small" noZoom alt="Try with Replit Badge"/></a></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td className="align-middle">VertexAI</td>
|
||||
<td className="align-middle"><a target="_blank" href="https://colab.research.google.com/github/embedchain/embedchain/blob/main/notebooks/vertex_ai.ipynb"><img src="https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg" noZoom alt="Open In Colab"/></a></td>
|
||||
<td className="align-middle"><a target="_blank" href="https://replit.com/@taranjeetio/vertexai#main.py"><img src="https://replit.com/badge?caption=Try%20with%20Replit&variant=small" noZoom alt="Try with Replit Badge"/></a></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td className="align-middle">Cohere</td>
|
||||
<td className="align-middle"><a target="_blank" href="https://colab.research.google.com/github/embedchain/embedchain/blob/main/notebooks/cohere.ipynb"><img src="https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg" noZoom alt="Open In Colab"/></a></td>
|
||||
<td className="align-middle"><a target="_blank" href="https://replit.com/@taranjeetio/cohere#main.py"><img src="https://replit.com/badge?caption=Try%20with%20Replit&variant=small" noZoom alt="Try with Replit Badge"/></a></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td className="align-middle">Together</td>
|
||||
<td className="align-middle"><a target="_blank" href="https://colab.research.google.com/github/embedchain/embedchain/blob/main/notebooks/together.ipynb"><img src="https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg" noZoom alt="Open In Colab"/></a></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td className="align-middle">Ollama</td>
|
||||
<td className="align-middle"><a target="_blank" href="https://colab.research.google.com/github/embedchain/embedchain/blob/main/notebooks/ollama.ipynb"><img src="https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg" noZoom alt="Open In Colab"/></a></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td className="align-middle">Hugging Face</td>
|
||||
<td className="align-middle"><a target="_blank" href="https://colab.research.google.com/github/embedchain/embedchain/blob/main/notebooks/hugging_face_hub.ipynb"><img src="https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg" noZoom alt="Open In Colab"/></a></td>
|
||||
<td className="align-middle"><a target="_blank" href="https://replit.com/@taranjeetio/huggingface#main.py"><img src="https://replit.com/badge?caption=Try%20with%20Replit&variant=small" noZoom alt="Try with Replit Badge"/></a></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td className="align-middle">JinaChat</td>
|
||||
<td className="align-middle"><a target="_blank" href="https://colab.research.google.com/github/embedchain/embedchain/blob/main/notebooks/jina.ipynb"><img src="https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg" noZoom alt="Open In Colab"/></a></td>
|
||||
<td className="align-middle"><a target="_blank" href="https://replit.com/@taranjeetio/jina#main.py"><img src="https://replit.com/badge?caption=Try%20with%20Replit&variant=small" noZoom alt="Try with Replit Badge"/></a></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td className="align-middle">GPT4All</td>
|
||||
<td className="align-middle"><a target="_blank" href="https://colab.research.google.com/github/embedchain/embedchain/blob/main/notebooks/gpt4all.ipynb"><img src="https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg" noZoom alt="Open In Colab"/></a></td>
|
||||
<td className="align-middle"><a target="_blank" href="https://replit.com/@taranjeetio/gpt4all#main.py"><img src="https://replit.com/badge?caption=Try%20with%20Replit&variant=small" noZoom alt="Try with Replit Badge"/></a></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td className="align-middle">Llama2</td>
|
||||
<td className="align-middle"><a target="_blank" href="https://colab.research.google.com/github/embedchain/embedchain/blob/main/notebooks/llama2.ipynb"><img src="https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg" noZoom alt="Open In Colab"/></a></td>
|
||||
<td className="align-middle"><a target="_blank" href="https://replit.com/@taranjeetio/llama2#main.py"><img src="https://replit.com/badge?caption=Try%20with%20Replit&variant=small" noZoom alt="Try with Replit Badge"/></a></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</tbody>
|
||||
</table>
|
||||
<table>
|
||||
<thead>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<th>Embedding model</th>
|
||||
<th>Google Colab</th>
|
||||
<th>Replit</th>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</thead>
|
||||
<tbody>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td className="align-middle">OpenAI</td>
|
||||
<td className="align-middle"><a target="_blank" href="https://colab.research.google.com/github/embedchain/embedchain/blob/main/notebooks/openai.ipynb"><img src="https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg" noZoom alt="Open In Colab"/></a></td>
|
||||
<td className="align-middle"><a target="_blank" href="https://replit.com/@taranjeetio/openai#main.py"><img src="https://replit.com/badge?caption=Try%20with%20Replit&variant=small" noZoom alt="Try with Replit Badge"/></a></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td className="align-middle">VertexAI</td>
|
||||
<td className="align-middle"><a target="_blank" href="https://colab.research.google.com/github/embedchain/embedchain/blob/main/notebooks/vertex_ai.ipynb"><img src="https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg" noZoom alt="Open In Colab"/></a></td>
|
||||
<td className="align-middle"><a target="_blank" href="https://replit.com/@taranjeetio/vertexai#main.py"><img src="https://replit.com/badge?caption=Try%20with%20Replit&variant=small" noZoom alt="Try with Replit Badge"/></a></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td className="align-middle">GPT4All</td>
|
||||
<td className="align-middle"><a target="_blank" href="https://colab.research.google.com/github/embedchain/embedchain/blob/main/notebooks/gpt4all.ipynb"><img src="https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg" noZoom alt="Open In Colab"/></a></td>
|
||||
<td className="align-middle"><a target="_blank" href="https://replit.com/@taranjeetio/gpt4all#main.py"><img src="https://replit.com/badge?caption=Try%20with%20Replit&variant=small" noZoom alt="Try with Replit Badge"/></a></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td className="align-middle">Hugging Face</td>
|
||||
<td className="align-middle"><a target="_blank" href="https://colab.research.google.com/github/embedchain/embedchain/blob/main/notebooks/hugging_face_hub.ipynb"><img src="https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg" noZoom alt="Open In Colab"/></a></td>
|
||||
<td className="align-middle"><a target="_blank" href="https://replit.com/@taranjeetio/huggingface#main.py"><img src="https://replit.com/badge?caption=Try%20with%20Replit&variant=small" noZoom alt="Try with Replit Badge"/></a></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</tbody>
|
||||
</table>
|
||||
<table>
|
||||
<thead>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<th>Vector DB</th>
|
||||
<th>Google Colab</th>
|
||||
<th>Replit</th>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</thead>
|
||||
<tbody>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td className="align-middle">ChromaDB</td>
|
||||
<td className="align-middle"><a target="_blank" href="https://colab.research.google.com/github/embedchain/embedchain/blob/main/notebooks/chromadb.ipynb"><img src="https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg" noZoom alt="Open In Colab"/></a></td>
|
||||
<td className="align-middle"><a target="_blank" href="https://replit.com/@taranjeetio/chromadb#main.py"><img src="https://replit.com/badge?caption=Try%20with%20Replit&variant=small" noZoom alt="Try with Replit Badge"/></a></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td className="align-middle">Elasticsearch</td>
|
||||
<td className="align-middle"><a target="_blank" href="https://colab.research.google.com/github/embedchain/embedchain/blob/main/notebooks/elasticsearch.ipynb"><img src="https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg" noZoom alt="Open In Colab"/></a></td>
|
||||
<td className="align-middle"><a target="_blank" href="https://replit.com/@taranjeetio/elasticsearchdb#main.py"><img src="https://replit.com/badge?caption=Try%20with%20Replit&variant=small" noZoom alt="Try with Replit Badge"/></a></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td className="align-middle">Opensearch</td>
|
||||
<td className="align-middle"><a target="_blank" href="https://colab.research.google.com/github/embedchain/embedchain/blob/main/notebooks/opensearch.ipynb"><img src="https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg" noZoom alt="Open In Colab"/></a></td>
|
||||
<td className="align-middle"><a target="_blank" href="https://replit.com/@taranjeetio/opensearchdb#main.py"><img src="https://replit.com/badge?caption=Try%20with%20Replit&variant=small" noZoom alt="Try with Replit Badge"/></a></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td className="align-middle">Pinecone</td>
|
||||
<td className="align-middle"><a target="_blank" href="https://colab.research.google.com/github/embedchain/embedchain/blob/main/notebooks/pinecone.ipynb"><img src="https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg" noZoom alt="Open In Colab"/></a></td>
|
||||
<td className="align-middle"><a target="_blank" href="https://replit.com/@taranjeetio/pineconedb#main.py"><img src="https://replit.com/badge?caption=Try%20with%20Replit&variant=small" noZoom alt="Try with Replit Badge"/></a></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</tbody>
|
||||
</table>
|
||||
60
embedchain/docs/examples/openai-assistant.mdx
Normal file
60
embedchain/docs/examples/openai-assistant.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,60 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: 'OpenAI Assistant'
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://blogs.swarthmore.edu/its/wp-content/uploads/2022/05/openai.jpg" align="center" width="500" alt="OpenAI Logo"/>
|
||||
|
||||
Embedchain now supports [OpenAI Assistants API](https://platform.openai.com/docs/assistants/overview) which allows you to build AI assistants within your own applications. An Assistant has instructions and can leverage models, tools, and knowledge to respond to user queries.
|
||||
|
||||
At a high level, an integration of the Assistants API has the following flow:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Create an Assistant in the API by defining custom instructions and picking a model
|
||||
2. Create a Thread when a user starts a conversation
|
||||
3. Add Messages to the Thread as the user ask questions
|
||||
4. Run the Assistant on the Thread to trigger responses. This automatically calls the relevant tools.
|
||||
|
||||
Creating an OpenAI Assistant using Embedchain is very simple 3 step process.
|
||||
|
||||
## Step 1: Create OpenAI Assistant
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure that you have `OPENAI_API_KEY` set in the environment variable.
|
||||
|
||||
```python Initialize
|
||||
from embedchain.store.assistants import OpenAIAssistant
|
||||
|
||||
assistant = OpenAIAssistant(
|
||||
name="OpenAI DevDay Assistant",
|
||||
instructions="You are an organizer of OpenAI DevDay",
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to use the existing assistant, you can do something like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```python Initialize
|
||||
# Load an assistant and create a new thread
|
||||
assistant = OpenAIAssistant(assistant_id="asst_xxx")
|
||||
|
||||
# Load a specific thread for an assistant
|
||||
assistant = OpenAIAssistant(assistant_id="asst_xxx", thread_id="thread_xxx")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Step-2: Add data to thread
|
||||
|
||||
You can add any custom data source that is supported by Embedchain. Else, you can directly pass the file path on your local system and Embedchain propagates it to OpenAI Assistant.
|
||||
```python Add data
|
||||
assistant.add("/path/to/file.pdf")
|
||||
assistant.add("https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=U9mJuUkhUzk")
|
||||
assistant.add("https://openai.com/blog/new-models-and-developer-products-announced-at-devday")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Step-3: Chat with your Assistant
|
||||
```python Chat
|
||||
assistant.chat("How much OpenAI credits were offered to attendees during OpenAI DevDay?")
|
||||
# Response: 'Every attendee of OpenAI DevDay 2023 was offered $500 in OpenAI credits.'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can try it out yourself using the following Google Colab notebook:
|
||||
|
||||
<a href="https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1BKlXZYSl6AFRgiHZ5XIzXrXC_24kDYHQ?usp=sharing">
|
||||
<img src="https://camo.githubusercontent.com/84f0493939e0c4de4e6dbe113251b4bfb5353e57134ffd9fcab6b8714514d4d1/68747470733a2f2f636f6c61622e72657365617263682e676f6f676c652e636f6d2f6173736574732f636f6c61622d62616467652e737667" alt="Open in Colab" />
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
51
embedchain/docs/examples/opensource-assistant.mdx
Normal file
51
embedchain/docs/examples/opensource-assistant.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,51 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: 'Open-Source AI Assistant'
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Embedchain also provides support for creating Open-Source AI Assistants (similar to [OpenAI Assistants API](https://platform.openai.com/docs/assistants/overview)) which allows you to build AI assistants within your own applications using any LLM (OpenAI or otherwise). An Assistant has instructions and can leverage models, tools, and knowledge to respond to user queries.
|
||||
|
||||
At a high level, the Open-Source AI Assistants API has the following flow:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Create an AI Assistant by picking a model
|
||||
2. Create a Thread when a user starts a conversation
|
||||
3. Add Messages to the Thread as the user ask questions
|
||||
4. Run the Assistant on the Thread to trigger responses. This automatically calls the relevant tools.
|
||||
|
||||
Creating an Open-Source AI Assistant is a simple 3 step process.
|
||||
|
||||
## Step 1: Instantiate AI Assistant
|
||||
|
||||
```python Initialize
|
||||
from embedchain.store.assistants import AIAssistant
|
||||
|
||||
assistant = AIAssistant(
|
||||
name="My Assistant",
|
||||
data_sources=[{"source": "https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=U9mJuUkhUzk"}])
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to use the existing assistant, you can do something like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```python Initialize
|
||||
# Load an assistant and create a new thread
|
||||
assistant = AIAssistant(assistant_id="asst_xxx")
|
||||
|
||||
# Load a specific thread for an assistant
|
||||
assistant = AIAssistant(assistant_id="asst_xxx", thread_id="thread_xxx")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Step-2: Add data to thread
|
||||
|
||||
You can add any custom data source that is supported by Embedchain. Else, you can directly pass the file path on your local system and Embedchain propagates it to OpenAI Assistant.
|
||||
|
||||
```python Add data
|
||||
assistant.add("/path/to/file.pdf")
|
||||
assistant.add("https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=U9mJuUkhUzk")
|
||||
assistant.add("https://openai.com/blog/new-models-and-developer-products-announced-at-devday")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Step-3: Chat with your AI Assistant
|
||||
|
||||
```python Chat
|
||||
assistant.chat("How much OpenAI credits were offered to attendees during OpenAI DevDay?")
|
||||
# Response: 'Every attendee of OpenAI DevDay 2023 was offered $500 in OpenAI credits.'
|
||||
```
|
||||
59
embedchain/docs/examples/poe_bot.mdx
Normal file
59
embedchain/docs/examples/poe_bot.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,59 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: '🔮 Poe Bot'
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
### 🚀 Getting started
|
||||
|
||||
1. Install embedchain python package:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install fastapi-poe==0.0.16
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. Create a free account on [Poe](https://www.poe.com?utm_source=embedchain).
|
||||
3. Click "Create Bot" button on top left.
|
||||
4. Give it a handle and an optional description.
|
||||
5. Select `Use API`.
|
||||
6. Under `API URL` enter your server or ngrok address. You can use your machine's public IP or DNS. Otherwise, employ a proxy server like [ngrok](https://ngrok.com/) to make your local bot accessible.
|
||||
7. Copy your api key and paste it in `.env` as `POE_API_KEY`.
|
||||
8. You will need to set `OPENAI_API_KEY` for generating embeddings and using LLM. Copy your OpenAI API key from [here](https://platform.openai.com/account/api-keys) and paste it in `.env` as `OPENAI_API_KEY`.
|
||||
9. Now create your bot using the following code snippet.
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# make sure that you have set OPENAI_API_KEY and POE_API_KEY in .env file
|
||||
from embedchain.bots import PoeBot
|
||||
|
||||
poe_bot = PoeBot()
|
||||
|
||||
# add as many data sources as you want
|
||||
poe_bot.add("https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Adam_D%27Angelo")
|
||||
poe_bot.add("https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pJQVAqmKua8")
|
||||
|
||||
# start the bot
|
||||
# this start the poe bot server on port 8080 by default
|
||||
poe_bot.start()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
10. You can paste the above in a file called `your_script.py` and then simply do
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python your_script.py
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now your bot will start running at port `8080` by default.
|
||||
|
||||
11. You can refer the [Supported Data formats](https://docs.embedchain.ai/advanced/data_types) section to refer the supported data types in embedchain.
|
||||
|
||||
12. Click `Run check` to make sure your machine can be reached.
|
||||
13. Make sure your bot is private if that's what you want.
|
||||
14. Click `Create bot` at the bottom to finally create the bot
|
||||
15. Now your bot is created.
|
||||
|
||||
### 💬 How to use
|
||||
|
||||
- To ask the bot questions, just type your query in the Poe interface:
|
||||
```text
|
||||
<your-question-here>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- If you wish to add more data source to the bot, simply update your script and add as many `.add` as you like. You need to restart the server.
|
||||
22
embedchain/docs/examples/rest-api/add-data.mdx
Normal file
22
embedchain/docs/examples/rest-api/add-data.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,22 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
openapi: post /{app_id}/add
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<RequestExample>
|
||||
|
||||
```bash Request
|
||||
curl --request POST \
|
||||
--url http://localhost:8080/{app_id}/add \
|
||||
-d "source=https://www.forbes.com/profile/elon-musk" \
|
||||
-d "data_type=web_page"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</RequestExample>
|
||||
|
||||
<ResponseExample>
|
||||
|
||||
```json Response
|
||||
{ "response": "fec7fe91e6b2d732938a2ec2e32bfe3f" }
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</ResponseExample>
|
||||
3
embedchain/docs/examples/rest-api/chat.mdx
Normal file
3
embedchain/docs/examples/rest-api/chat.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,3 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
openapi: post /{app_id}/chat
|
||||
---
|
||||
20
embedchain/docs/examples/rest-api/check-status.mdx
Normal file
20
embedchain/docs/examples/rest-api/check-status.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,20 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
openapi: get /ping
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<RequestExample>
|
||||
|
||||
```bash Request
|
||||
curl --request GET \
|
||||
--url http://localhost:8080/ping
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</RequestExample>
|
||||
|
||||
<ResponseExample>
|
||||
|
||||
```json Response
|
||||
{ "ping": "pong" }
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</ResponseExample>
|
||||
96
embedchain/docs/examples/rest-api/create.mdx
Normal file
96
embedchain/docs/examples/rest-api/create.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,96 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
openapi: post /create
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<RequestExample>
|
||||
|
||||
```bash Request
|
||||
curl --request POST \
|
||||
--url http://localhost:8080/create?app_id=app1 \
|
||||
-F "config=@/path/to/config.yaml"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</RequestExample>
|
||||
|
||||
<ResponseExample>
|
||||
|
||||
```json Response
|
||||
{ "response": "App created successfully. App ID: app1" }
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</ResponseExample>
|
||||
|
||||
By default we will use the opensource **gpt4all** model to get started. You can also specify your own config by uploading a config YAML file.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, create a `config.yaml` file (adjust according to your requirements):
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
app:
|
||||
config:
|
||||
id: "default-app"
|
||||
|
||||
llm:
|
||||
provider: openai
|
||||
config:
|
||||
model: "gpt-3.5-turbo"
|
||||
temperature: 0.5
|
||||
max_tokens: 1000
|
||||
top_p: 1
|
||||
stream: false
|
||||
prompt: |
|
||||
Use the following pieces of context to answer the query at the end.
|
||||
If you don't know the answer, just say that you don't know, don't try to make up an answer.
|
||||
|
||||
$context
|
||||
|
||||
Query: $query
|
||||
|
||||
Helpful Answer:
|
||||
|
||||
vectordb:
|
||||
provider: chroma
|
||||
config:
|
||||
collection_name: "rest-api-app"
|
||||
dir: db
|
||||
allow_reset: true
|
||||
|
||||
embedder:
|
||||
provider: openai
|
||||
config:
|
||||
model: "text-embedding-ada-002"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
To learn more about custom configurations, check out the [custom configurations docs](https://docs.embedchain.ai/advanced/configuration). To explore more examples of config yamls for embedchain, visit [embedchain/configs](https://github.com/embedchain/embedchain/tree/main/configs).
|
||||
|
||||
Now, you can upload this config file in the request body.
|
||||
|
||||
For example,
|
||||
|
||||
```bash Request
|
||||
curl --request POST \
|
||||
--url http://localhost:8080/create?app_id=my-app \
|
||||
-F "config=@/path/to/config.yaml"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Note:** To use custom models, an **API key** might be required. Refer to the table below to determine the necessary API key for your provider.
|
||||
|
||||
| Keys | Providers |
|
||||
| -------------------------- | ------------------------------ |
|
||||
| `OPENAI_API_KEY ` | OpenAI, Azure OpenAI, Jina etc |
|
||||
| `OPENAI_API_TYPE` | Azure OpenAI |
|
||||
| `OPENAI_API_BASE` | Azure OpenAI |
|
||||
| `OPENAI_API_VERSION` | Azure OpenAI |
|
||||
| `COHERE_API_KEY` | Cohere |
|
||||
| `TOGETHER_API_KEY` | Together |
|
||||
| `ANTHROPIC_API_KEY` | Anthropic |
|
||||
| `JINACHAT_API_KEY` | Jina |
|
||||
| `HUGGINGFACE_ACCESS_TOKEN` | Huggingface |
|
||||
| `REPLICATE_API_TOKEN` | LLAMA2 |
|
||||
|
||||
To add env variables, you can simply run the docker command with the `-e` flag.
|
||||
|
||||
For example,
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
docker run --name embedchain -p 8080:8080 -e OPENAI_API_KEY=<YOUR_OPENAI_API_KEY> embedchain/rest-api:latest
|
||||
```
|
||||
21
embedchain/docs/examples/rest-api/delete.mdx
Normal file
21
embedchain/docs/examples/rest-api/delete.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,21 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
openapi: delete /{app_id}/delete
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<RequestExample>
|
||||
|
||||
```bash Request
|
||||
curl --request DELETE \
|
||||
--url http://localhost:8080/{app_id}/delete
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</RequestExample>
|
||||
|
||||
<ResponseExample>
|
||||
|
||||
```json Response
|
||||
{ "response": "App with id {app_id} deleted successfully." }
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</ResponseExample>
|
||||
22
embedchain/docs/examples/rest-api/deploy.mdx
Normal file
22
embedchain/docs/examples/rest-api/deploy.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,22 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
openapi: post /{app_id}/deploy
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<RequestExample>
|
||||
|
||||
```bash Request
|
||||
curl --request POST \
|
||||
--url http://localhost:8080/{app_id}/deploy \
|
||||
-d "api_key=ec-xxxx"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</RequestExample>
|
||||
|
||||
<ResponseExample>
|
||||
|
||||
```json Response
|
||||
{ "response": "App deployed successfully." }
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</ResponseExample>
|
||||
33
embedchain/docs/examples/rest-api/get-all-apps.mdx
Normal file
33
embedchain/docs/examples/rest-api/get-all-apps.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,33 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
openapi: get /apps
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<RequestExample>
|
||||
|
||||
```bash Request
|
||||
curl --request GET \
|
||||
--url http://localhost:8080/apps
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</RequestExample>
|
||||
|
||||
<ResponseExample>
|
||||
|
||||
```json Response
|
||||
{
|
||||
"results": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"config": "config1.yaml",
|
||||
"id": 1,
|
||||
"app_id": "app1"
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"config": "config2.yaml",
|
||||
"id": 2,
|
||||
"app_id": "app2"
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</ResponseExample>
|
||||
28
embedchain/docs/examples/rest-api/get-data.mdx
Normal file
28
embedchain/docs/examples/rest-api/get-data.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,28 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
openapi: get /{app_id}/data
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<RequestExample>
|
||||
|
||||
```bash Request
|
||||
curl --request GET \
|
||||
--url http://localhost:8080/{app_id}/data
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</RequestExample>
|
||||
|
||||
<ResponseExample>
|
||||
|
||||
```json Response
|
||||
{
|
||||
"results": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"data_type": "web_page",
|
||||
"data_value": "https://www.forbes.com/profile/elon-musk/",
|
||||
"metadata": "null"
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</ResponseExample>
|
||||
294
embedchain/docs/examples/rest-api/getting-started.mdx
Normal file
294
embedchain/docs/examples/rest-api/getting-started.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,294 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: "🌍 Getting Started"
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## Quickstart
|
||||
|
||||
To use Embedchain as a REST API service, run the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
docker run --name embedchain -p 8080:8080 embedchain/rest-api:latest
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Navigate to [http://localhost:8080/docs](http://localhost:8080/docs) to interact with the API. There is a full-fledged Swagger docs playground with all the information about the API endpoints.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## ⚡ Steps to get started
|
||||
|
||||
<Steps>
|
||||
<Step title="⚙️ Create an app">
|
||||
<Tabs>
|
||||
<Tab title="cURL">
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
curl --request POST "http://localhost:8080/create?app_id=my-app" \
|
||||
-H "accept: application/json"
|
||||
```
|
||||
</Tab>
|
||||
<Tab title="python">
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import requests
|
||||
|
||||
url = "http://localhost:8080/create?app_id=my-app"
|
||||
|
||||
payload={}
|
||||
|
||||
response = requests.request("POST", url, data=payload)
|
||||
|
||||
print(response)
|
||||
```
|
||||
</Tab>
|
||||
<Tab title="javascript">
|
||||
```javascript
|
||||
const data = fetch("http://localhost:8080/create?app_id=my-app", {
|
||||
method: "POST",
|
||||
}).then((res) => res.json());
|
||||
|
||||
console.log(data);
|
||||
```
|
||||
</Tab>
|
||||
<Tab title="go">
|
||||
```go
|
||||
package main
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"net/http"
|
||||
"io/ioutil"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
func main() {
|
||||
|
||||
url := "http://localhost:8080/create?app_id=my-app"
|
||||
|
||||
payload := strings.NewReader("")
|
||||
|
||||
req, _ := http.NewRequest("POST", url, payload)
|
||||
|
||||
req.Header.Add("Content-Type", "application/json")
|
||||
|
||||
res, _ := http.DefaultClient.Do(req)
|
||||
|
||||
defer res.Body.Close()
|
||||
body, _ := ioutil.ReadAll(res.Body)
|
||||
|
||||
fmt.Println(res)
|
||||
fmt.Println(string(body))
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
</Tab>
|
||||
</Tabs>
|
||||
|
||||
</Step>
|
||||
<Step title="🗃️ Add data sources">
|
||||
<Tabs>
|
||||
<Tab title="cURL">
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
curl --request POST \
|
||||
--url http://localhost:8080/my-app/add \
|
||||
-d "source=https://www.forbes.com/profile/elon-musk" \
|
||||
-d "data_type=web_page"
|
||||
```
|
||||
</Tab>
|
||||
<Tab title="python">
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import requests
|
||||
|
||||
url = "http://localhost:8080/my-app/add"
|
||||
|
||||
payload = "source=https://www.forbes.com/profile/elon-musk&data_type=web_page"
|
||||
headers = {}
|
||||
|
||||
response = requests.request("POST", url, headers=headers, data=payload)
|
||||
|
||||
print(response)
|
||||
```
|
||||
</Tab>
|
||||
<Tab title="javascript">
|
||||
```javascript
|
||||
const data = fetch("http://localhost:8080/my-app/add", {
|
||||
method: "POST",
|
||||
body: "source=https://www.forbes.com/profile/elon-musk&data_type=web_page",
|
||||
}).then((res) => res.json());
|
||||
|
||||
console.log(data);
|
||||
```
|
||||
</Tab>
|
||||
<Tab title="go">
|
||||
```go
|
||||
package main
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
"net/http"
|
||||
"io/ioutil"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
func main() {
|
||||
|
||||
url := "http://localhost:8080/my-app/add"
|
||||
|
||||
payload := strings.NewReader("source=https://www.forbes.com/profile/elon-musk&data_type=web_page")
|
||||
|
||||
req, _ := http.NewRequest("POST", url, payload)
|
||||
|
||||
req.Header.Add("Content-Type", "application/x-www-form-urlencoded")
|
||||
|
||||
res, _ := http.DefaultClient.Do(req)
|
||||
|
||||
defer res.Body.Close()
|
||||
body, _ := ioutil.ReadAll(res.Body)
|
||||
|
||||
fmt.Println(res)
|
||||
fmt.Println(string(body))
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
</Tab>
|
||||
</Tabs>
|
||||
|
||||
</Step>
|
||||
<Step title="💬 Query on your data">
|
||||
<Tabs>
|
||||
<Tab title="cURL">
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
curl --request POST \
|
||||
--url http://localhost:8080/my-app/query \
|
||||
-d "query=Who is Elon Musk?"
|
||||
```
|
||||
</Tab>
|
||||
<Tab title="python">
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import requests
|
||||
|
||||
url = "http://localhost:8080/my-app/query"
|
||||
|
||||
payload = "query=Who is Elon Musk?"
|
||||
headers = {}
|
||||
|
||||
response = requests.request("POST", url, headers=headers, data=payload)
|
||||
|
||||
print(response)
|
||||
```
|
||||
</Tab>
|
||||
<Tab title="javascript">
|
||||
```javascript
|
||||
const data = fetch("http://localhost:8080/my-app/query", {
|
||||
method: "POST",
|
||||
body: "query=Who is Elon Musk?",
|
||||
}).then((res) => res.json());
|
||||
|
||||
console.log(data);
|
||||
```
|
||||
</Tab>
|
||||
<Tab title="go">
|
||||
```go
|
||||
package main
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
"net/http"
|
||||
"io/ioutil"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
func main() {
|
||||
|
||||
url := "http://localhost:8080/my-app/query"
|
||||
|
||||
payload := strings.NewReader("query=Who is Elon Musk?")
|
||||
|
||||
req, _ := http.NewRequest("POST", url, payload)
|
||||
|
||||
req.Header.Add("Content-Type", "application/x-www-form-urlencoded")
|
||||
|
||||
res, _ := http.DefaultClient.Do(req)
|
||||
|
||||
defer res.Body.Close()
|
||||
body, _ := ioutil.ReadAll(res.Body)
|
||||
|
||||
fmt.Println(res)
|
||||
fmt.Println(string(body))
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
</Tab>
|
||||
</Tabs>
|
||||
|
||||
</Step>
|
||||
<Step title="🚀 (Optional) Deploy your app to Embedchain Platform">
|
||||
<Tabs>
|
||||
<Tab title="cURL">
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
curl --request POST \
|
||||
--url http://localhost:8080/my-app/deploy \
|
||||
-d "api_key=ec-xxxx"
|
||||
```
|
||||
</Tab>
|
||||
<Tab title="python">
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import requests
|
||||
|
||||
url = "http://localhost:8080/my-app/deploy"
|
||||
|
||||
payload = "api_key=ec-xxxx"
|
||||
|
||||
response = requests.request("POST", url, data=payload)
|
||||
|
||||
print(response)
|
||||
```
|
||||
</Tab>
|
||||
<Tab title="javascript">
|
||||
```javascript
|
||||
const data = fetch("http://localhost:8080/my-app/deploy", {
|
||||
method: "POST",
|
||||
body: "api_key=ec-xxxx",
|
||||
}).then((res) => res.json());
|
||||
|
||||
console.log(data);
|
||||
```
|
||||
</Tab>
|
||||
<Tab title="go">
|
||||
```go
|
||||
package main
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
"net/http"
|
||||
"io/ioutil"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
func main() {
|
||||
|
||||
url := "http://localhost:8080/my-app/deploy"
|
||||
|
||||
payload := strings.NewReader("api_key=ec-xxxx")
|
||||
|
||||
req, _ := http.NewRequest("POST", url, payload)
|
||||
|
||||
req.Header.Add("Content-Type", "application/x-www-form-urlencoded")
|
||||
|
||||
res, _ := http.DefaultClient.Do(req)
|
||||
|
||||
defer res.Body.Close()
|
||||
body, _ := ioutil.ReadAll(res.Body)
|
||||
|
||||
fmt.Println(res)
|
||||
fmt.Println(string(body))
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
</Tab>
|
||||
</Tabs>
|
||||
|
||||
</Step>
|
||||
</Steps>
|
||||
|
||||
And you're ready! 🎉
|
||||
|
||||
If you run into issues, please feel free to contact us using below links:
|
||||
|
||||
<Snippet file="get-help.mdx" />
|
||||
21
embedchain/docs/examples/rest-api/query.mdx
Normal file
21
embedchain/docs/examples/rest-api/query.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,21 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
openapi: post /{app_id}/query
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<RequestExample>
|
||||
|
||||
```bash Request
|
||||
curl --request POST \
|
||||
--url http://localhost:8080/{app_id}/query \
|
||||
-d "query=who is Elon Musk?"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</RequestExample>
|
||||
|
||||
<ResponseExample>
|
||||
|
||||
```json Response
|
||||
{ "response": "Net worth of Elon Musk is $218 Billion." }
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</ResponseExample>
|
||||
Some files were not shown because too many files have changed in this diff Show More
Reference in New Issue
Block a user